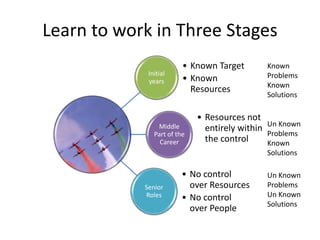
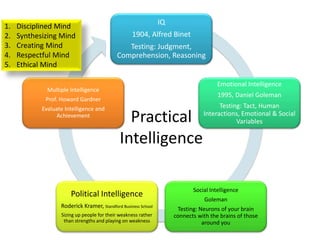
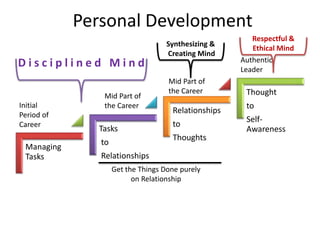
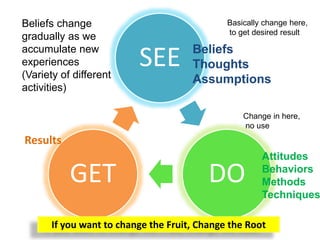
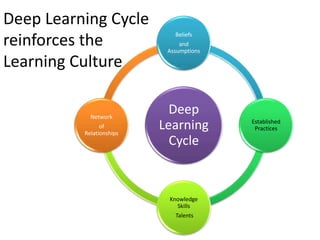
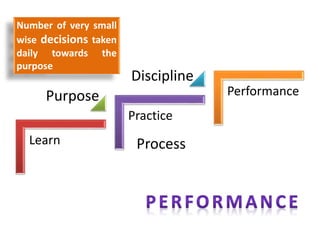
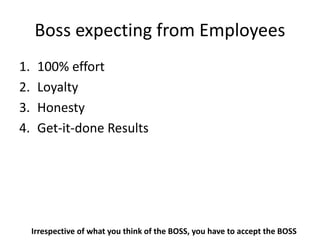The document discusses various topics related to performance and personal development. It emphasizes that an organization exists for a purpose of performance, defined as outcomes deemed valuable by customers. Performance results from thousands of tiny decisions made each day. It also discusses key aspects like assumptions, discipline, culture, decisions, relationships and accountability. The document stresses on concepts like synchronizing efforts, identifying weakest links, embracing failures as learning opportunities, and continually revisiting assumptions to adapt to changes. Overall, it provides guidance on driving performance through focusing on purpose, decision-making, culture, accountability and continuous learning.