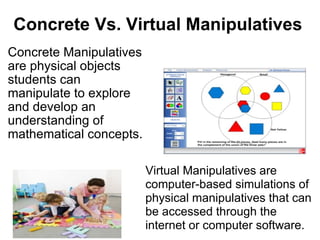
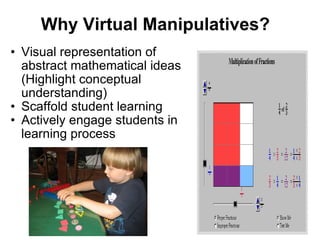
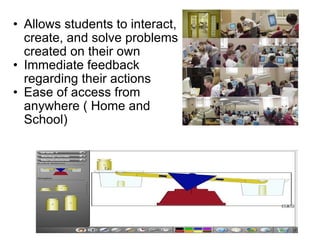
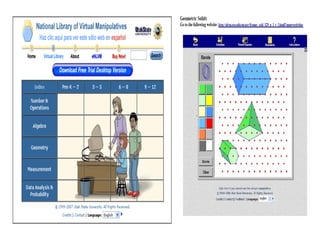
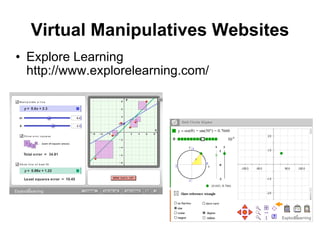
Virtual manipulatives are computer-based simulations of physical objects that allow students to explore mathematical concepts. They have several benefits over physical manipulatives, including visual representations of abstract ideas, scaffolding of student learning, and active engagement through student-created problems. Popular websites for virtual manipulatives include the National Library of Virtual Manipulatives and Illuminations. According to theories of cognitive development and constructivism, virtual manipulatives can support students' learning as they develop reasoning skills and actively construct understanding.