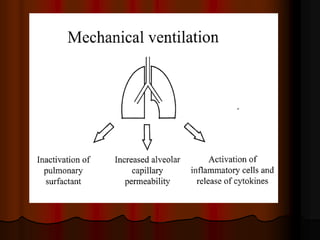
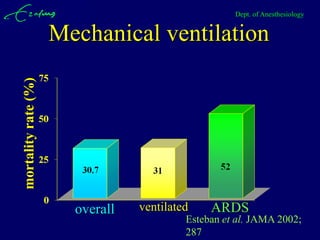
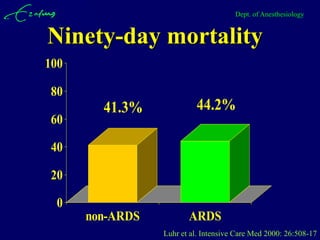
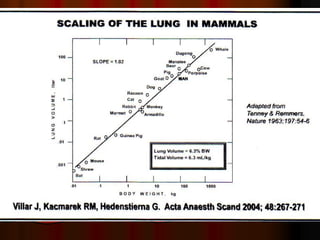
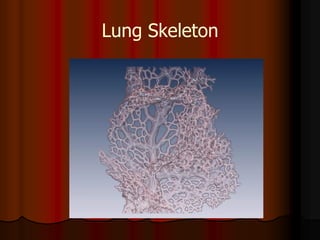
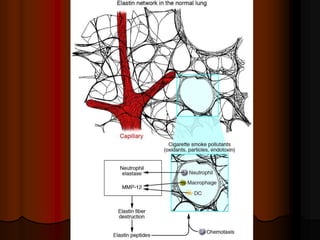
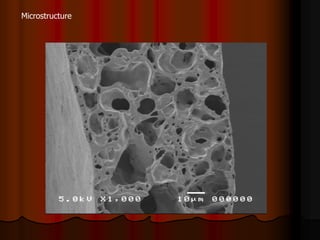
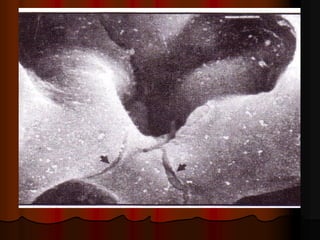
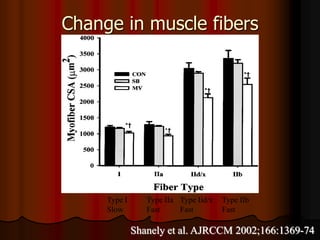
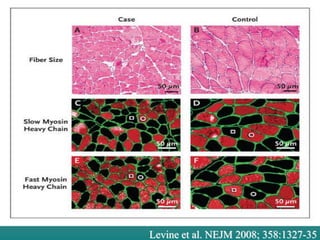
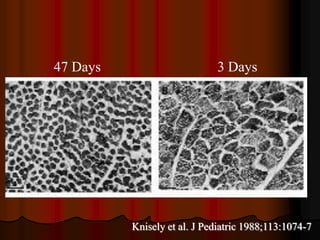
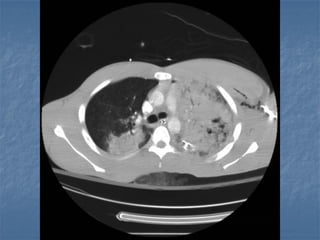
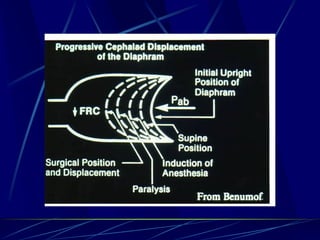
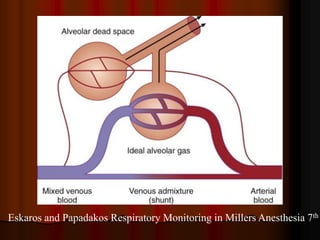
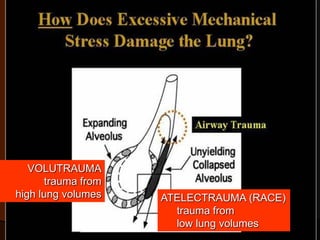
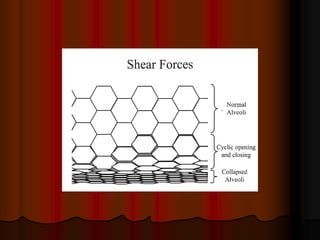
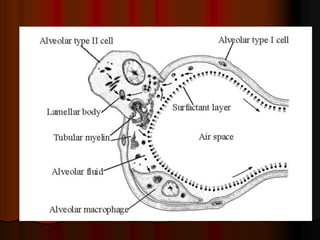
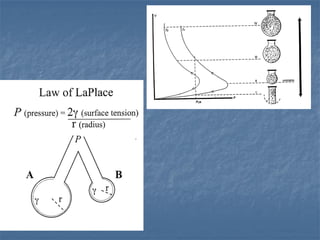
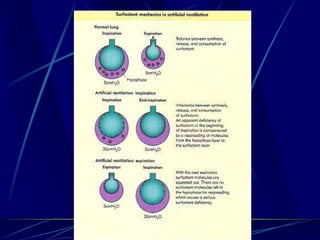
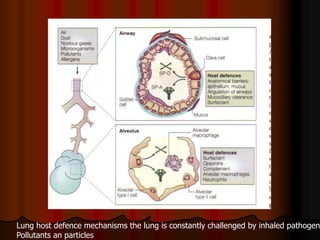
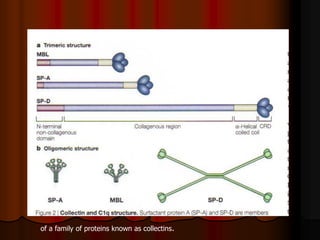
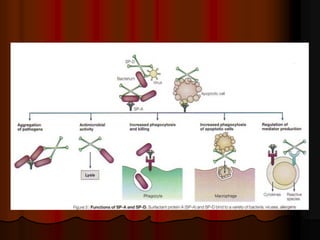
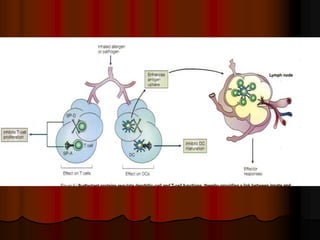
