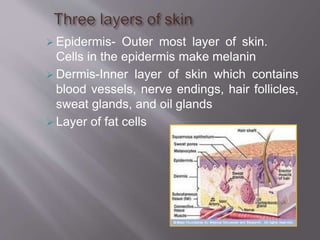
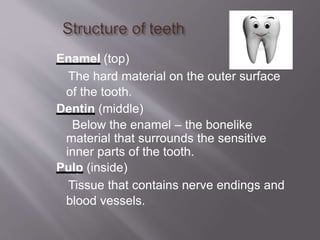
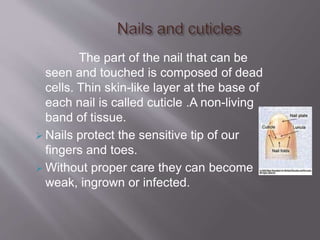
This document discusses personal hygiene and provides guidance on maintaining cleanliness of various body parts. It covers care of hair, skin, teeth, ears, hands, nails and feet. Regular washing, grooming and cleaning is important for personal hygiene. Failure to maintain hygiene can increase health risks and affect social and psychological well-being. Key practices include proper bathing, washing hands and face, dental care including brushing and flossing, nail care, and foot hygiene including washing daily and changing socks.