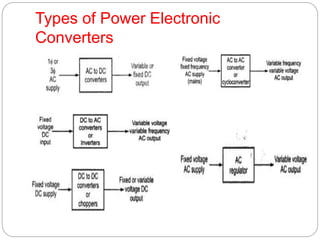
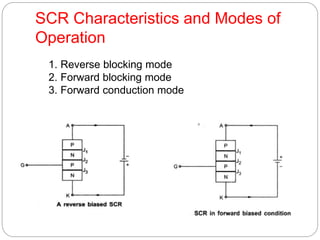
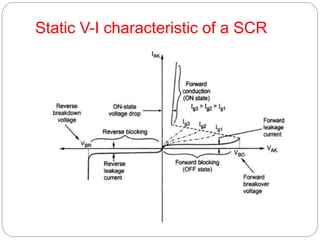
Power electronics deals with controlling and converting electric power using solid-state electronics. It involves power equipment for generation, transmission and distribution as well as electronic devices and circuits for signal processing and control objectives. Some key developments include the mercury arc rectifier in 1900, silicon transistor in 1948, and thyristor or SCR in 1956. Power electronic converters are now used for applications like UPS, motor speed control, power transmission, and power supplies due to advantages like fast response, high efficiency and compact size, though they can generate harmonics and have low power factors requiring correction. Power electronic converters work by classifying and controlling the operation of power semiconductor devices like power diodes, SCRs, BJTs, MOSFETs