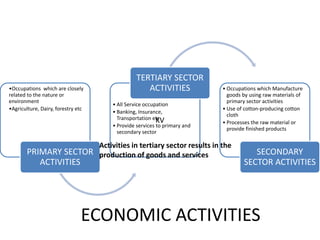
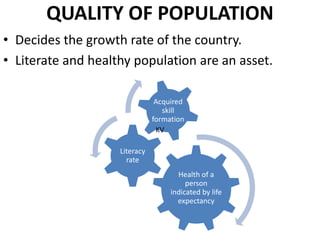
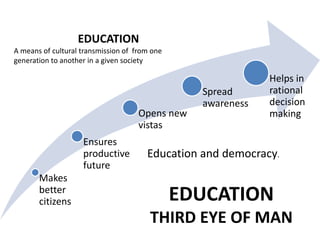
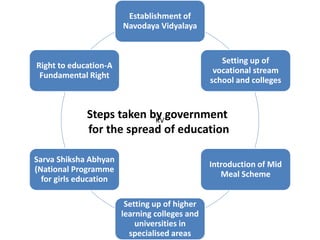
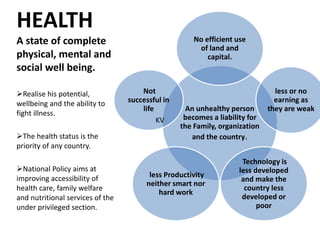
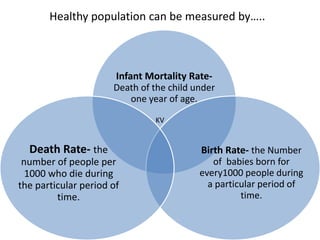
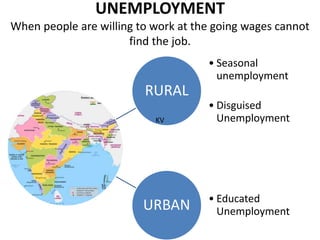
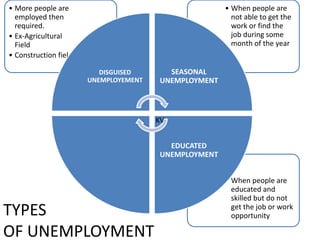
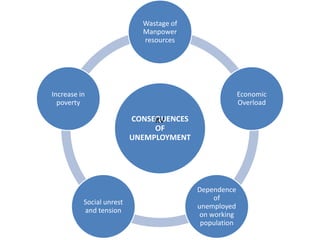
The document discusses the concept of 'people as a resource,' emphasizing the importance of human resource development, education, and health in economic growth and productivity. It highlights different economic activities across primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors, as well as the challenges faced by women in the workforce, particularly regarding low wages and job security. Additionally, the document outlines types of unemployment and the consequences of unemployment on society.