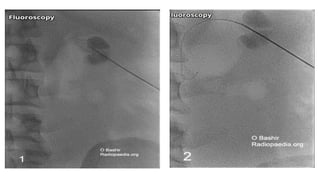
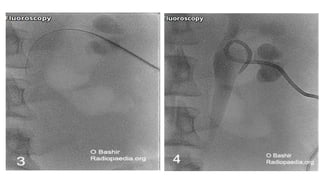
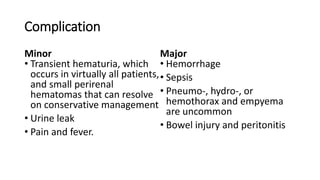
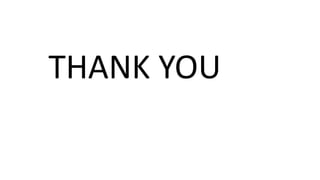Percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) is an interventional procedure used to decompress the renal collecting system through temporary drainage of an obstructed system. It is done under imaging guidance such as fluoroscopy, ultrasound, or CT. PCN is indicated for obstructive uropathy from various benign or malignant causes, and can provide access for chemotherapy, antibiotics, stent placement, or diagnostic procedures. The key steps of PCN involve pre-procedural evaluation and imaging, local anesthesia, needle puncture of the kidney under imaging, insertion of a guidewire and dilators, and placement of a pigtail drain catheter under imaging guidance. Complications can include minor issues like hematuria or urine leak, or major issues such