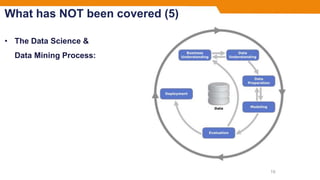
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, including:
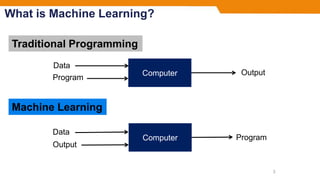
- Machine learning allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed by using data to find patterns and make predictions.
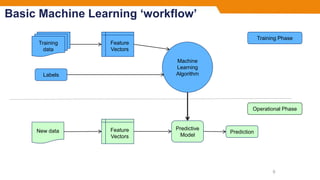
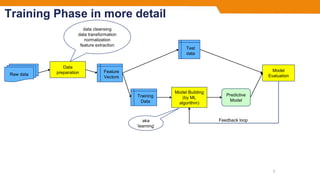
- There are two main phases: the training phase where a model is built using sample data, and the operational phase where the model is used to make predictions on new data.
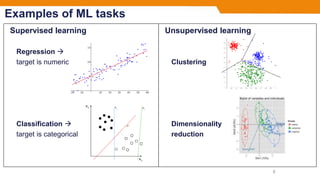
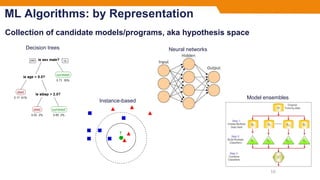
- Common machine learning tasks include supervised learning techniques like regression and classification, as well as unsupervised learning techniques like clustering and dimensionality reduction.
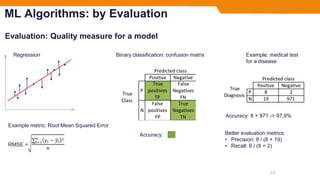
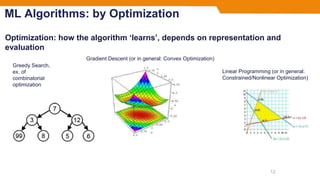
- The document outlines different machine learning algorithms categorized by their representation, evaluation, and optimization methods, but does not cover specifics of individual algorithms.