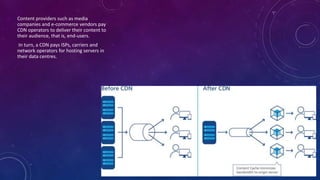
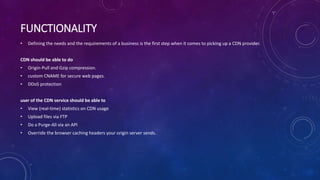
A content delivery network (CDN) distributes content globally to provide faster delivery and availability. Content is replicated across servers in the CDN so clients can access a nearby copy rather than overloading a central server. CDNs are paid by content providers to deliver their media and files to end users. When choosing a CDN, functionality, performance, costs, and service should be considered. Functionality includes features like compression and security. Performance is critical and is measured by latency and throughput. Cost structures vary between providers so custom plans should be explored. Quality customer support is also important.