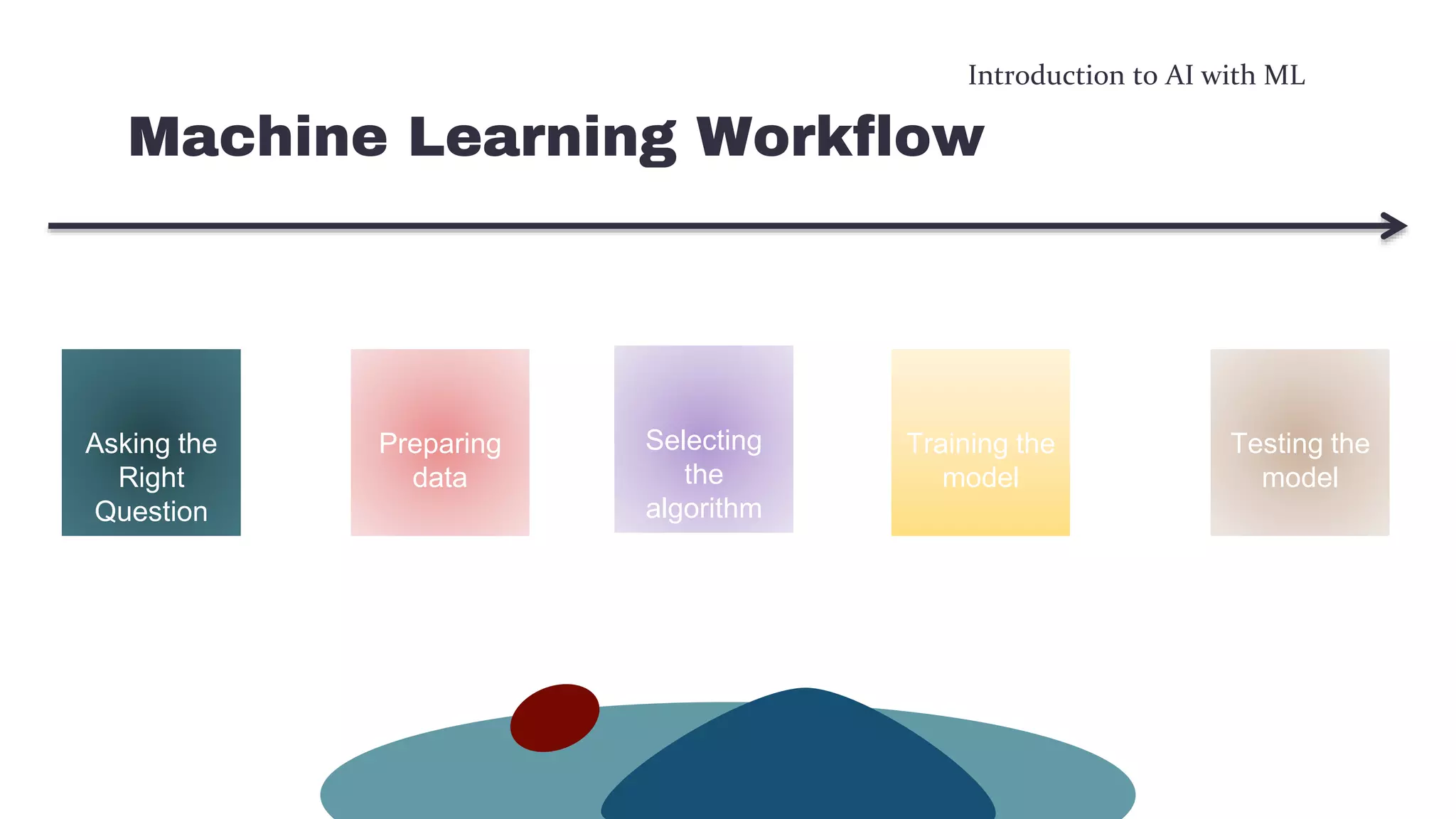
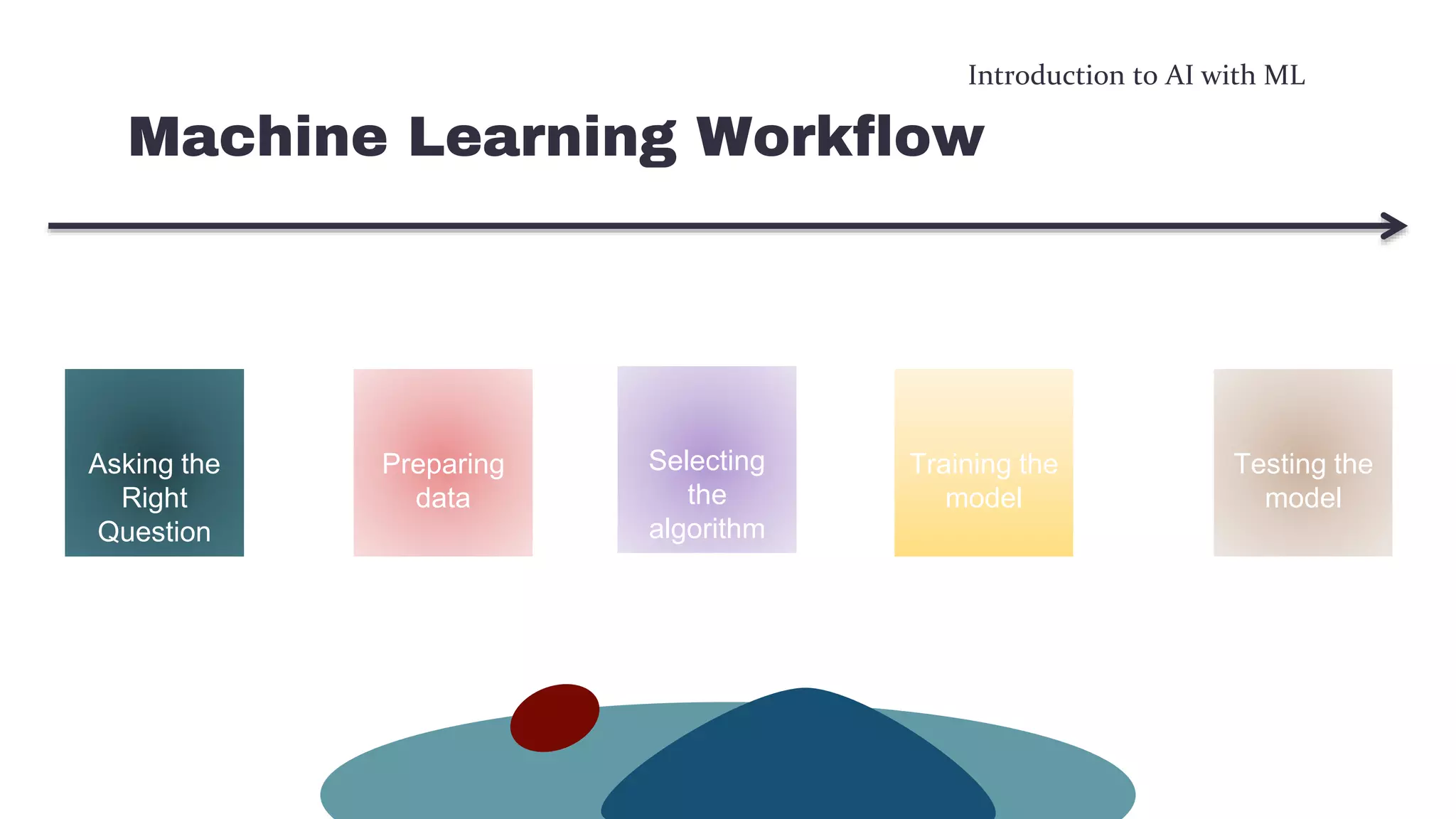
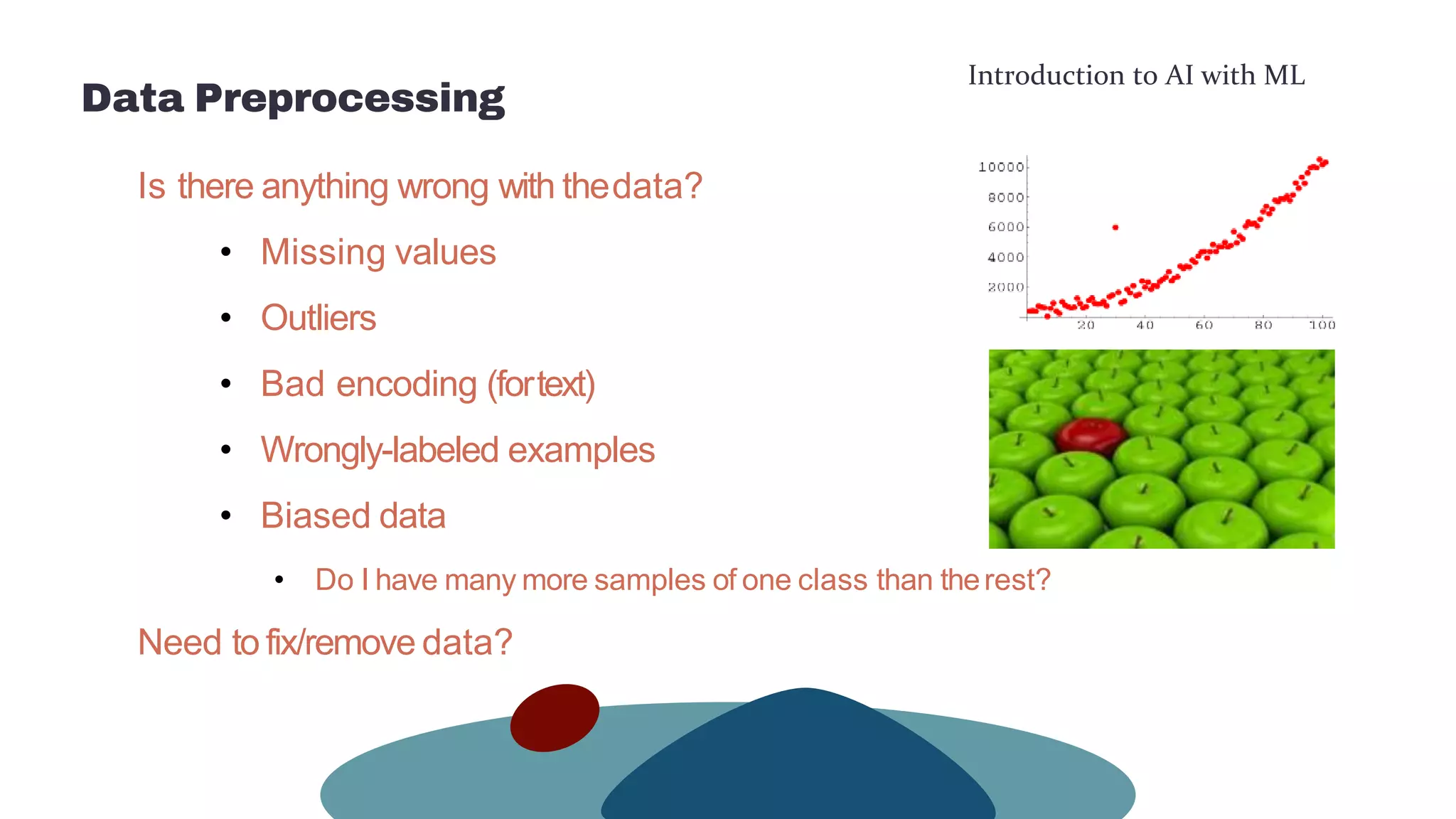
