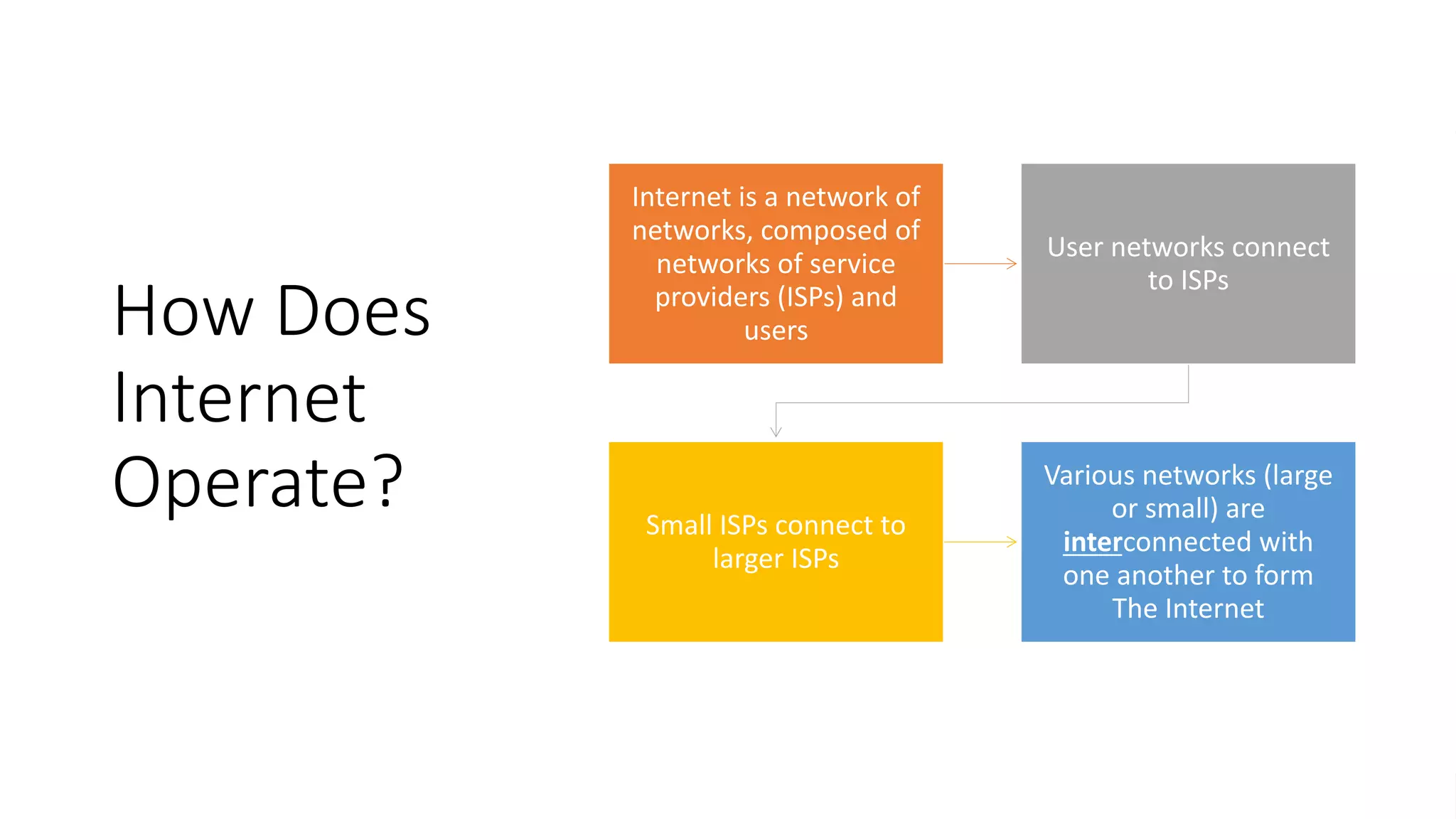
