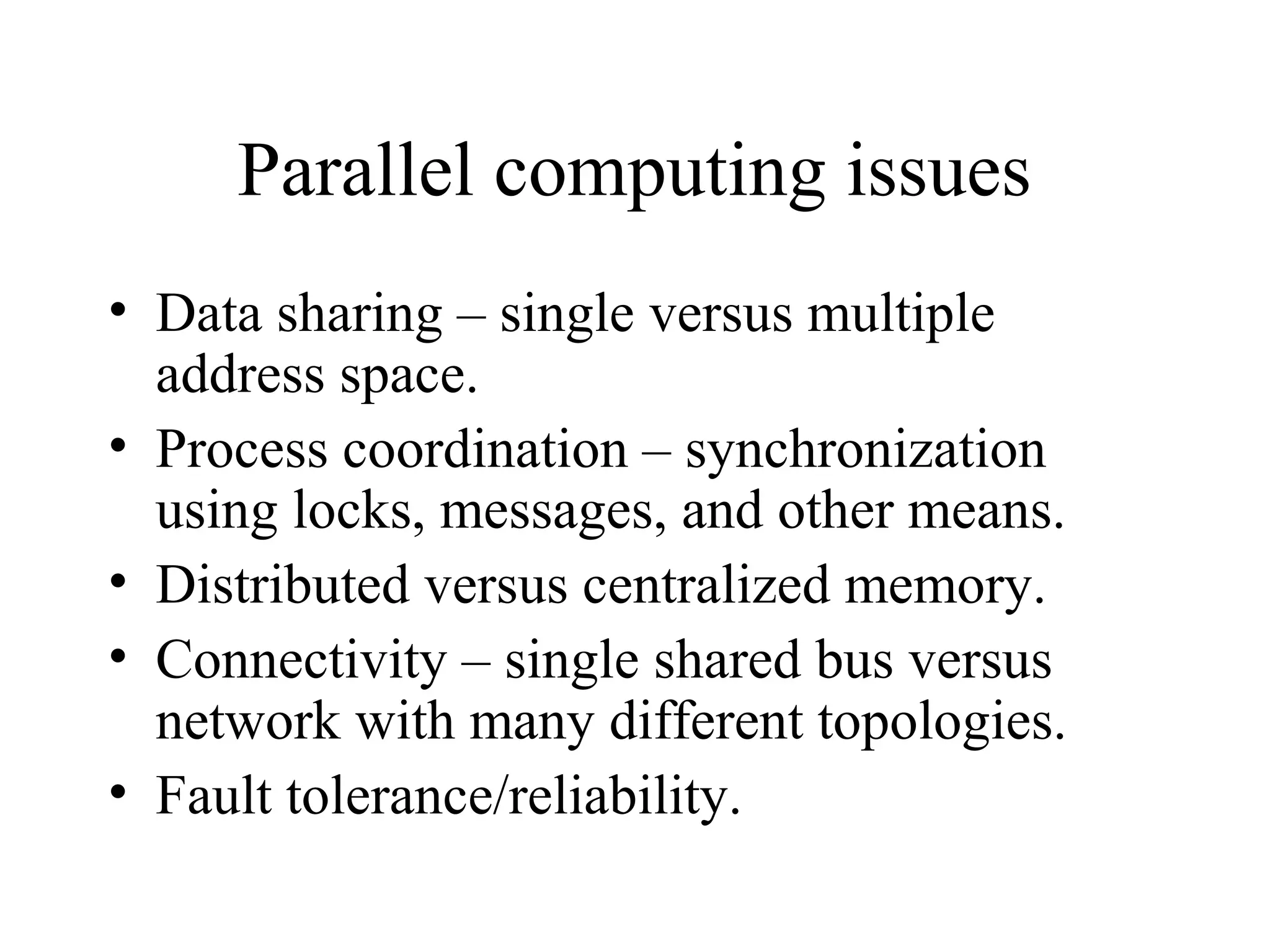
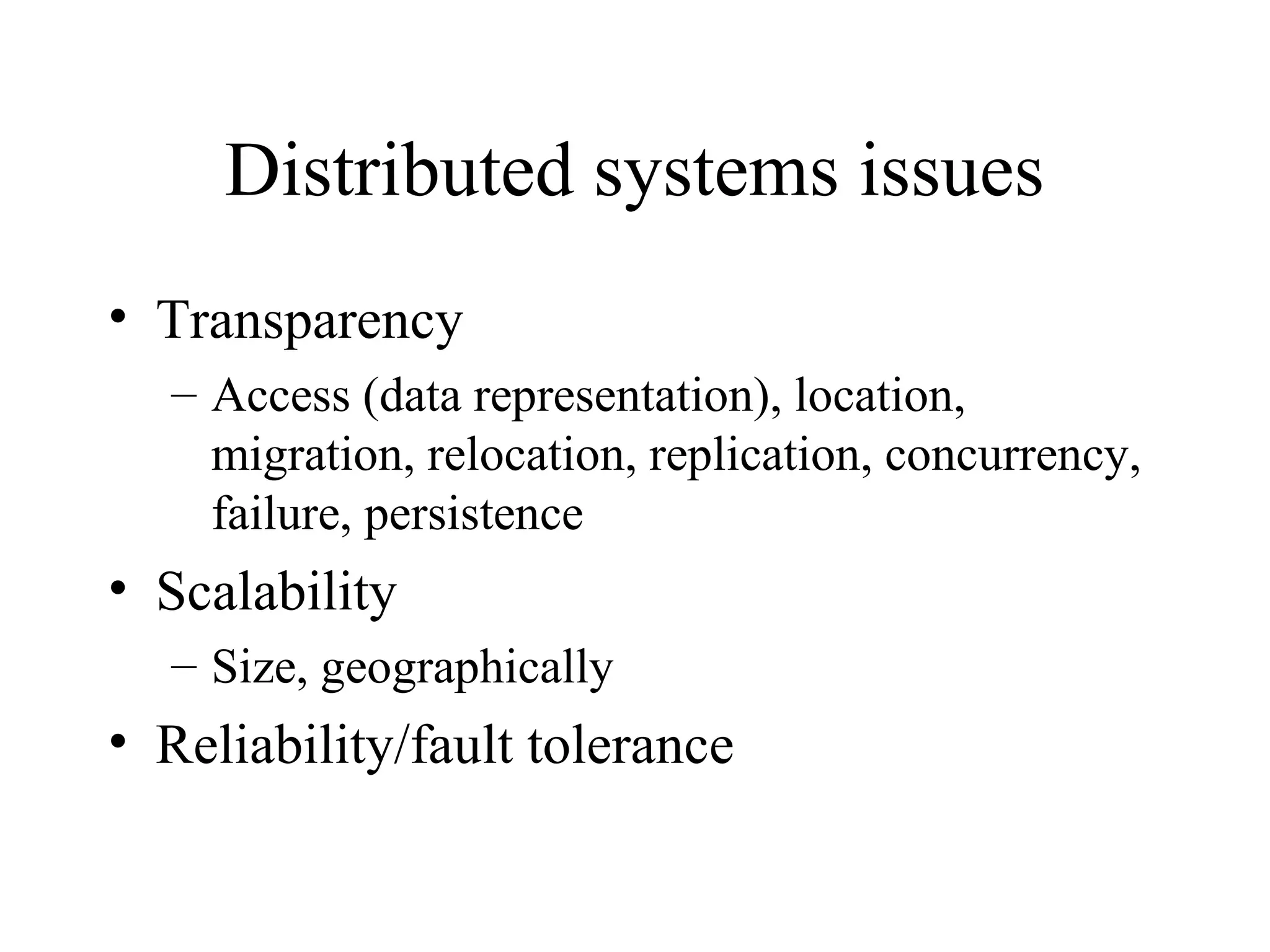
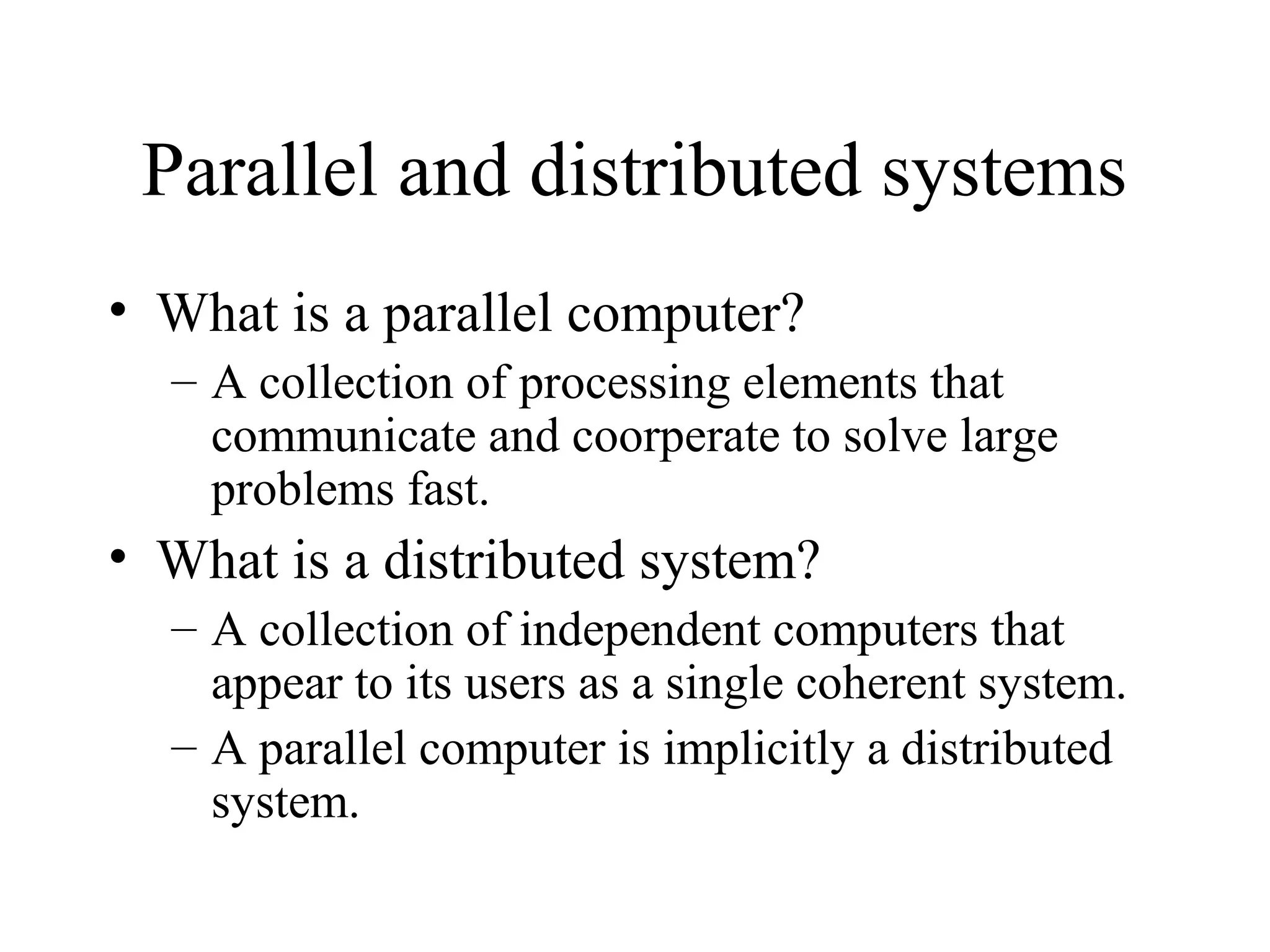
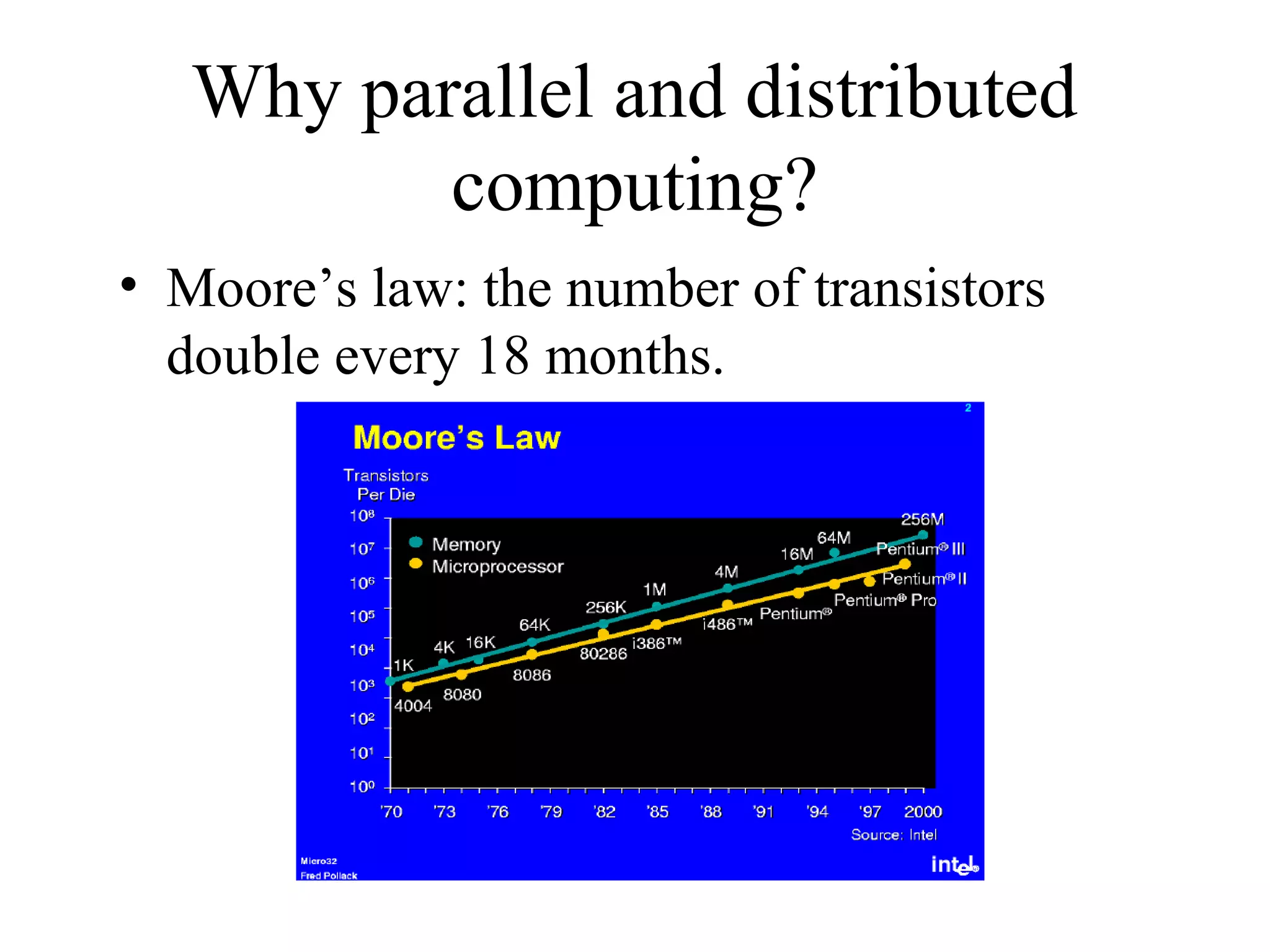