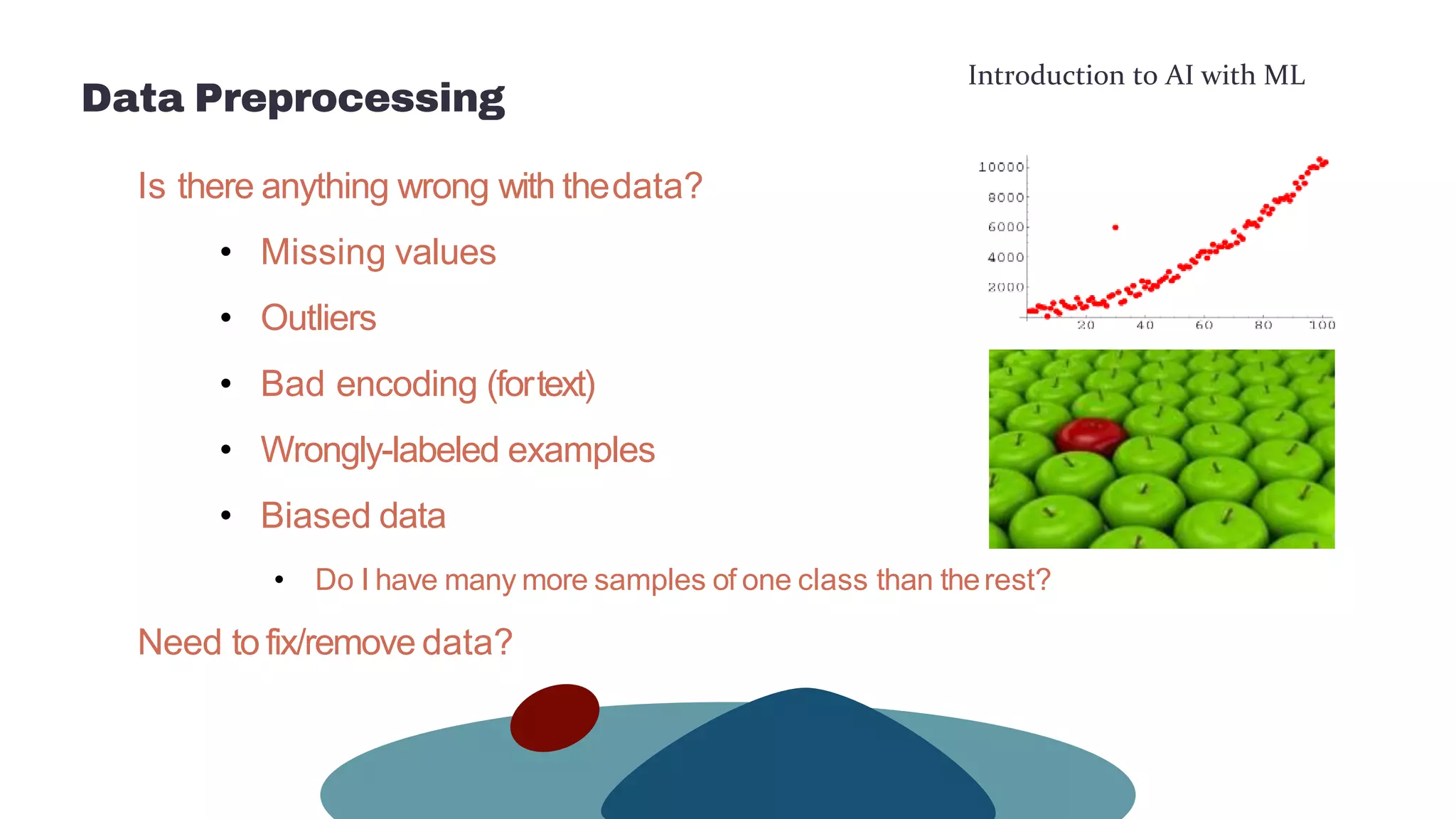
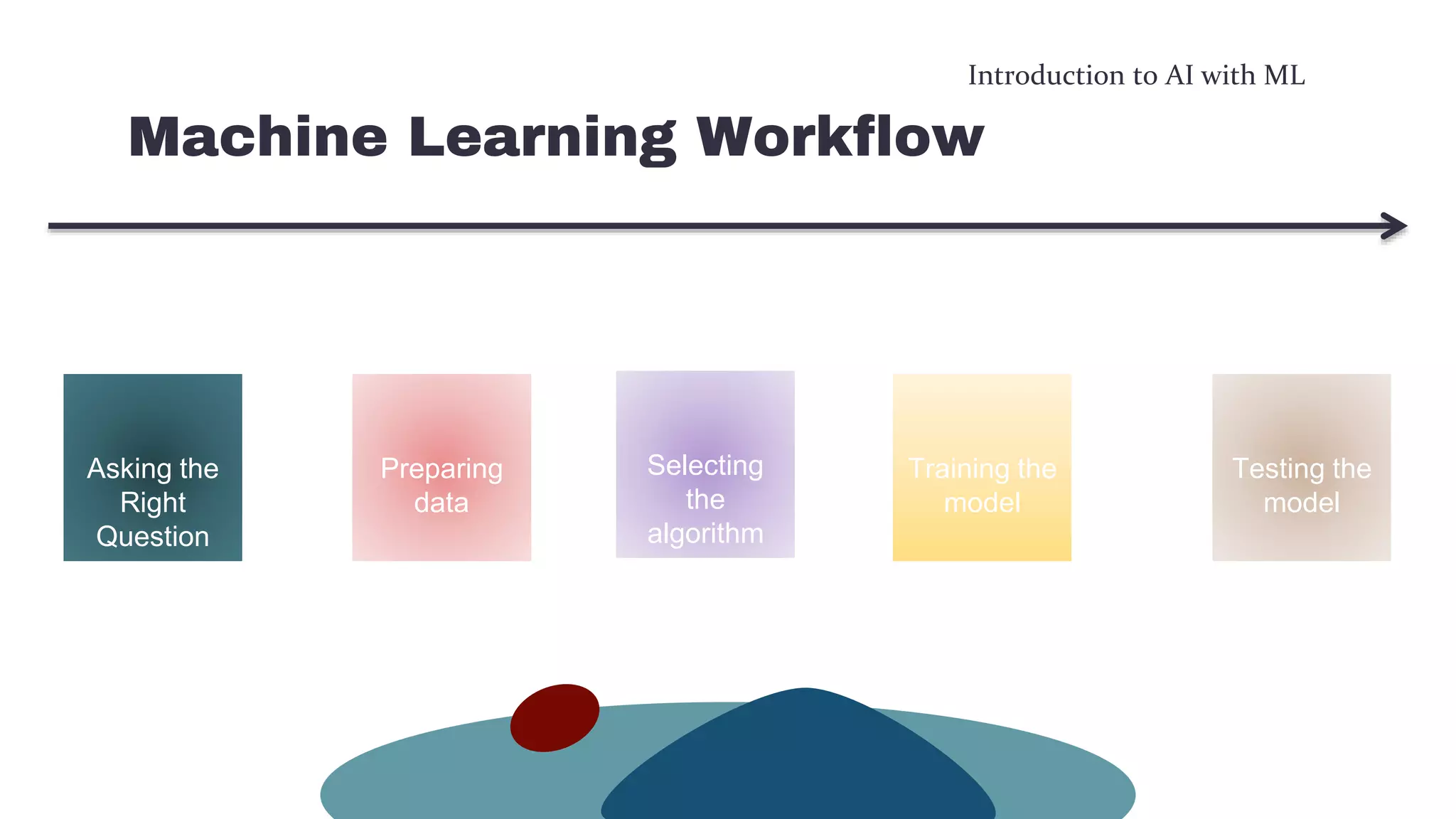
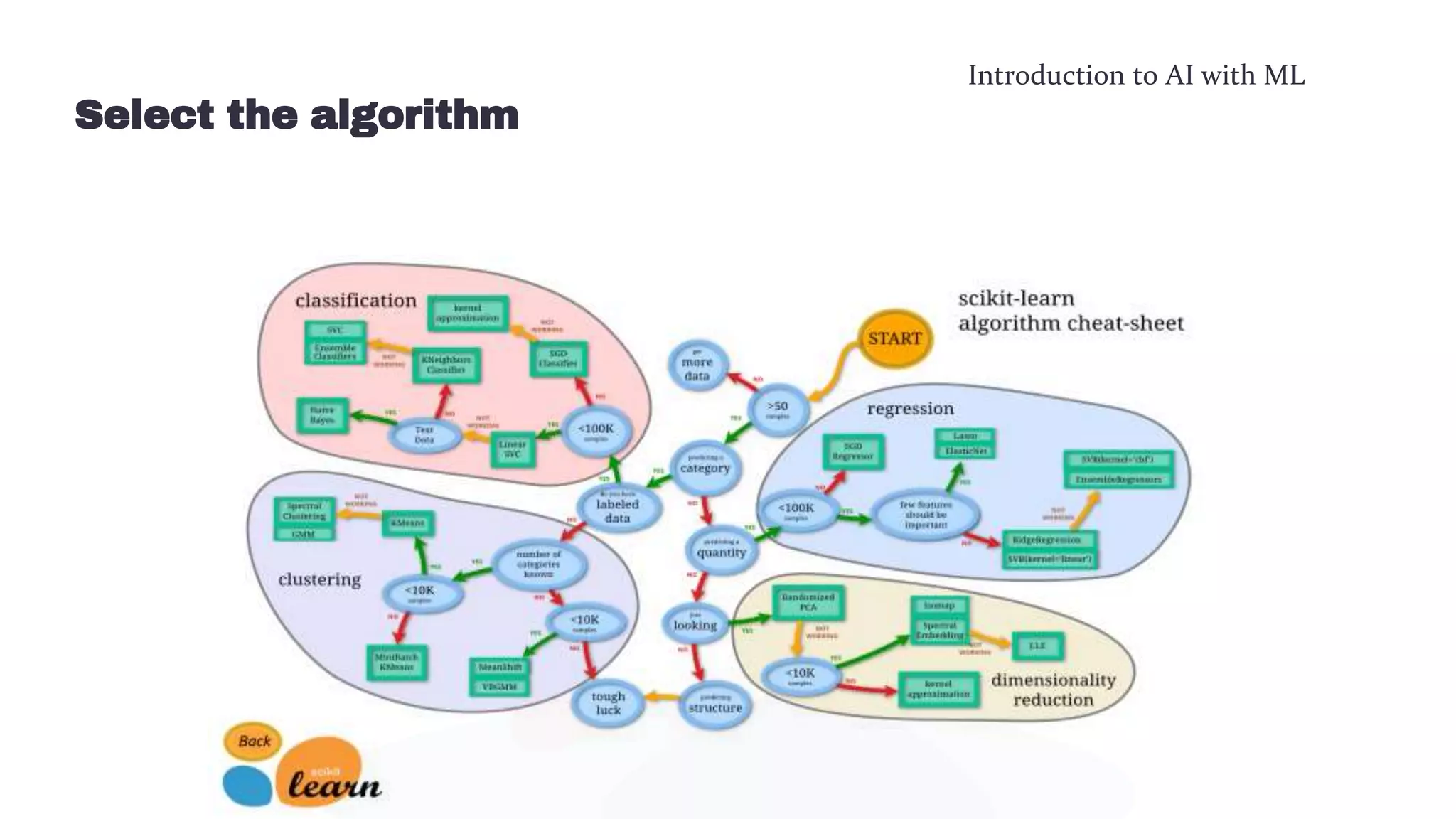
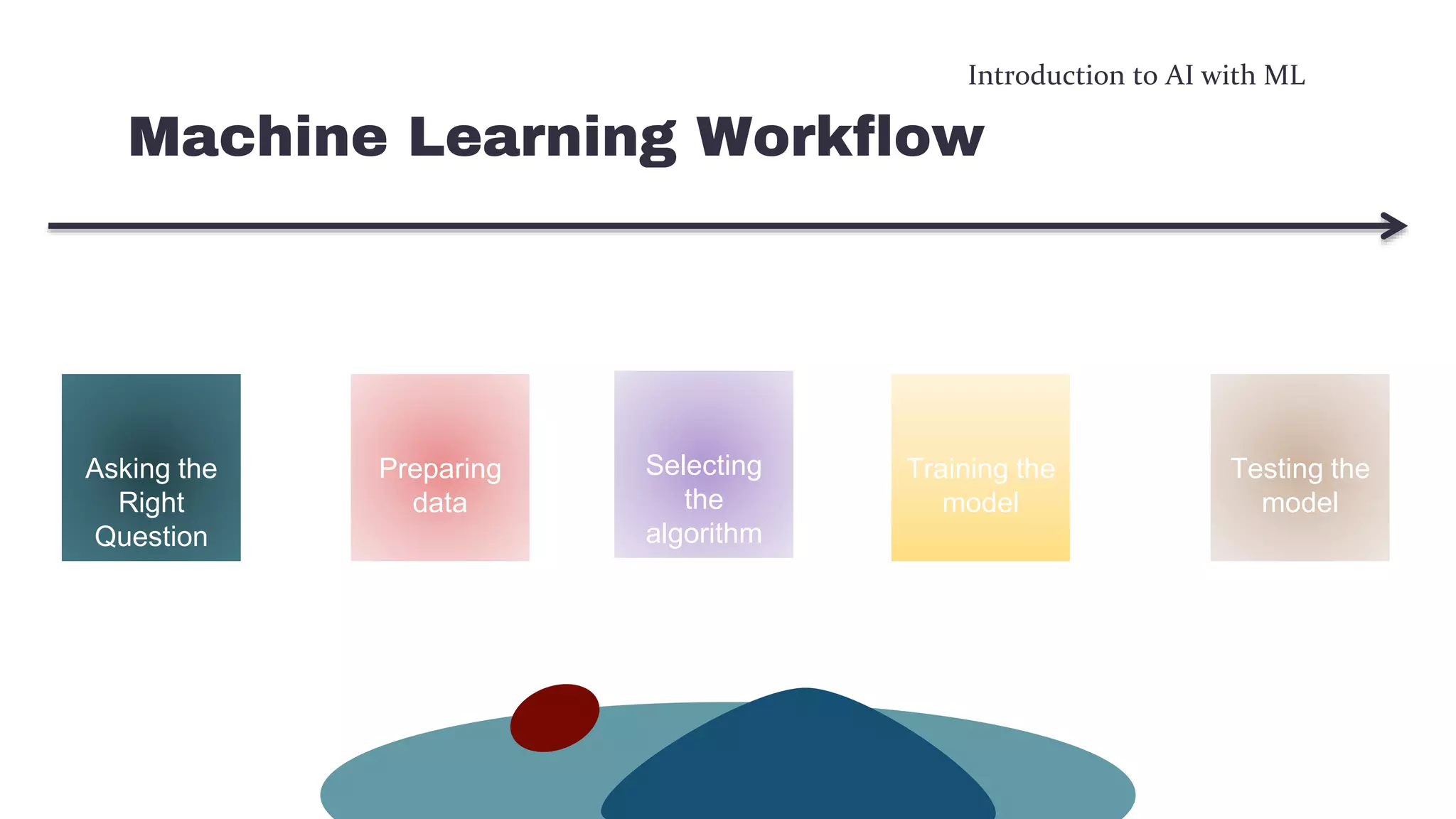
