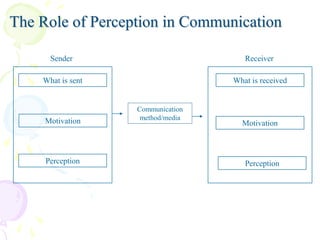
This document discusses perception, attitude, values and their impact on communication. It begins by defining perception as the organization, identification and interpretation of sensory information to understand one's environment. There are four steps in the perception process: selection, organization, interpretation and negotiation. The role of perception in communication is that the sender's perception impacts what is sent and the receiver's perception impacts what is received. There are different types of perception including self, environmental, learned and physical/cultural. The document also discusses attitudes, defining them as mental predispositions that are expressed through favorability or unfavorability. Attitudes can be positive or negative. Finally, the document defines values as preferences for certain modes of conduct or end states. It