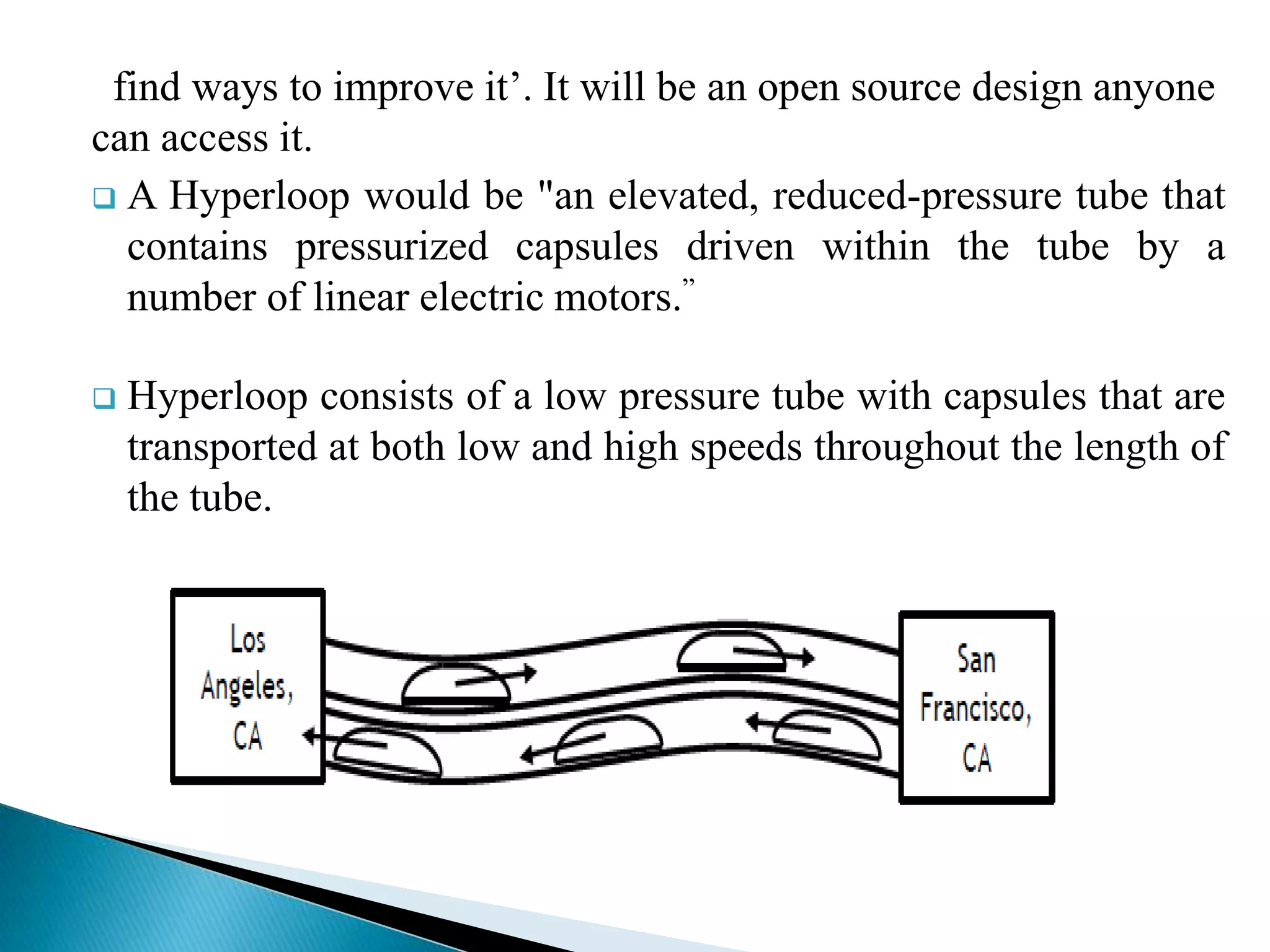
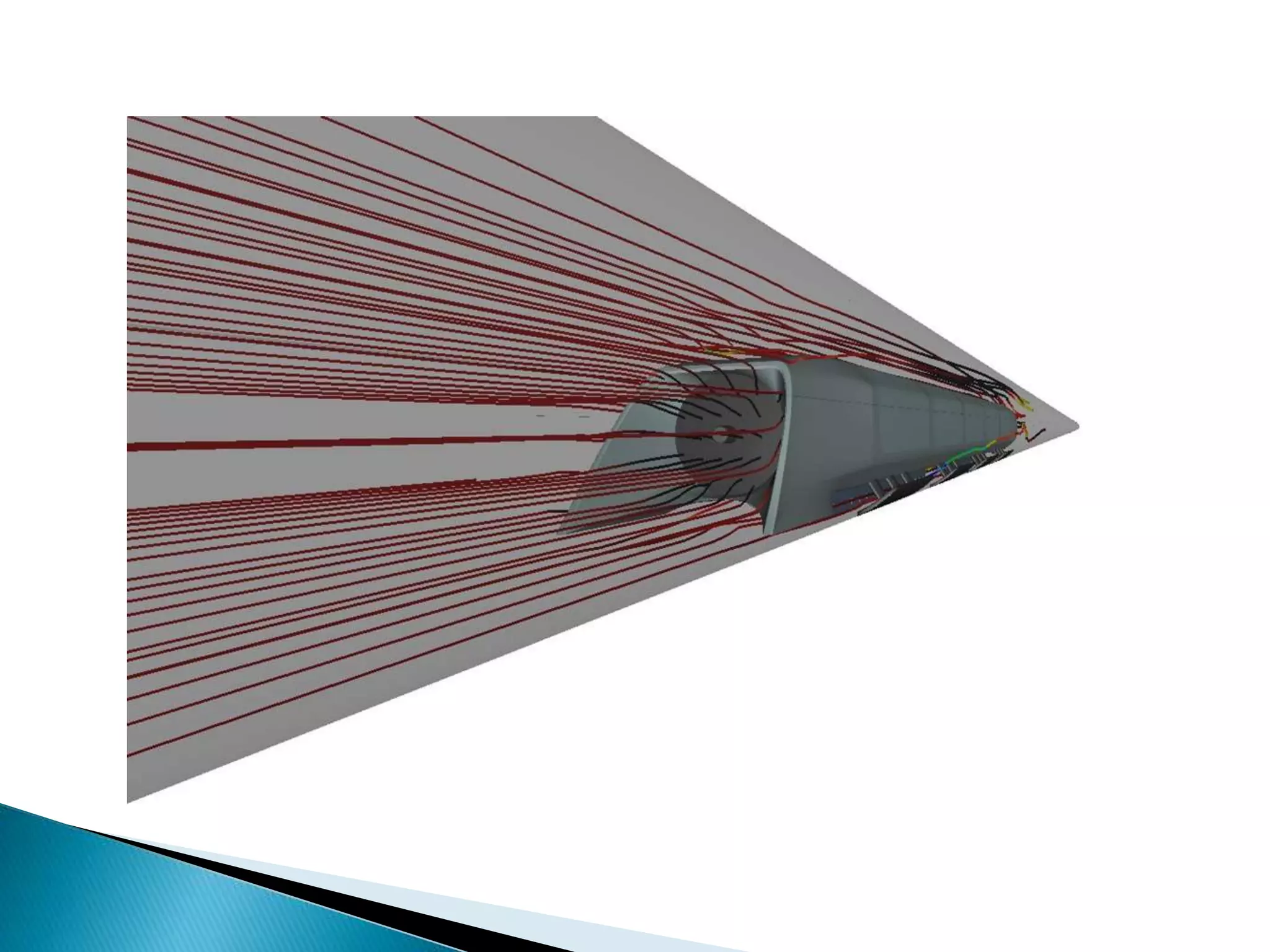
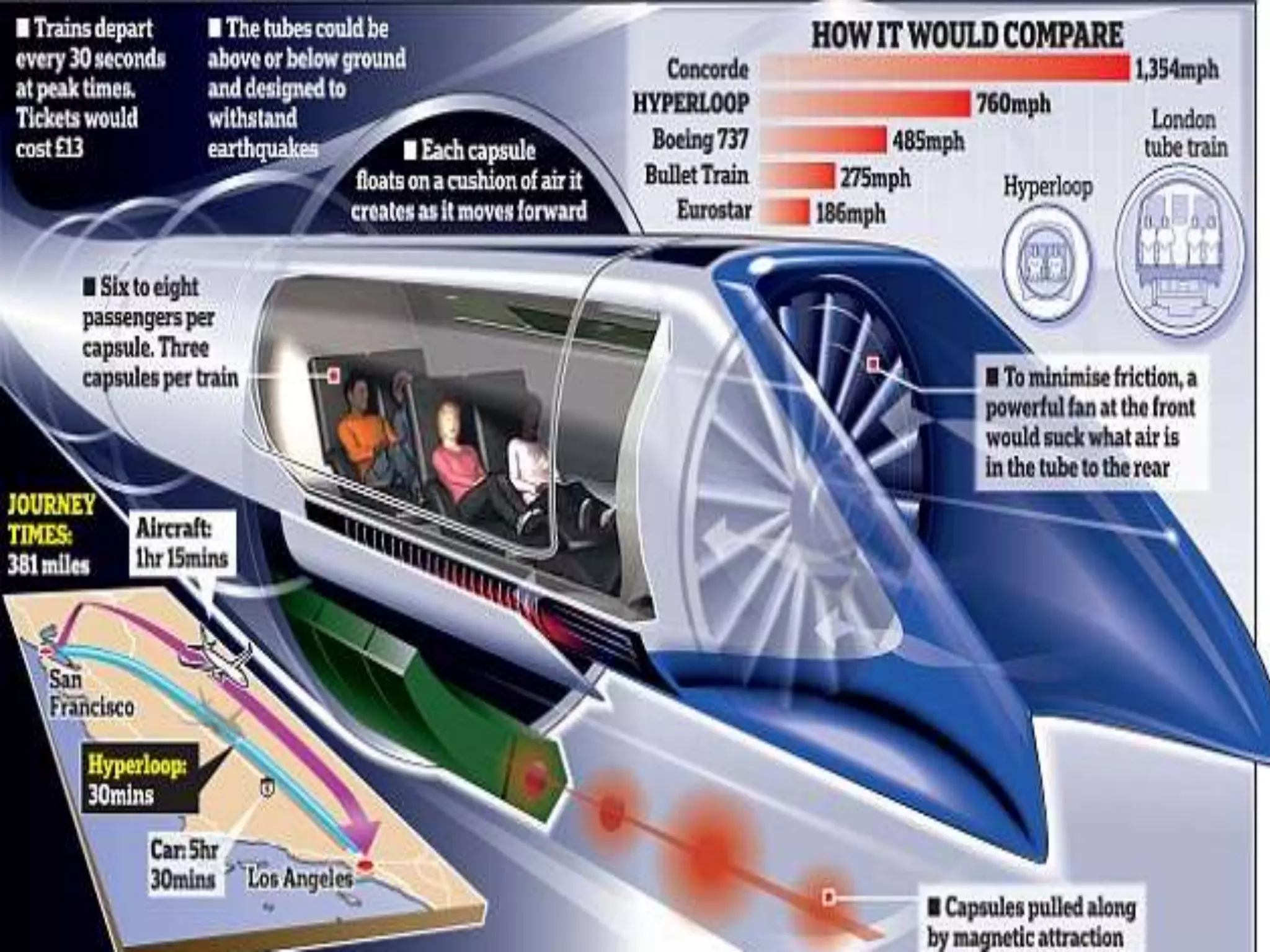
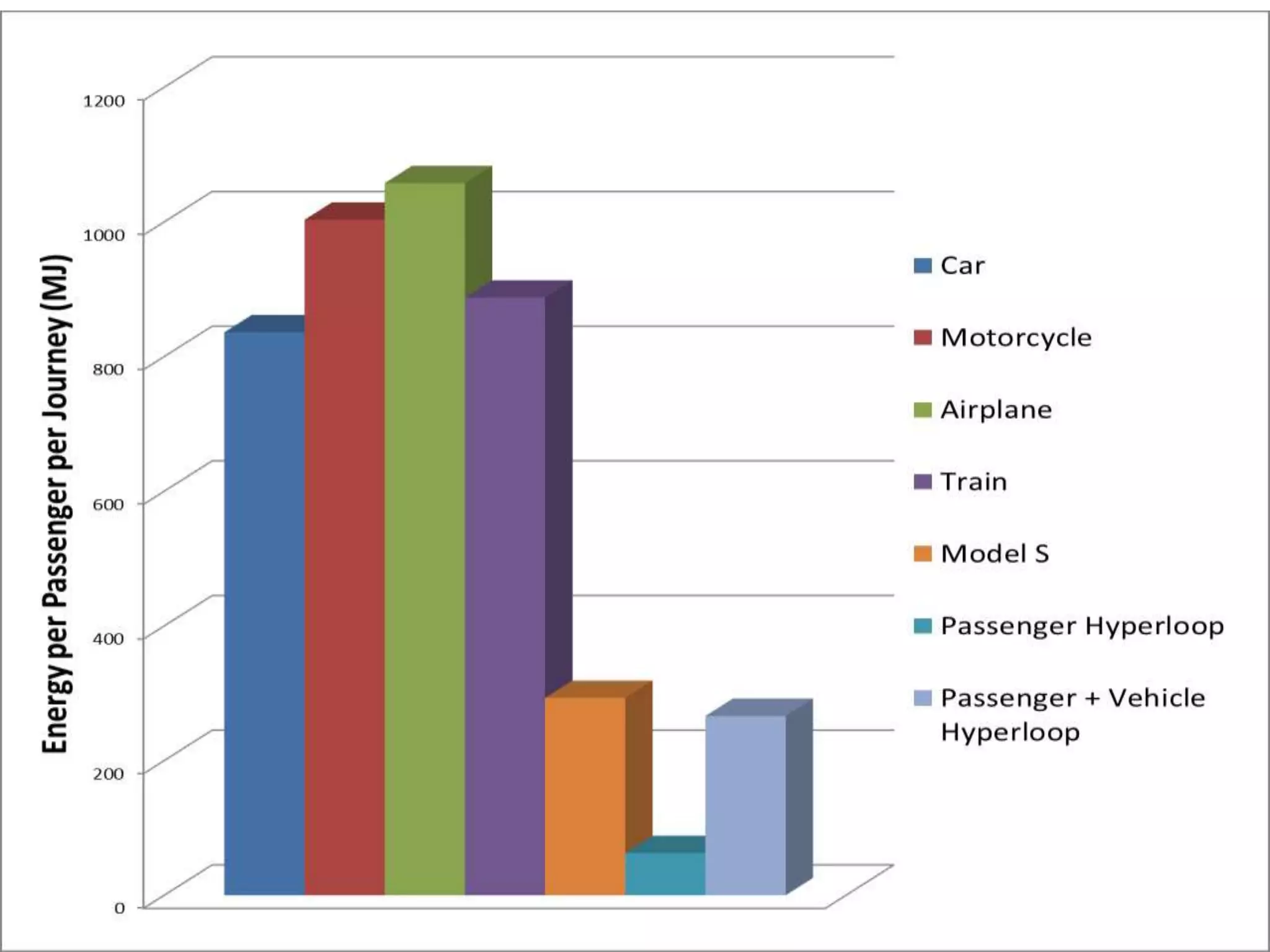