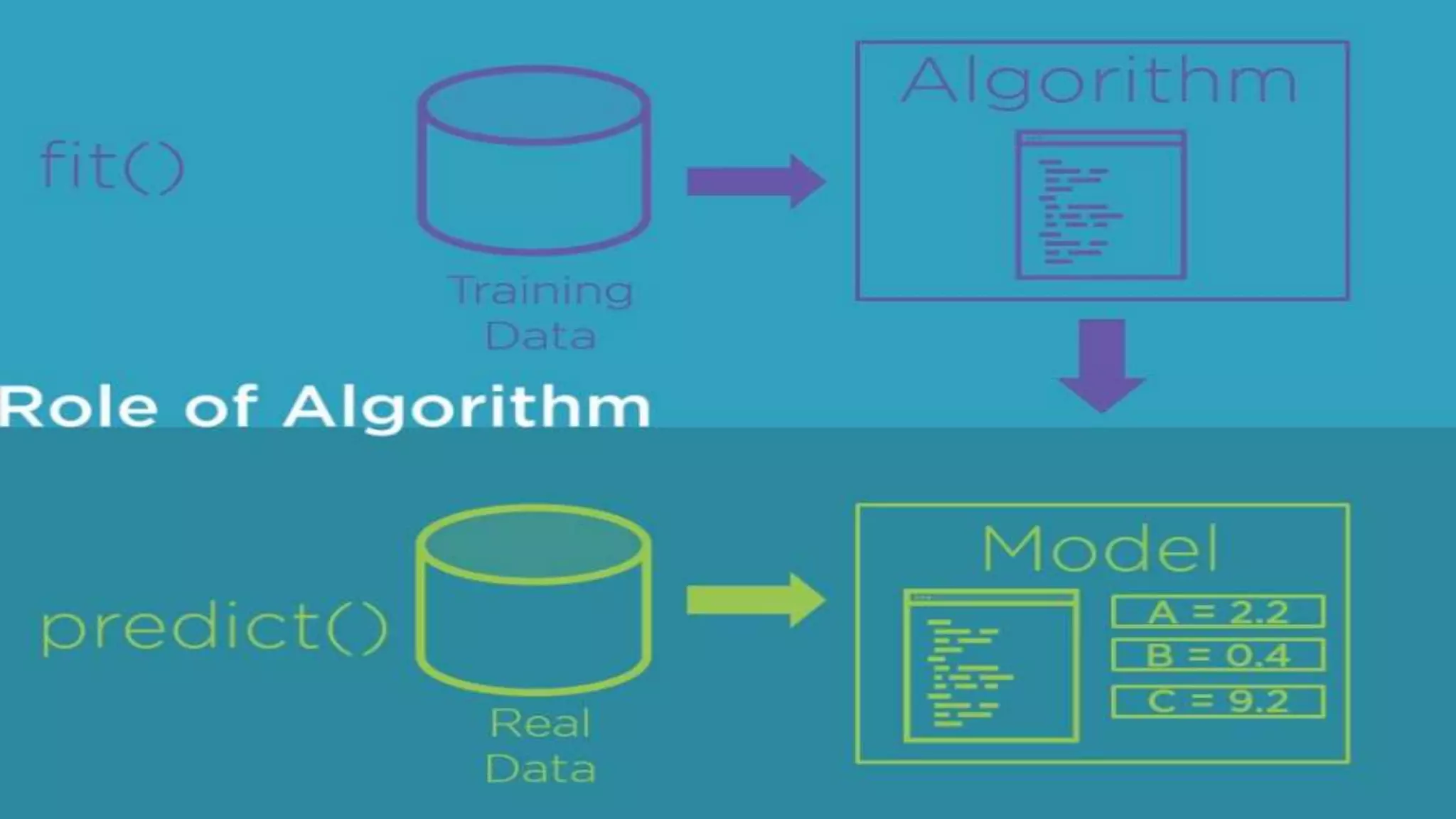
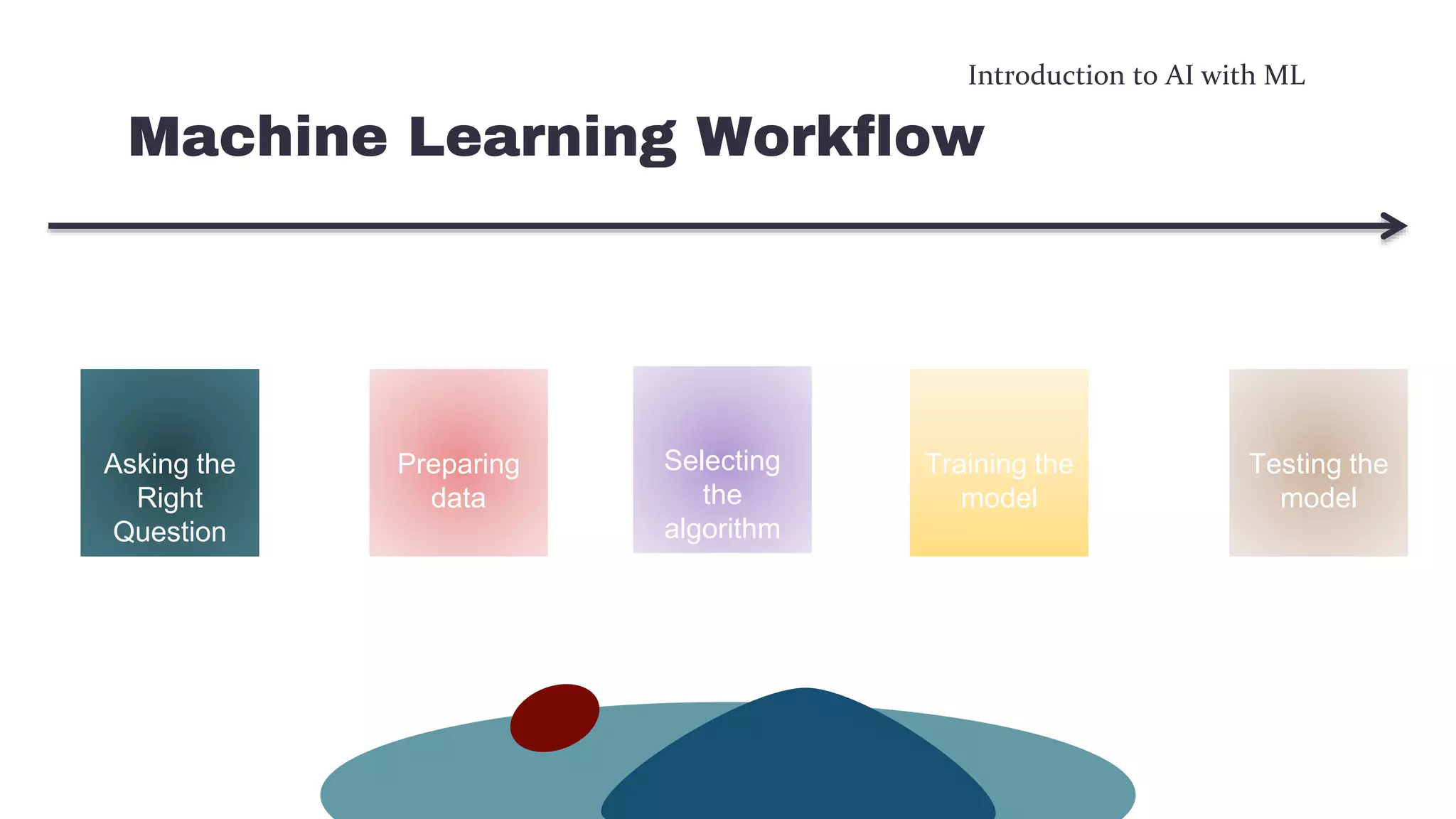
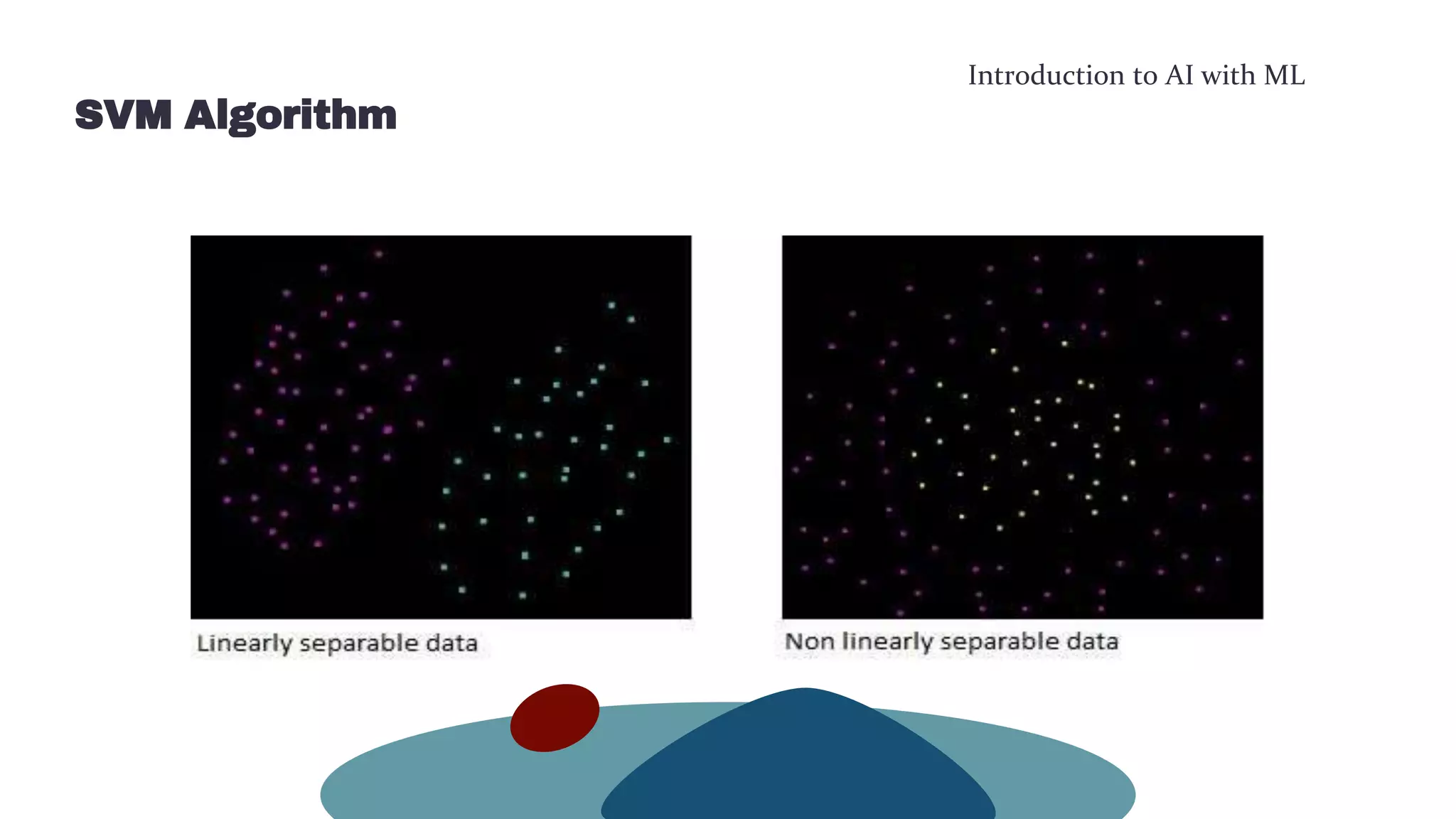