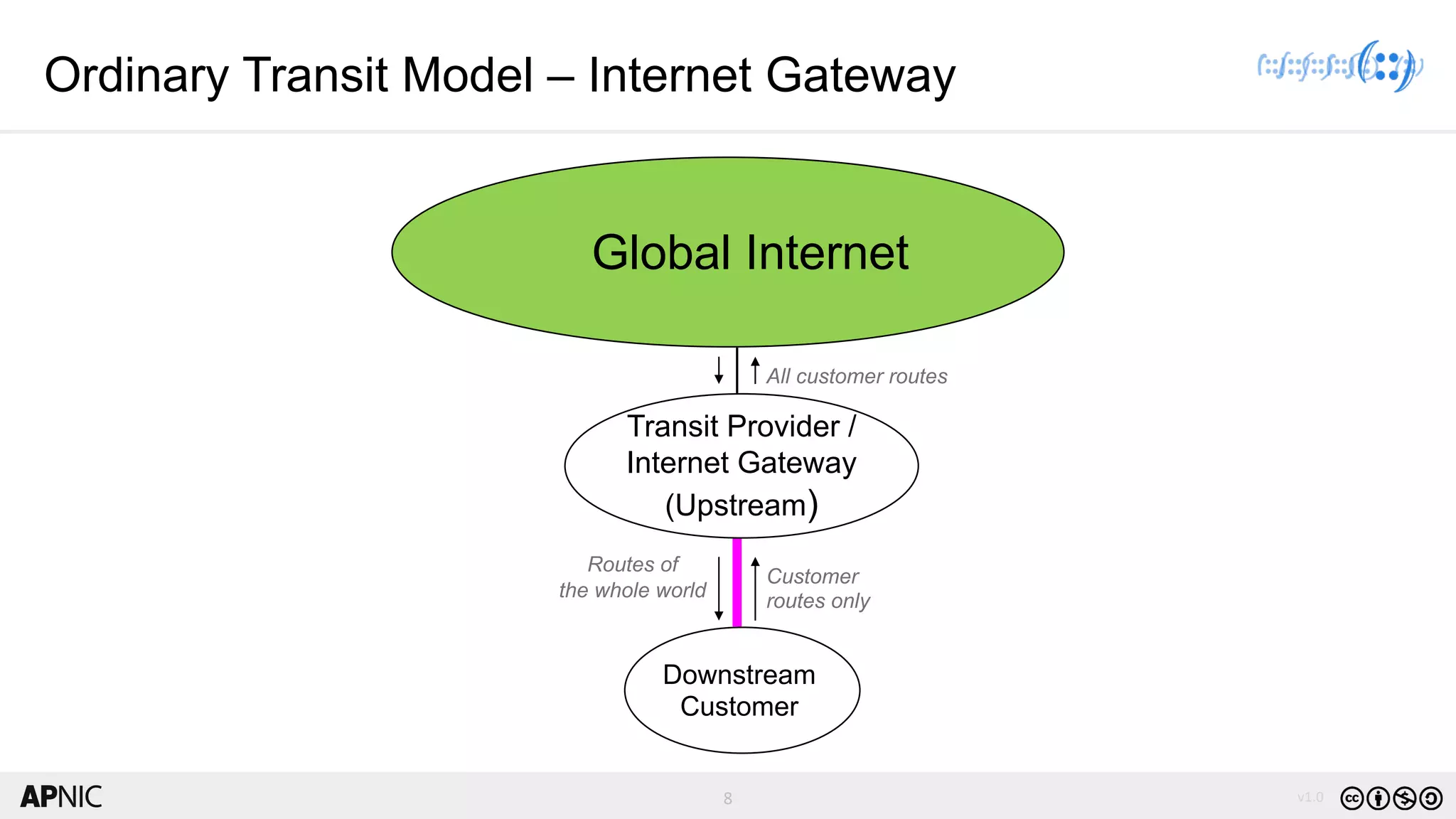
