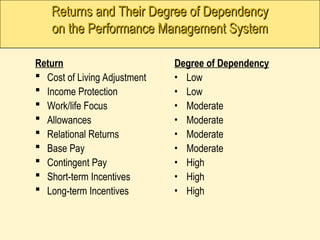
The document outlines the definition, benefits, and purposes of performance management (PM) systems, emphasizing their role in enhancing individual and organizational performance. It highlights the significance of aligning individual goals with organizational objectives while detailing the characteristics of an ideal PM system and the repercussions of poorly implemented systems. Additionally, it discusses the importance of integrating PM with other human resource activities to foster employee development and organizational growth.