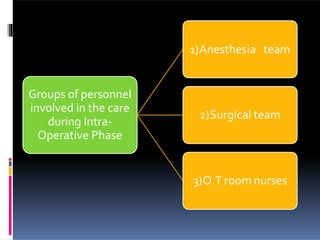
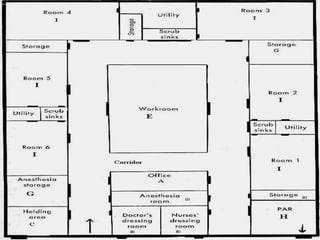
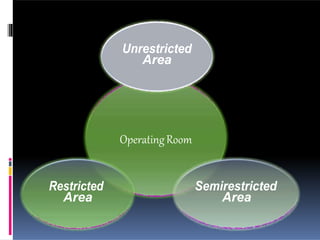
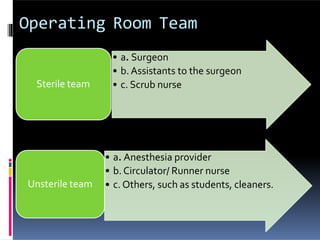
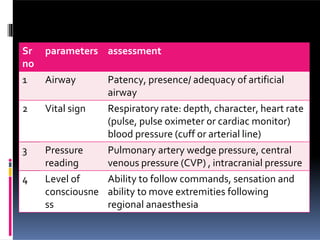
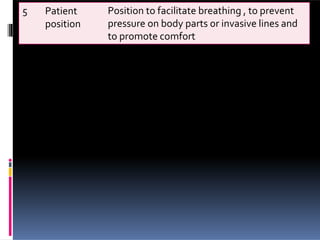
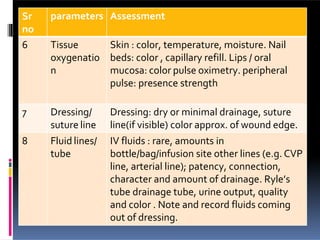
Perioperative nursing involves caring for patients before, during, and after surgery. The document outlines the three phases of perioperative care: [1] preoperative, [2] intraoperative, and [3] postoperative. It describes the nursing responsibilities in each phase, including assessing patients, providing education, monitoring patients' condition, and ensuring safety. Perioperative nurses play a critical role in preparing patients for surgery, assisting in the operating room, and observing patients as they recover.