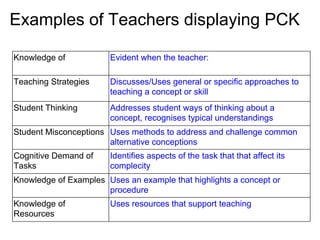
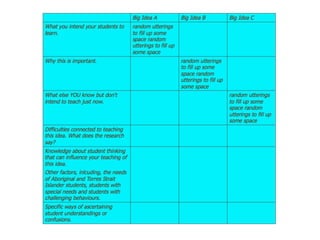
This document discusses the importance of pedagogical content knowledge for beginning teachers. It defines pedagogical content knowledge as understanding how to best represent and formulate a subject to make it comprehensible to others, including understanding what makes learning topics easy or difficult based on students' backgrounds and preconceptions. The document also notes that teachers need a range of pedagogical content knowledge to address different student learning styles and the broader purposes of education like literacy and respect. Teaching strategies, student thinking, addressing misconceptions, cognitive demand of tasks, use of examples, and knowledge of resources are provided as examples of displaying pedagogical content knowledge. The document concludes by encouraging the use of a planning template to make


![Pedagogical Content Knowledge
"the most useful forms of representation of [topics], the most
powerful analogies, illustrations, examples, explanations, and
demonstrations - in a word, the ways of representing and
formulating the subject that make it comprehensible to others ...
Pedagogical content knowledge also includes an understanding
of what makes the learning of specific topics easy or difficult:
the conceptions and preconceptions that students of different
ages and backgrounds bring with them to the learning of those
most frequently taught topics and lessons." (Shulman, 1986).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pedagogicalthi-100811152614-phpapp02/85/Pedagogical-thinking-3-320.jpg)