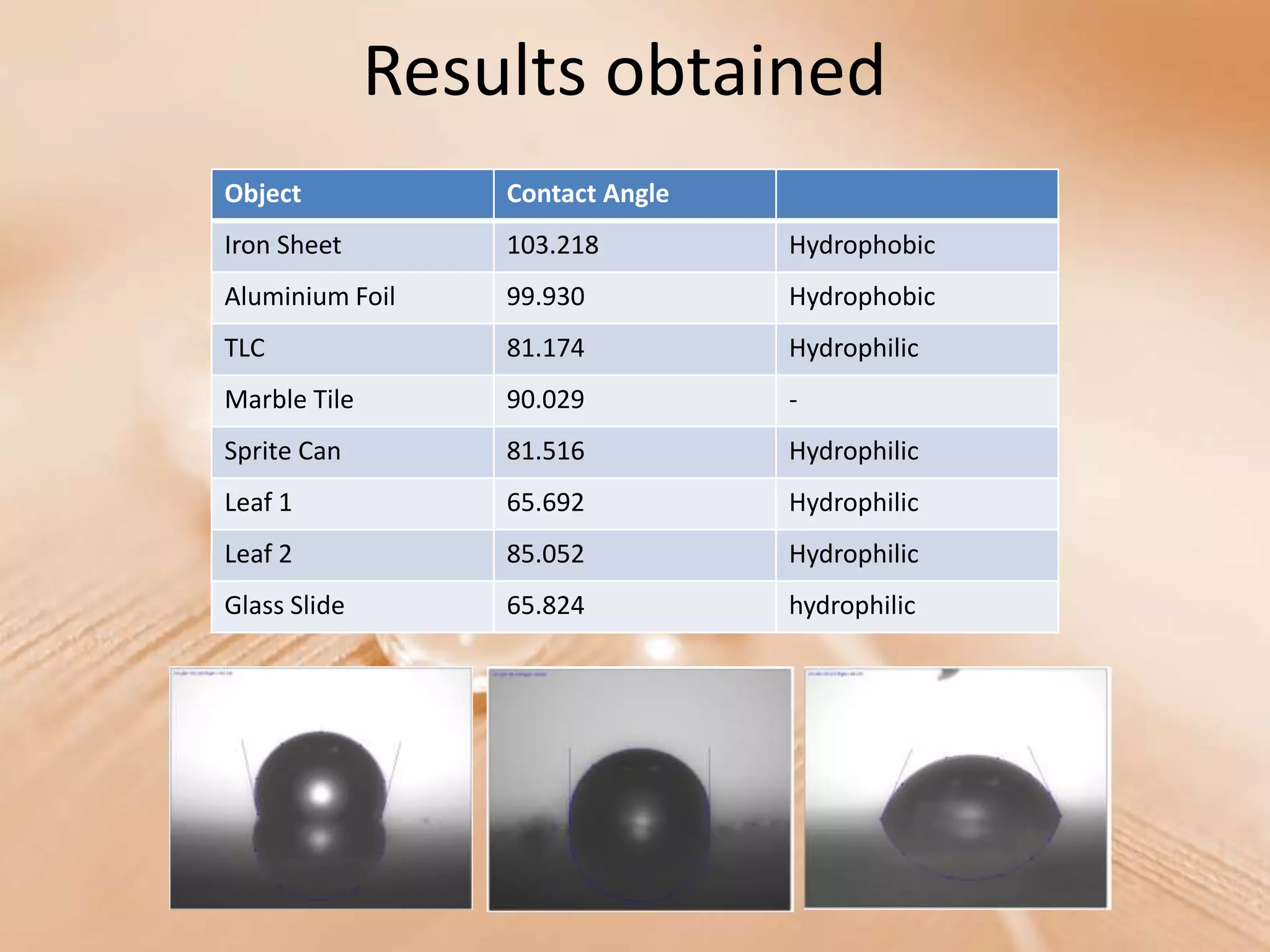
This document discusses contact angle measurement and how surface roughness affects contact angle. It describes how contact angle is measured and depends on factors like temperature, humidity, and surface roughness. The document outlines an experiment where different surfaces were tested to find the relationship between surface roughness and contact angle. The results found that rougher surfaces like iron sheets and aluminum foil had higher contact angles, making them more hydrophobic, while smoother surfaces like glass slides and plant leaves had lower contact angles and were more hydrophilic. The experiment suggests hydrophobic surfaces have smaller distances between surface peaks, preventing water droplets from sitting on the surface.