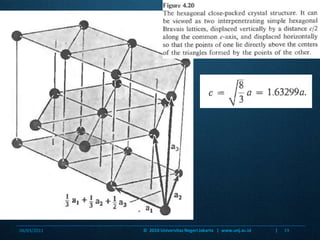
This document discusses close packing structures in crystals. It explains that there are two main types of close packing: hexagonal close packing (hcp) and cubic close packing (ccp). Ccp packing is equivalent to a face-centered cubic unit cell. Both hcp and ccp structures make efficient use of space with a packing fraction of 0.74, while other structures like primitive unit cells have lower packing fractions with more empty space. The document provides examples of calculating packing fractions and analyzing the geometry of close packed structures.