Pes cavus is a foot deformity characterized by an abnormally high plantar arch, which can lead to associated conditions like metatarsalgia and claw toes. The condition can be classified into different types such as pes cavovarus and pes calcaneocavus, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Treatment approaches include medical management, physiotherapy, and surgical interventions depending on the severity and underlying causes.





![ORTHOPAEDIC ASSESSMENT
A] DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
B] CHIEF COMPLAINT
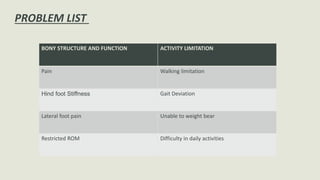
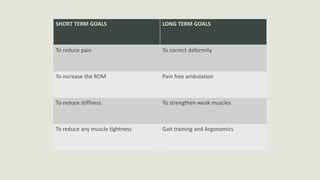
Patients complains of pain , instability , difficulty walking and problems with footwear.
The symptoms vary with the degree of deformity.
Also presents with lateral foot pain from increased weight bearing on the lateral foot](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pescavus-salonipatil-200408154211/85/Pes-cavus-High-ArchFoot-PHYSIO-7-320.jpg)
![C] HISTORY
• The presentation for patients with pes cavus is highly variable, depending largely on the extent of the deformity.
• Patients can present with lateral foot pain from increased weightbearing on the lateral foot.
• Metatarsalgia is a frequent symptom. Ankle instability can be a presenting symptom, especially in patients with hindfoot
varus and weak peroneus brevis.
• Weakness and fatigue can be observed in patients with neuromuscular disease.
• Evaluation of a patient who presents with pes cavus begins with a thorough history and complete examination to
determine the etiology.
• Patients with a unilateral deformity frequently have a history of major trauma.
• Patients should be questioned about weakness/clumsiness, indicating intrinsic muscle involvement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pescavus-salonipatil-200408154211/85/Pes-cavus-High-ArchFoot-PHYSIO-8-320.jpg)
![D] BODY CHART
Area – Foot and Ankle
Onset – Gradual / Insidious
Type – Dull Aching
Depth – Deep
Constancy – Intermittent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pescavus-salonipatil-200408154211/85/Pes-cavus-High-ArchFoot-PHYSIO-9-320.jpg)
![E] AGGRAVATING FACTOR – prolonged standing and during activities of daily living.
F] RELIEVING FACTOR – Rest
G] SEVERITY – Vas Scale
H] IRRITABILITY – Moderate
I] 24 HOURS PATTERN
J] PAST HISTORY – Ask for any h/o trauma
K] MEDICAL HISTORY – Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
L] FAMILY HISTORY – Clinically significant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pescavus-salonipatil-200408154211/85/Pes-cavus-High-ArchFoot-PHYSIO-10-320.jpg)
![M] SOCIAL HISTORY – Work / Sports / Hobbies affected
N] ECONOMIC HISTORY – Modified KuppuSwamy Scale.
OBJECTIVE ASSESMENT
OBSERVATION
POSTURE –
• Observe foot posture in standing and arch posture
• Subtle evidence of foot drop may be evident, if there is calf wasting (stork leg deformity)
MOTOR EXAMINATION
• Rigidity maybe present [ Modified Ashworth Scale ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pescavus-salonipatil-200408154211/85/Pes-cavus-High-ArchFoot-PHYSIO-11-320.jpg)