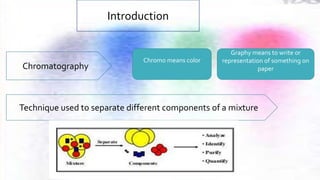
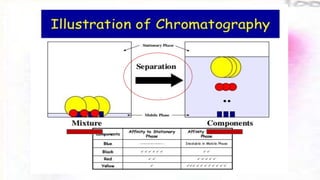
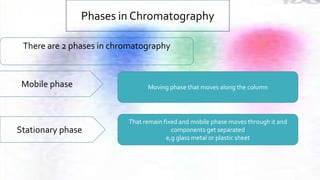
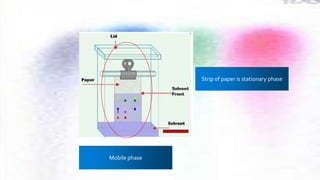
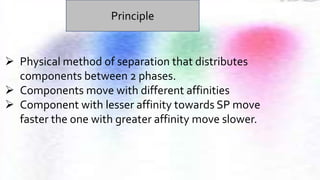
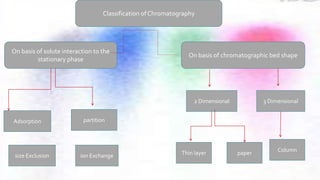
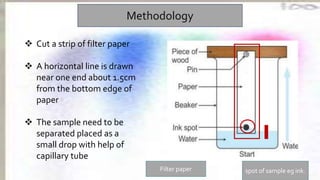
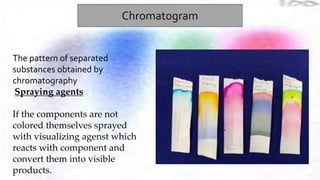
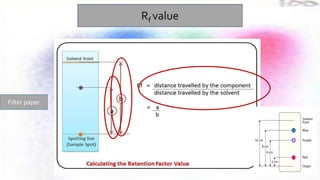
Chromatography is a technique used to separate different components of a mixture. It involves two phases - a stationary phase that remains fixed and a mobile phase that moves through the stationary phase. Components separate as they move through the phases at different rates depending on their affinity for each phase. Paper chromatography uses a strip of paper as the stationary phase and a solvent as the mobile phase. Components separate as the solvent rises up the paper at different speeds. Their positions after drying can be observed to identify the different components or substances in the original mixture.