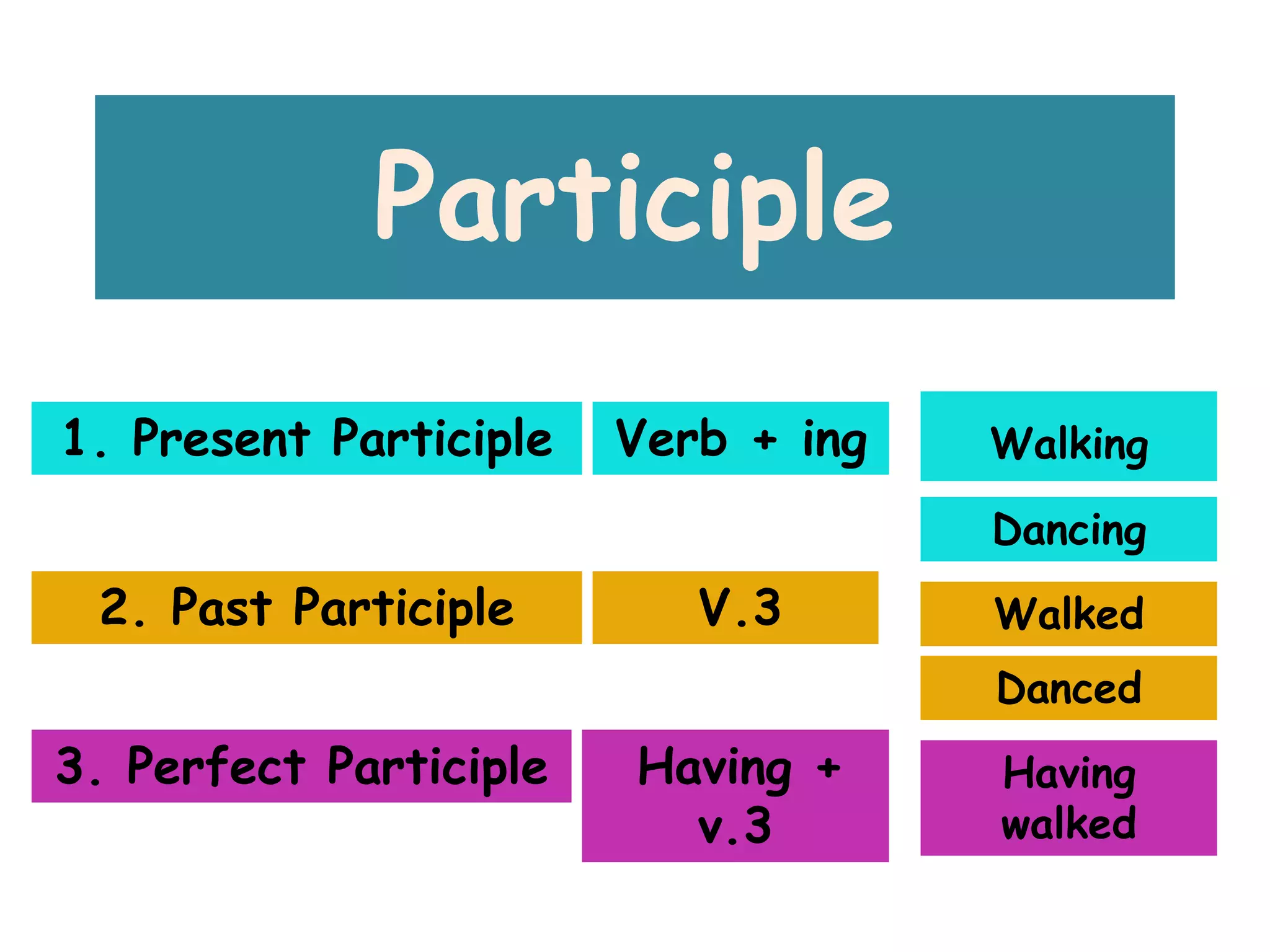
This document defines and provides examples of different types of participles in English grammar:
1. Present participles are formed with a verb plus "-ing" (e.g. walking, dancing).
2. Past participles are usually formed as the third principal part of a verb (e.g. walked, danced).
3. Perfect participles are formed with "having" plus the past participle (e.g. having walked).
Participial phrases using these different participles can function adjectivally or adverbially in sentences.