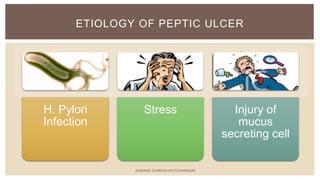
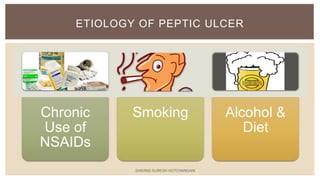
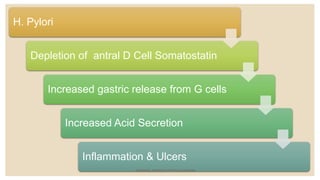
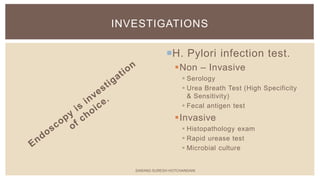
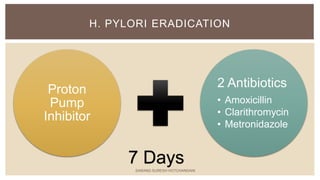
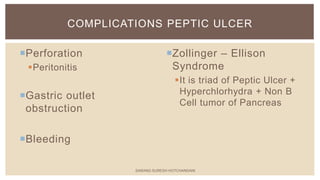
This document summarizes peptic ulcers, which are ulcers that can form in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Peptic ulcers are commonly caused by H. pylori infections or NSAID use. H. pylori infections are usually treated with a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors. Treatment aims to eliminate H. pylori and reduce stomach acid levels to allow ulcers to heal. Surgery may be needed for complications like bleeding or perforation. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent ulcer recurrence.