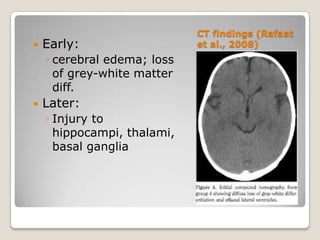
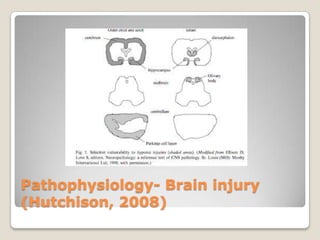
This document discusses pediatric drowning. It begins with terminology used in drowning and then covers epidemiology, noting it is a leading cause of death worldwide in boys aged 5-14 and the second leading cause of death in US children aged 1-4. Mechanisms, injuries, and presentations are described for different age groups. Pathophysiology explores effects of drowning on the lungs, brain, and autonomic function. Pre-hospital care emphasizes removing the child from water and starting CPR. The trauma evaluation and treatments in the emergency department are outlined. Prevention strategies target fencing pools for toddlers and supervision for children, while advising life jackets and avoiding alcohol for adolescents.