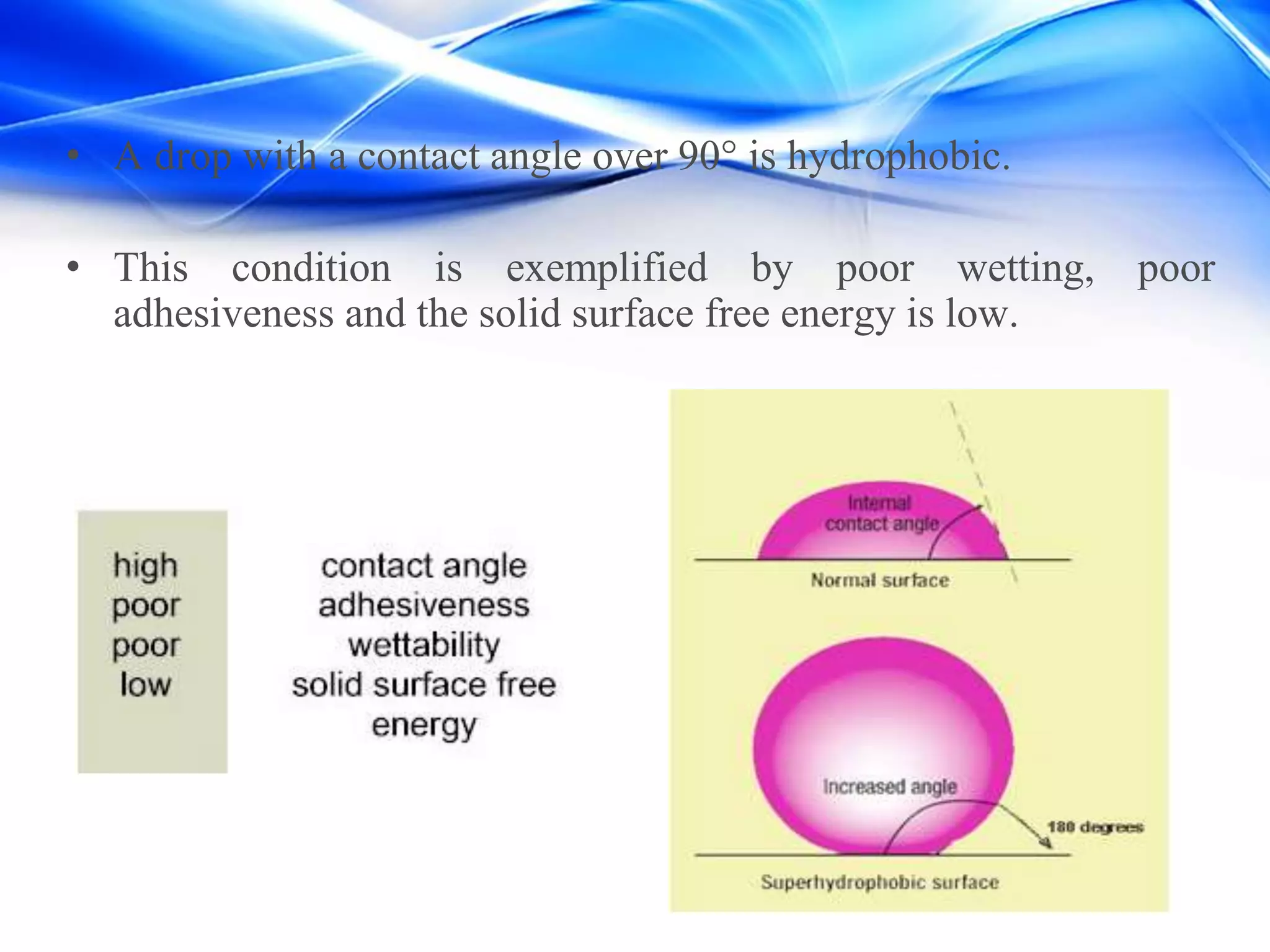
This document discusses hydrophobic materials and how they are formed. Hydrophobicity refers to materials that repel water due to having a water contact angle over 90 degrees. Hydrophobicity is achieved through microscale and nanoscale surface roughness and low surface energy. Some natural hydrophobic materials include waxes, oils, and lotus leaves. The document describes different models for how water interacts with rough hydrophobic surfaces and various methods for creating artificial superhydrophobic surfaces, such as layer-by-layer assembly and sol-gel processing. Potential applications of hydrophobic coatings include anti-corrosion, anti-icing, self-cleaning surfaces, and textiles.