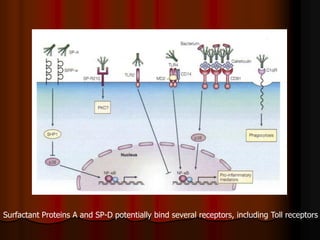
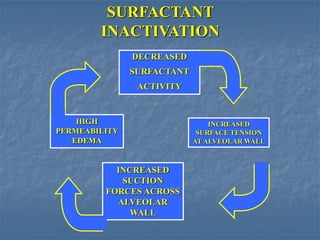
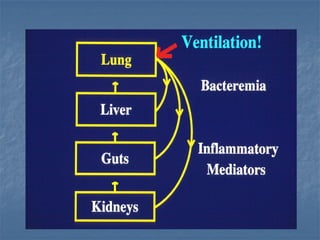
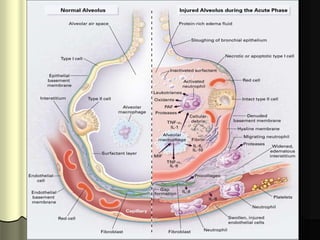
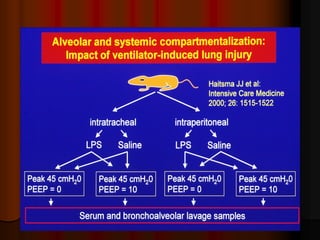
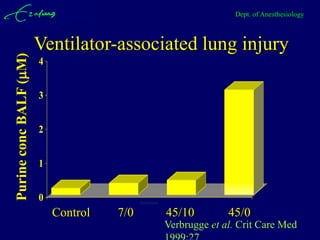
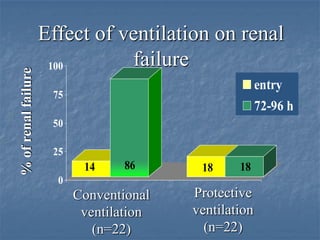
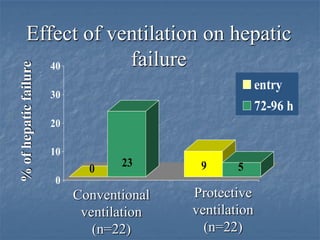
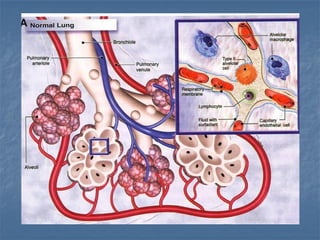
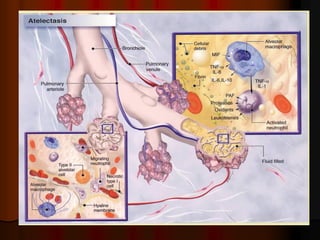
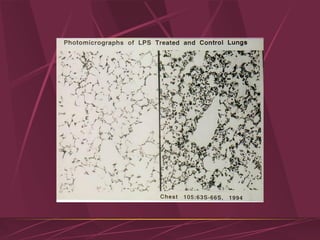
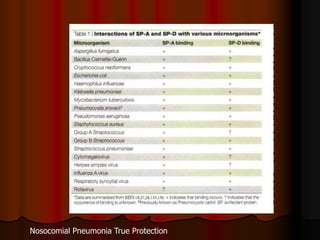
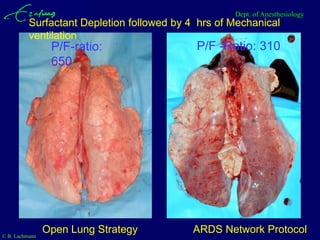
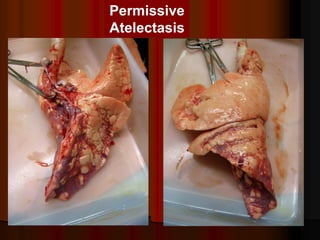
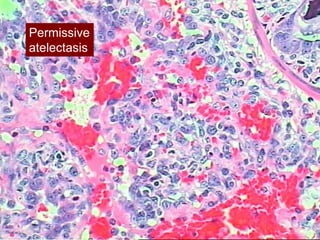
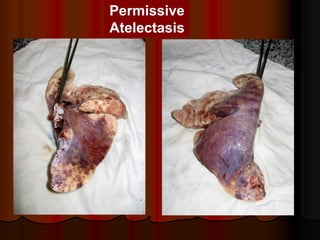
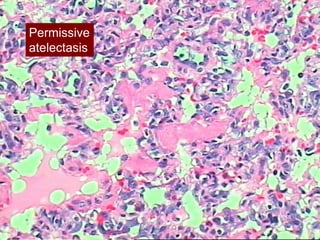
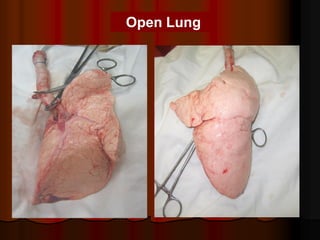
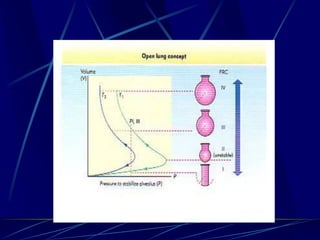
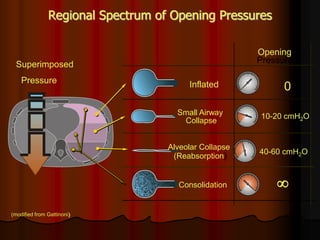
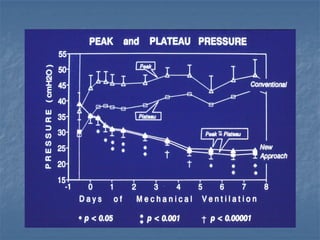
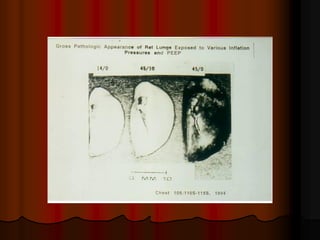
