1) Persister bacterial cells are dormant, non-dividing cells that are tolerant to antibiotics but not resistant. They are genetically identical to actively growing cells.
2) Persister cells are found in all bacterial species and are enriched in biofilms, making chronic infections difficult to treat. They are responsible for treatment failure and relapse.
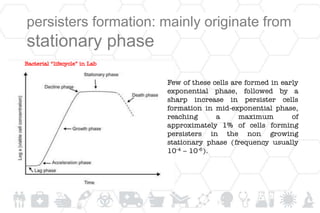
3) Persister cells form through spontaneous switching or in response to stress like nutrient starvation. Overexpressed toxin/antitoxin systems enable drug tolerance in persisters.