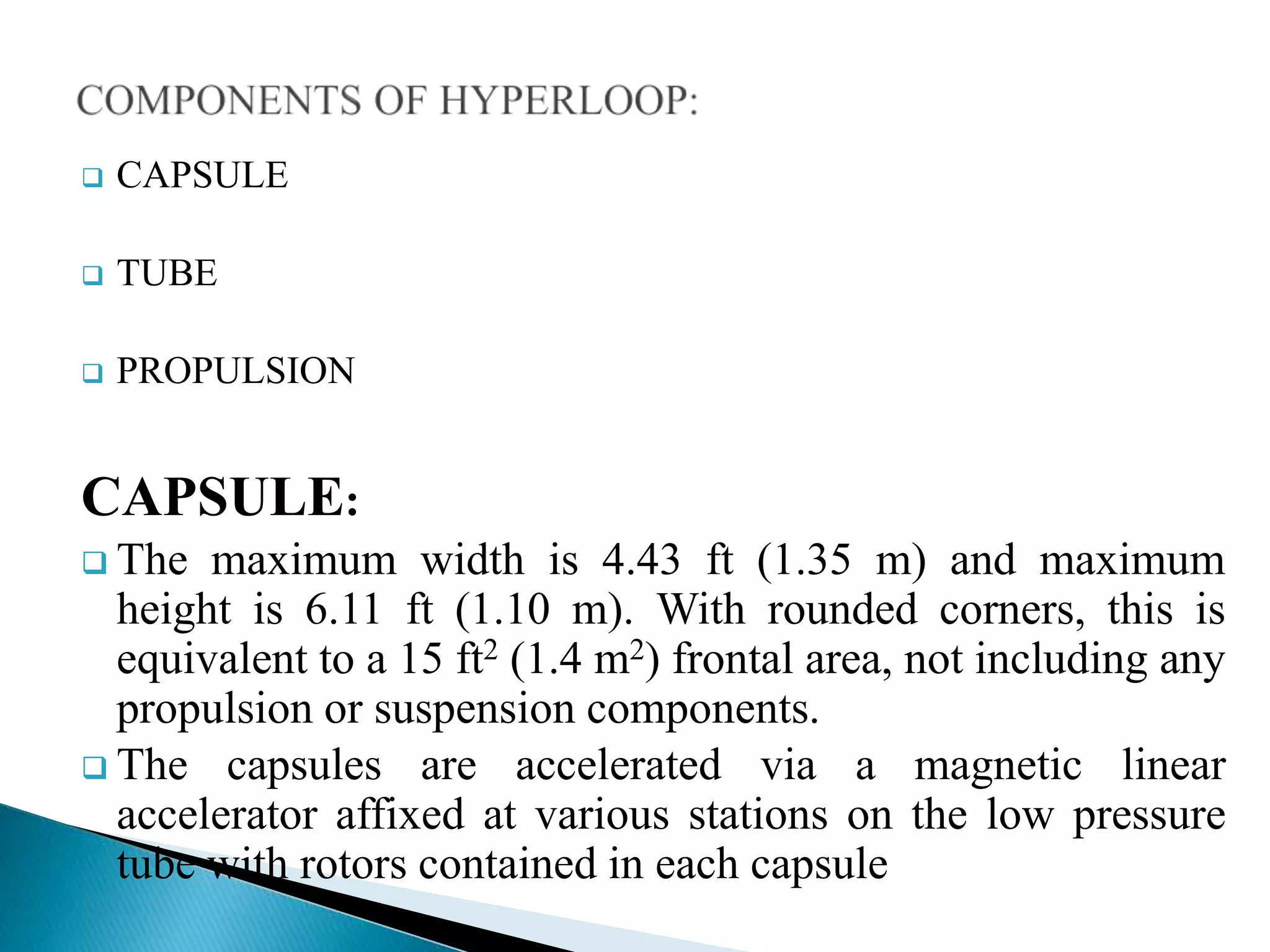
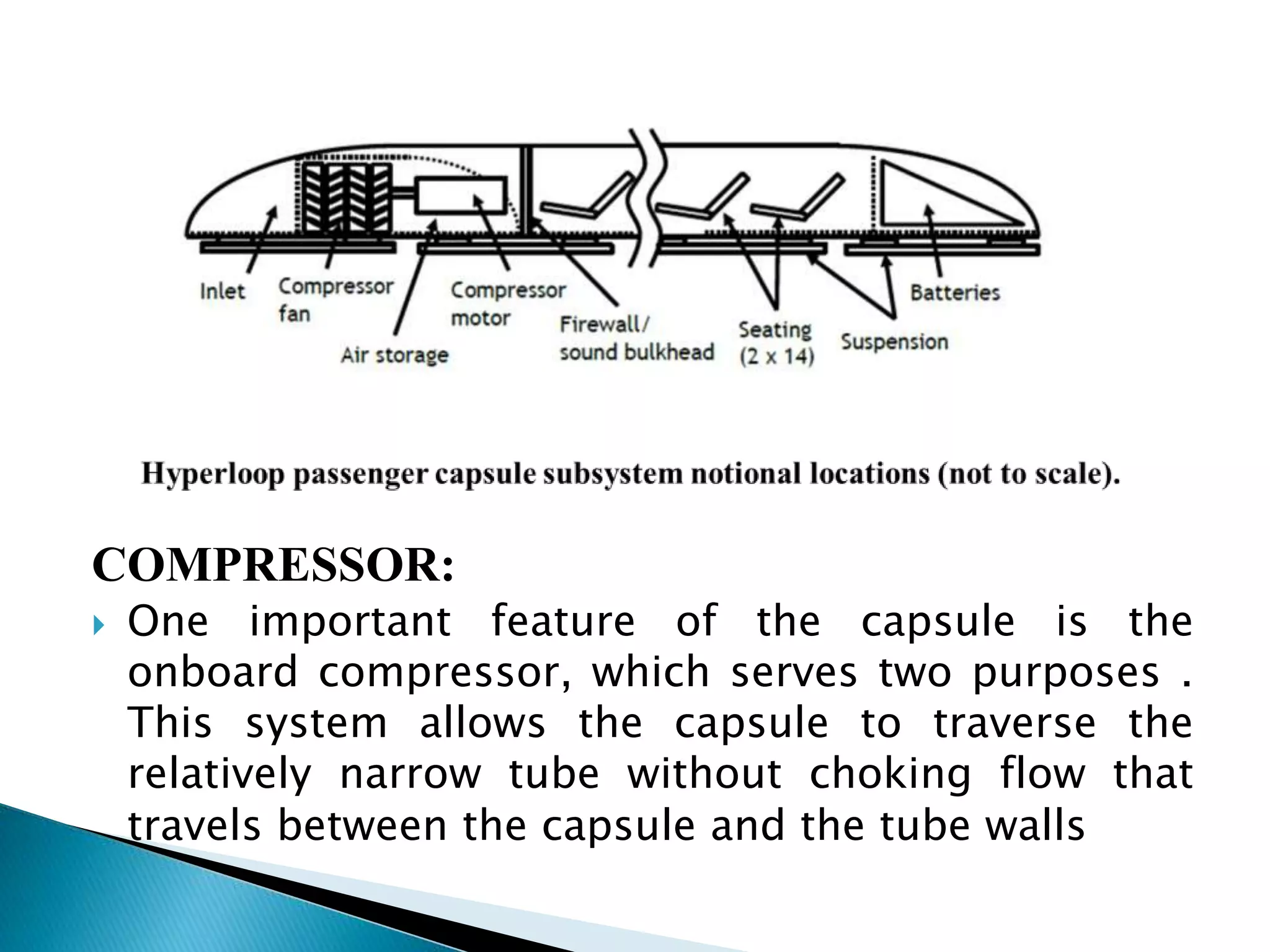
The document presents information about Hyperloop, a proposed mode of transportation consisting of passenger capsules that travel at both low and high speeds through a low pressure tube. Key points include that it was proposed by Elon Musk as a faster and cheaper alternative to existing high speed rail projects. Hyperloop is designed to transport passengers at speeds up to 800 mph using linear induction motors and air bearings to accelerate and levitate capsules through the tube. Technical details covered include the capsule design, tube construction, propulsion and levitation systems, and safety considerations.