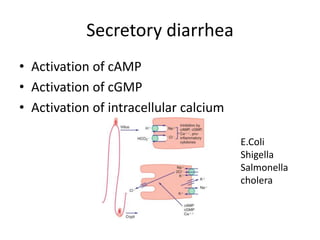
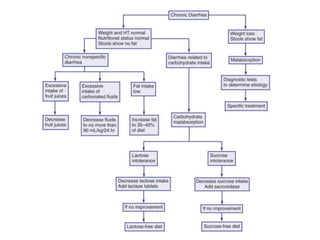
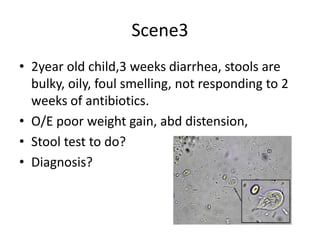
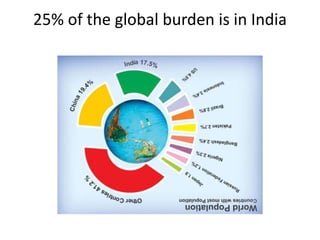
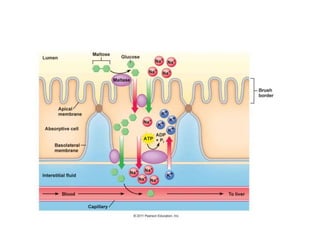
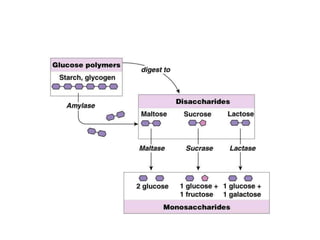
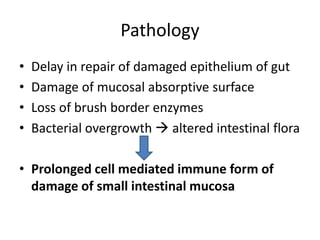
This document discusses persistent and chronic diarrhea. Persistent diarrhea is defined as diarrhea lasting more than 14 days, and can be caused by persistent infections, parasites, malabsorption issues, or protein allergies/intolerances. It presents a significant disease burden, with 25% of the global burden occurring in India. Chronic diarrhea lasts more than 2 weeks and can be due to conditions like cow's milk protein allergy, malnutrition, lactose intolerance, or disorders like celiac disease. The document outlines diagnostic tests, management strategies including specialized diets and antibiotics, and prevention through proper treatment, judicious antibiotic use, and promoting breastfeeding.


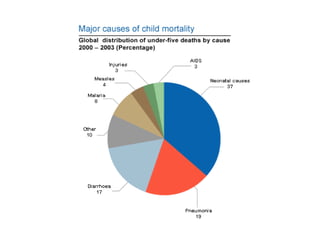
![Disease burden
• 24 lakh child deaths in India each year
• 5 children die every minute
• 25% of the global burden is in India
• More in infancy [31 episodes per 100 child
years]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-140719070248-phpapp02/85/persisitent-diarrhea-in-children-3-320.jpg)






![Antibiotics
• Blood in stool [quinolones]
• Systemic sepsis [ampicillin & amikacin]
• Severe malnutrition
• Young infants
• Discharge criteria
• Regular diet: when?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-140719070248-phpapp02/85/persisitent-diarrhea-in-children-15-320.jpg)