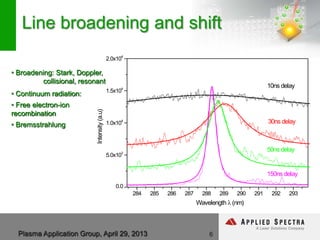
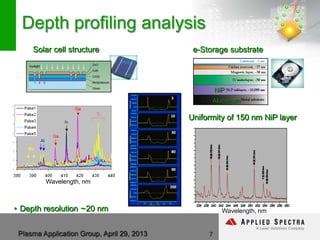
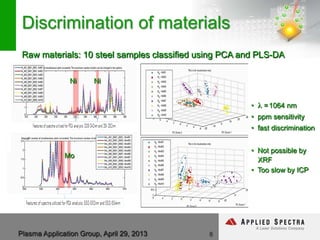
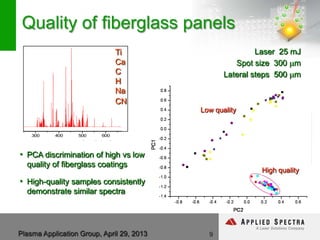
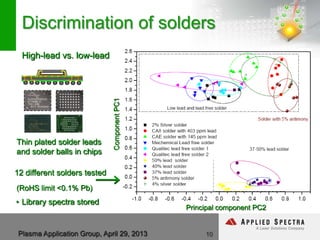
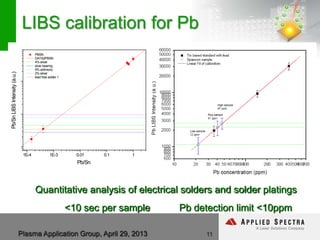
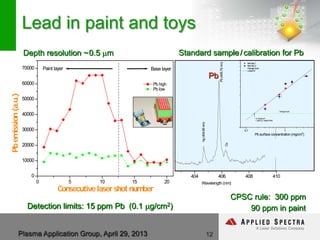
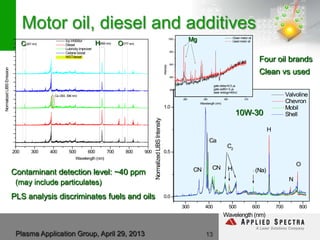
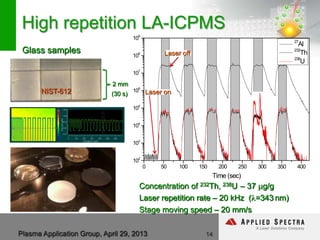
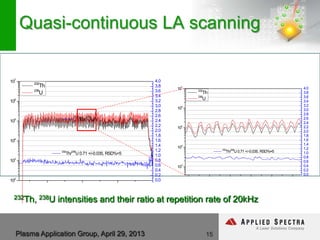
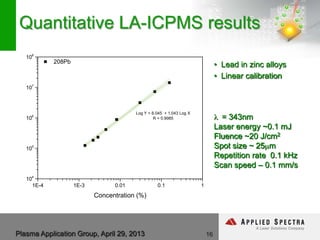
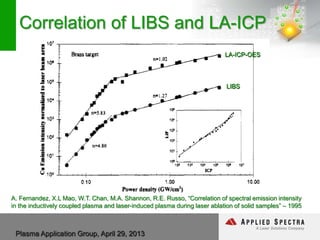
The document discusses advancements in laser ablation techniques combined with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS) for real-time analysis of materials. It highlights applications in micro-machining, chemical analysis, and depth profiling, emphasizing rapid and high-resolution methods without sample preparation. The conclusions note the versatility and efficiency of these technologies across various fields, including electronics and pharmaceuticals.