Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times




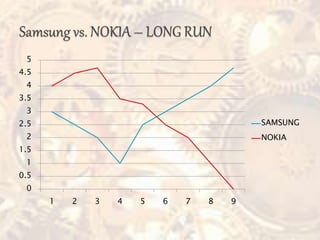


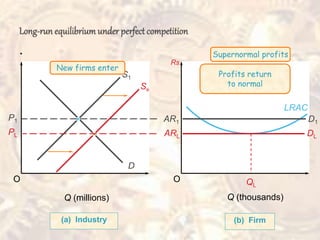


The document discusses the concept of perfect competition in three main points: 1. Perfect competition describes a market structure where competition is at its highest level, with many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and perfect information. 2. Under perfect competition, firms aim to maximize profits by producing at the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. 3. In the long run, if profits are above normal, more firms will enter the market, increasing supply and driving prices and profits back down to normal.








