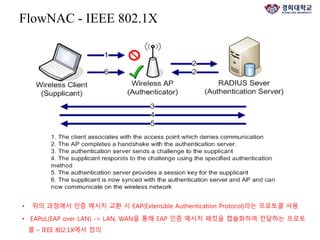
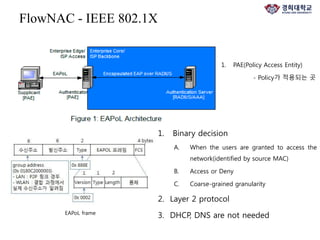
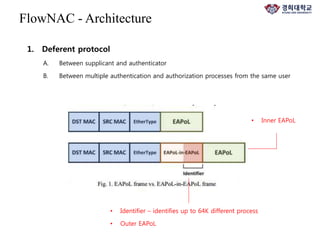
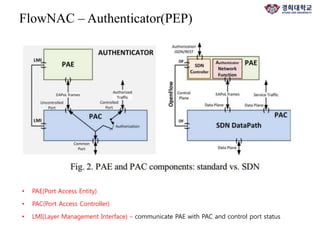
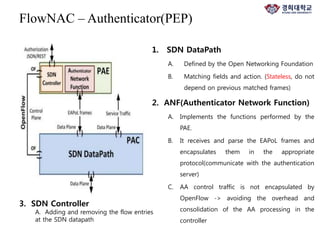
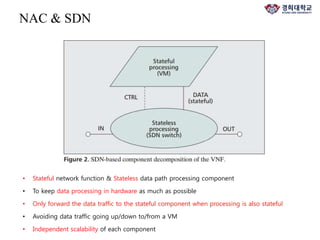
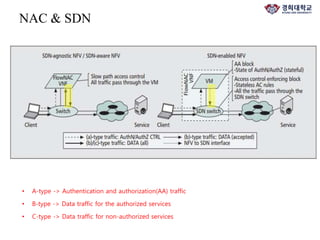
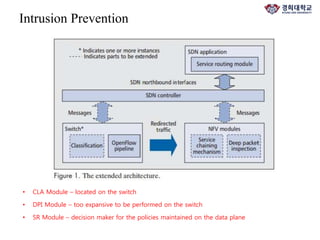
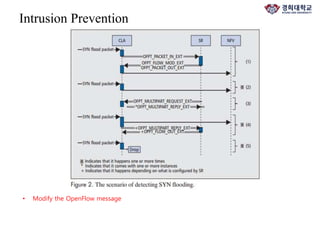
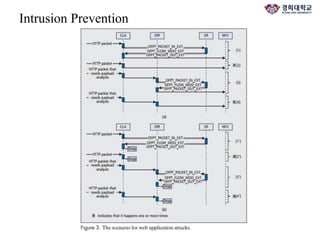
The document discusses FlowNAC, which is a flow-based network access control solution that allows granting users access to the network depending on the requested service. It operates at a fine-grained level based on traffic flows and can authorize access to specific services independently. FlowNAC relies on a modified version of IEEE 802.1X and does not require IP addresses or DHCP. It uses encapsulated EAPoL frames between the supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server. The authenticator enforces access control based on authorized flows defined in the SDN controller. The document also discusses how SDN and network function virtualization can be combined for intrusion prevention by processing some traffic in the data plane and forwarding other