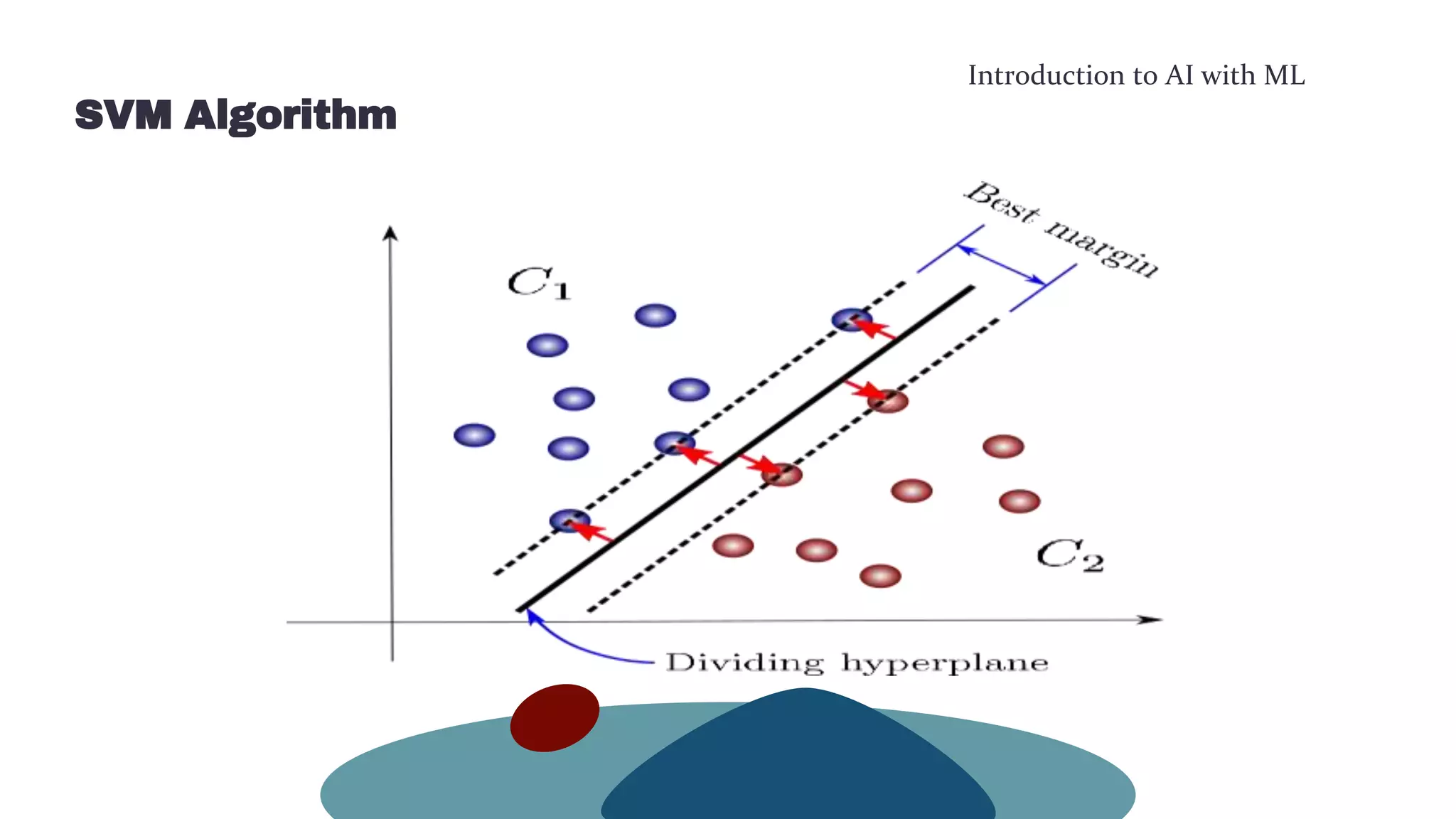
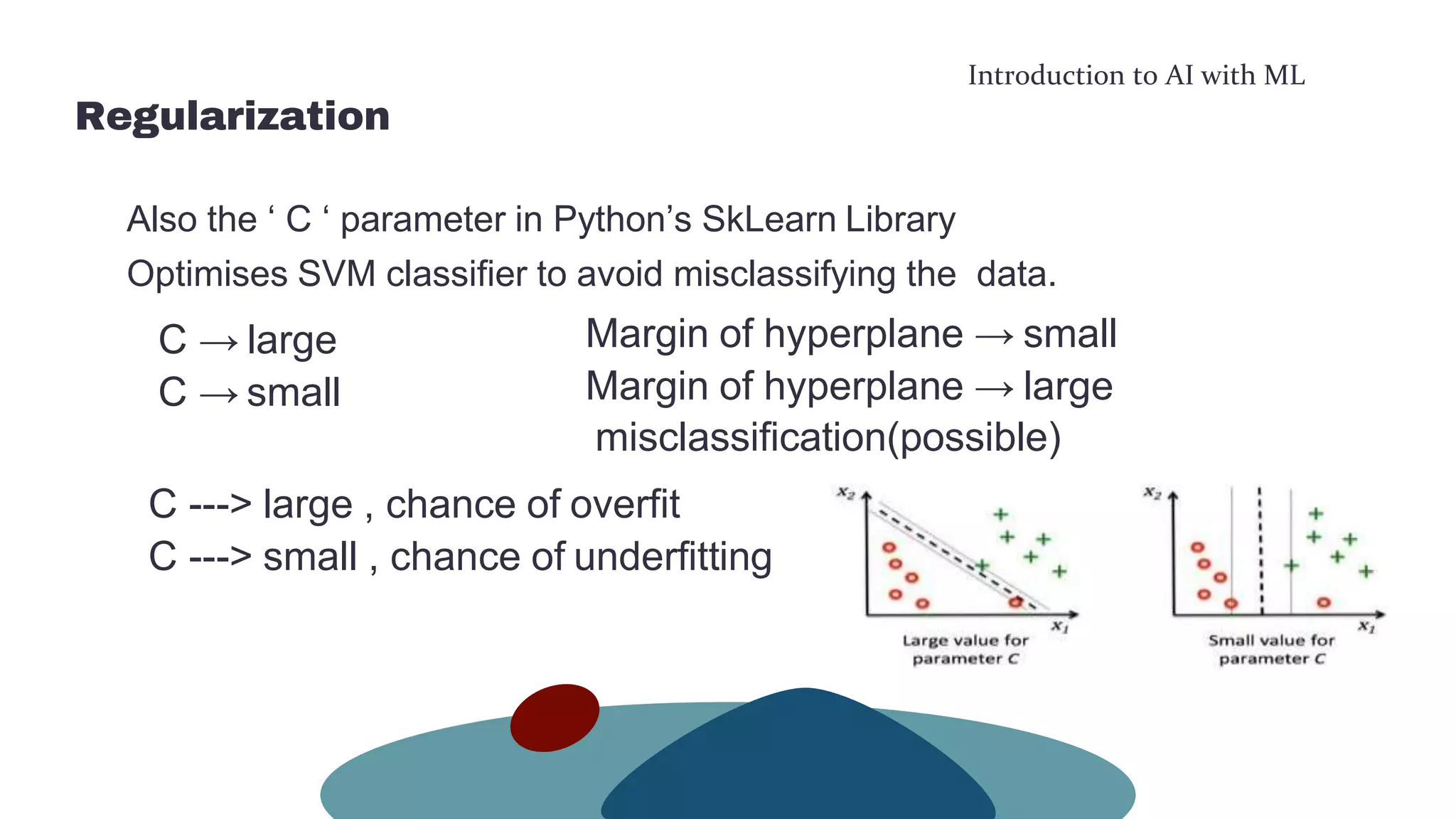
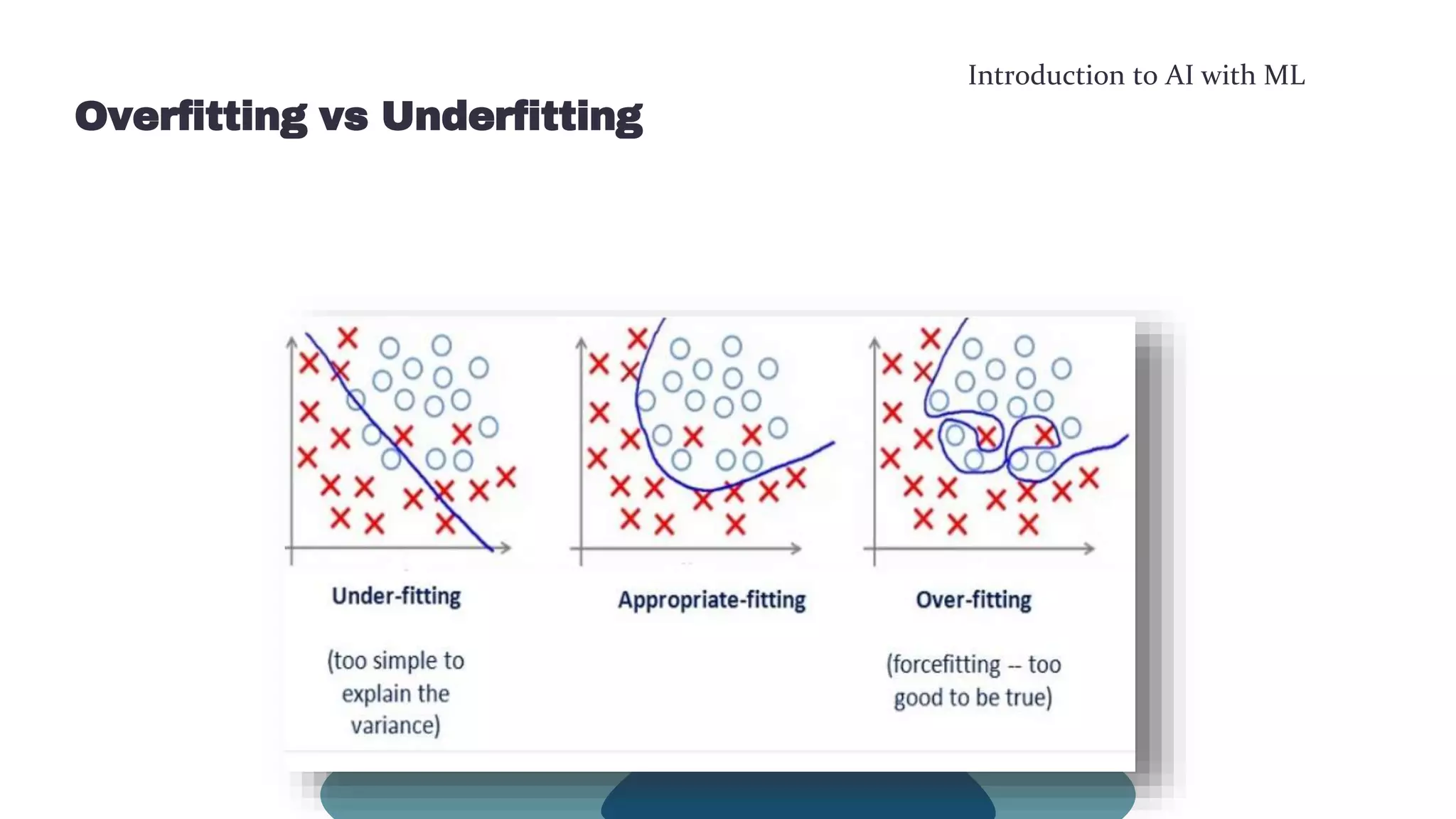
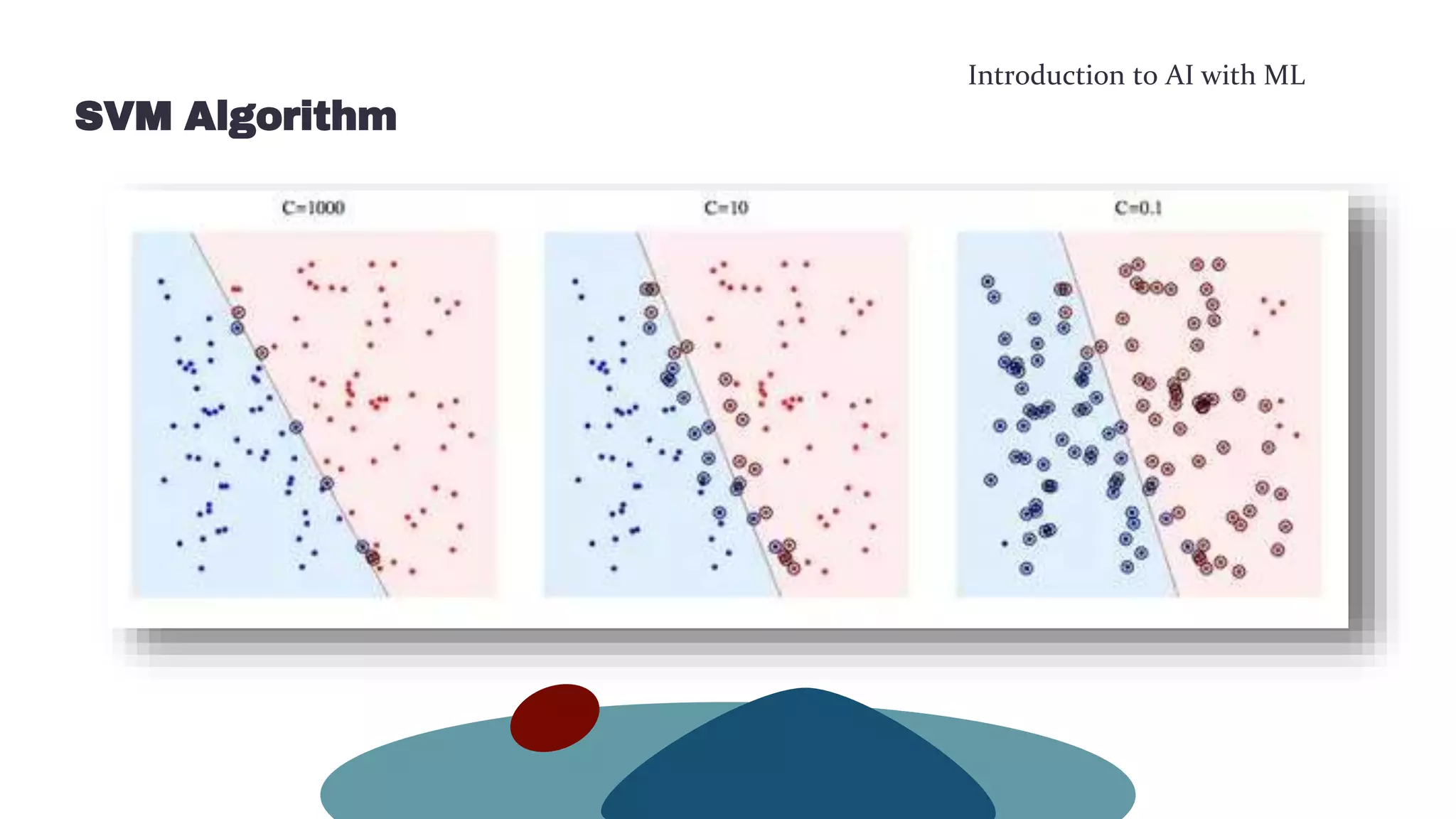
