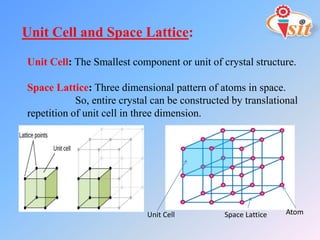
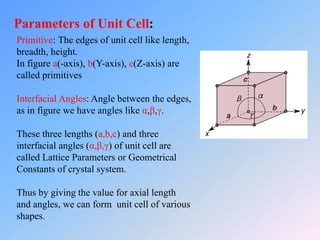
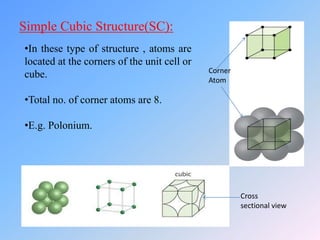
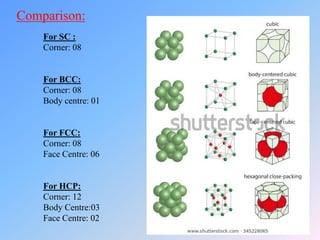
The document discusses different crystal structures and their properties. It defines a unit cell as the smallest component of a crystal structure and describes four common crystal structures: simple cubic (SC), body centered cubic (BCC), face centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal close packed (HCP). It calculates the average number of atoms per unit cell (Nav) for each as well as the packing efficiency or atomic packing factor (APF), with SC having the lowest efficiency at 52% and BCC, FCC, and HCP all having the highest at 74%.