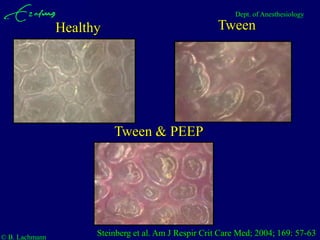
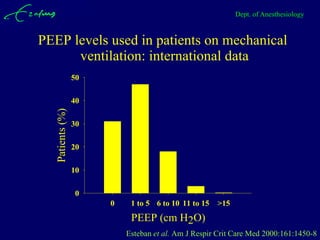
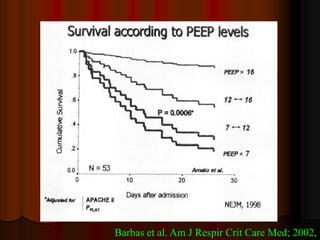
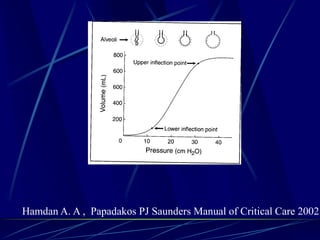
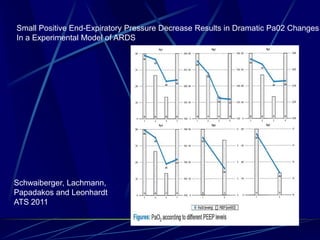
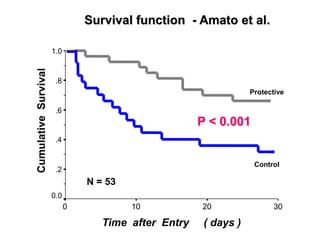
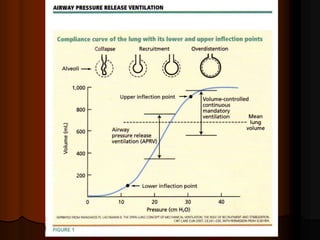
Mechanical ventilation can lead to mortality in trauma and ARDS patients. The basic physiology of ventilation involves the lung skeleton, breathing muscles, and changes in lung mechanics with collapse. Ventilation can lead to volutrauma from high volumes and atelectrauma from low volumes. Surfactant is depleted by the opening and closing of alveoli. This can increase surface tension and promote collapse. Ventilation may also trigger a systemic inflammatory response. Nosocomial pneumonia is a complication that protocols aim to prevent through various measures. Newer ventilation strategies like open lung aim to recruit and keep alveoli open to prevent injury.