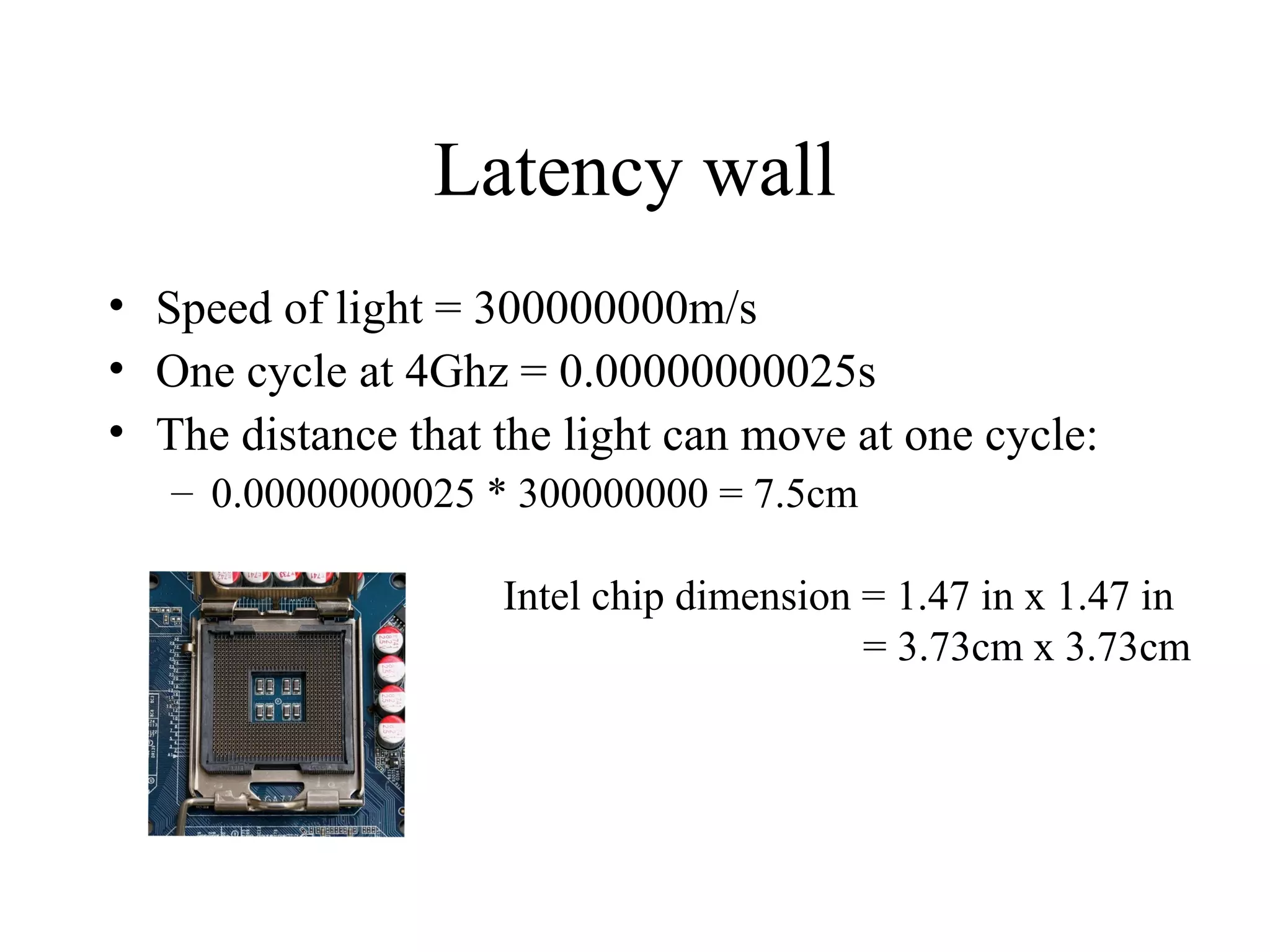
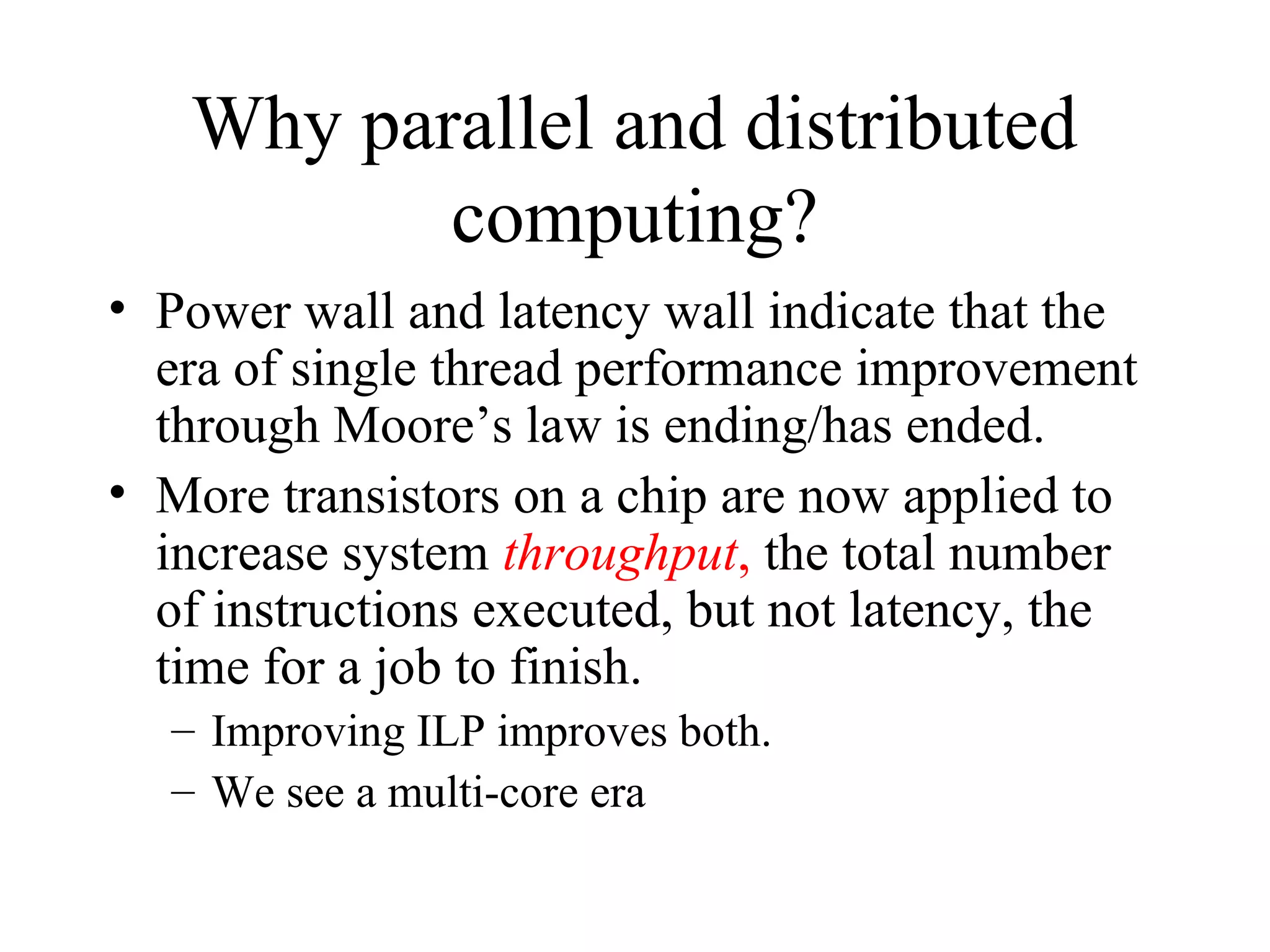
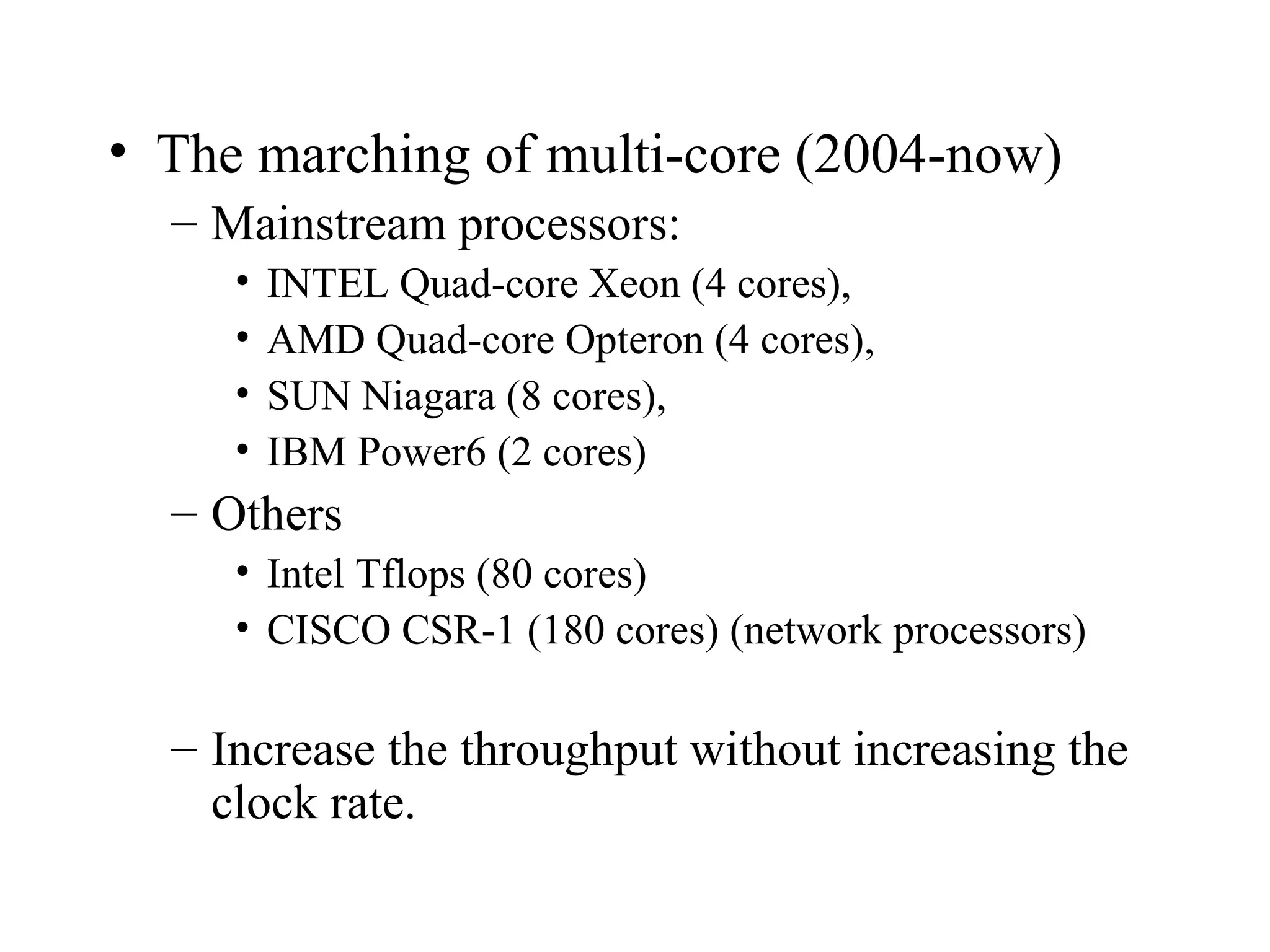
This document provides an overview of parallel and distributed systems. It discusses that a parallel computer contains multiple processing elements that communicate and cooperate to solve problems quickly, while a distributed system contains independent computers that appear as a single system. It notes that parallel computers are implicitly distributed systems. It then discusses reasons for using parallel and distributed computing like Moore's law and limitations of sequential processing due to power and latency walls. Finally, it outlines some topics that will be covered in the course like different parallel computing platforms, programming paradigms, and challenges in parallel and distributed systems.





![For (I=0; I<500; I++)
a[I] = 0;
1970 1980 200620001990
Performance
GO PARALLEL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdclecture1-180408111654/75/Pdc-lecture1-12-2048.jpg)