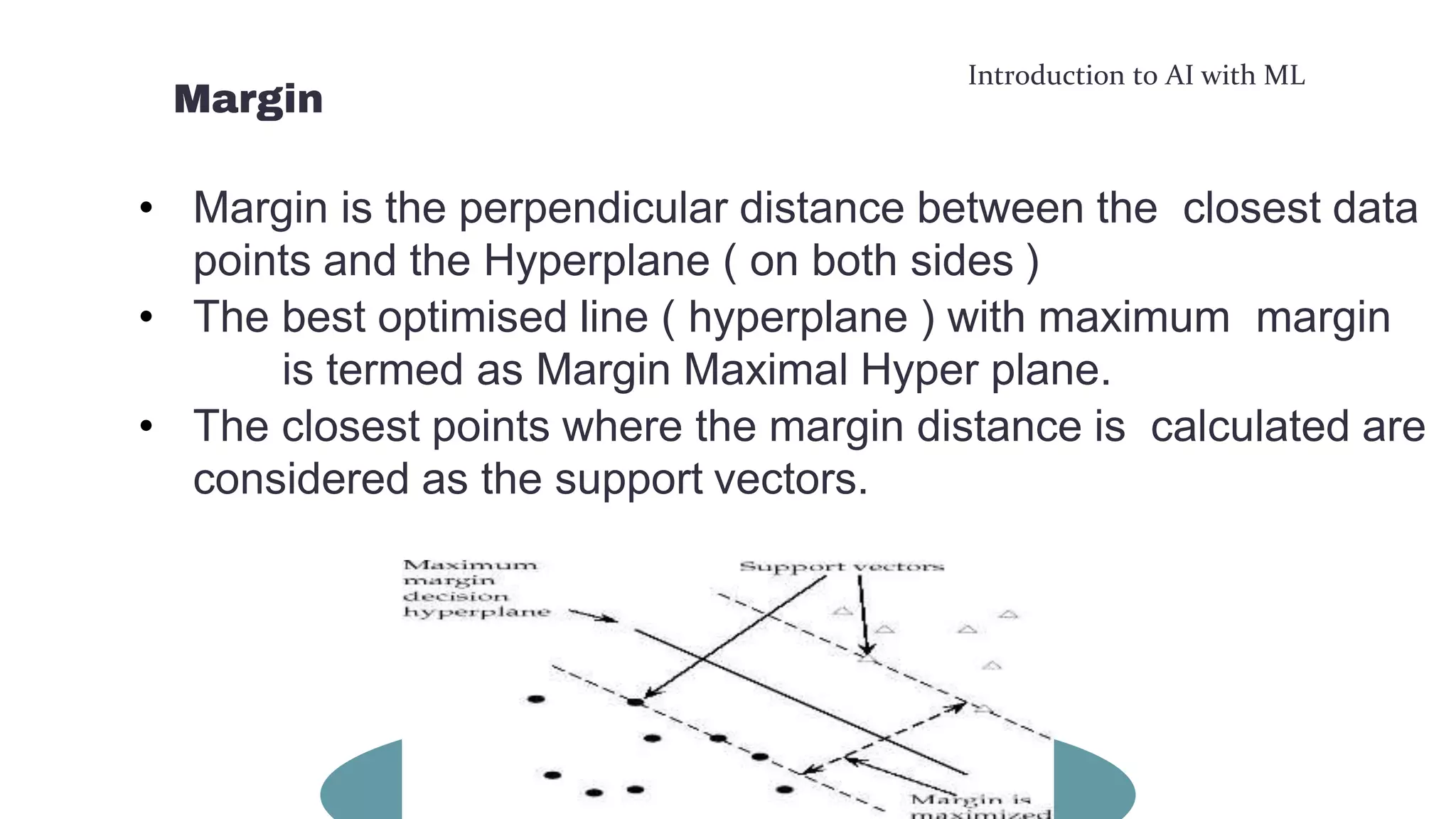
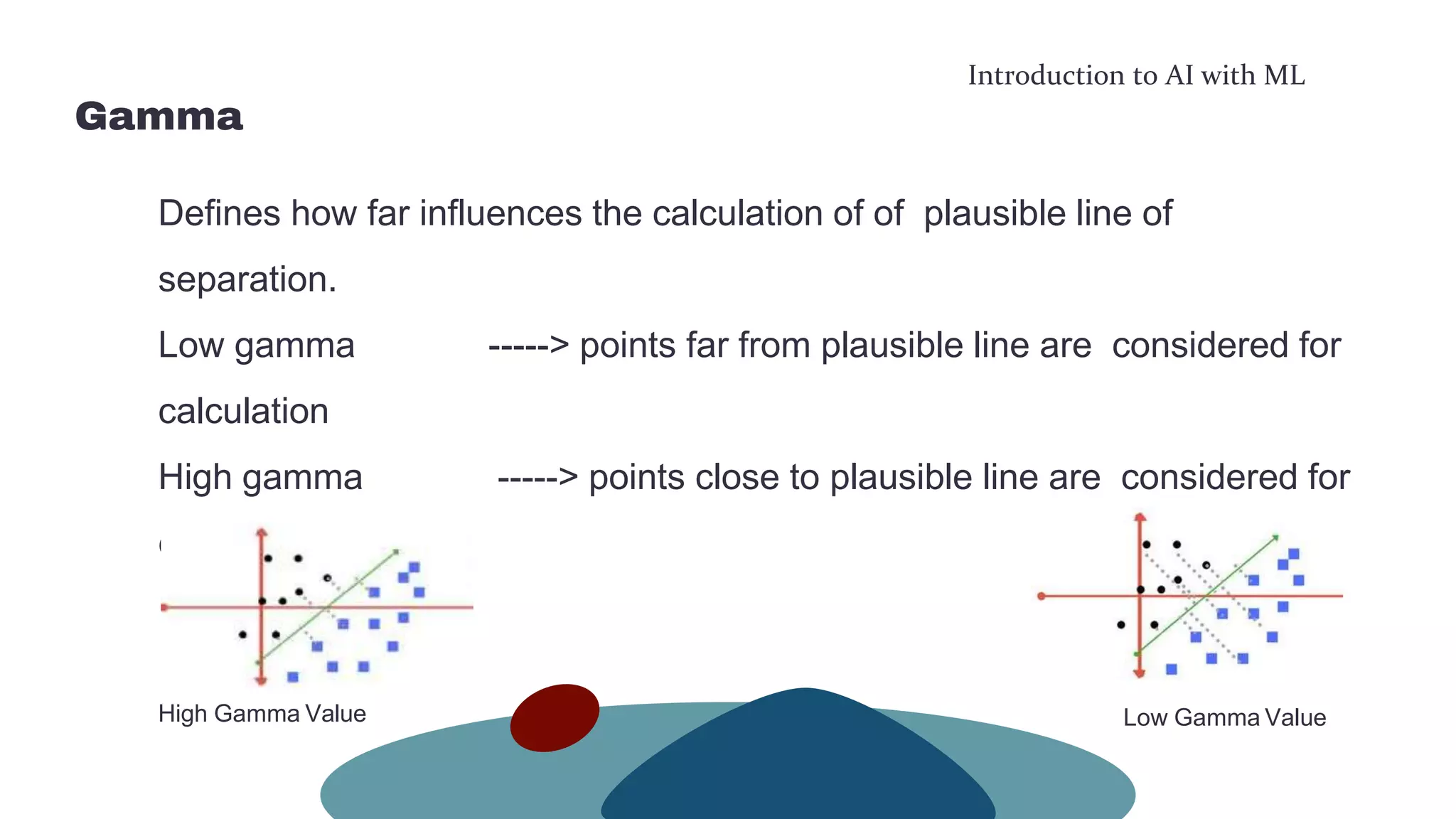
This document provides an overview of machine learning concepts including the machine learning workflow, algorithms, and techniques. It discusses the machine learning workflow which includes asking the right question, preparing data, selecting an algorithm, training a model, and testing the model. It also covers machine learning algorithms like SVM and techniques such as feature scaling. The document is intended to introduce readers to artificial intelligence using machine learning.