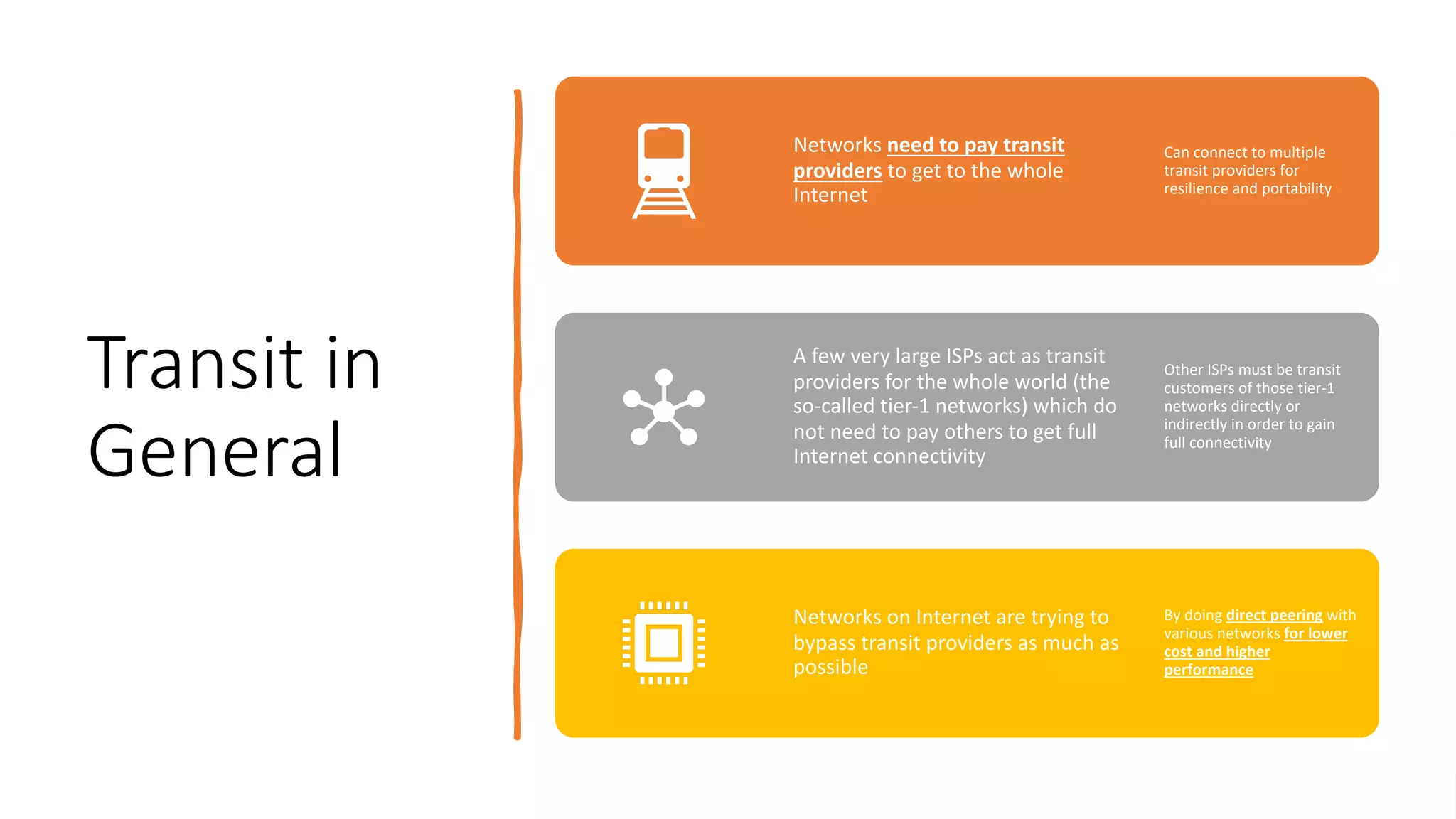
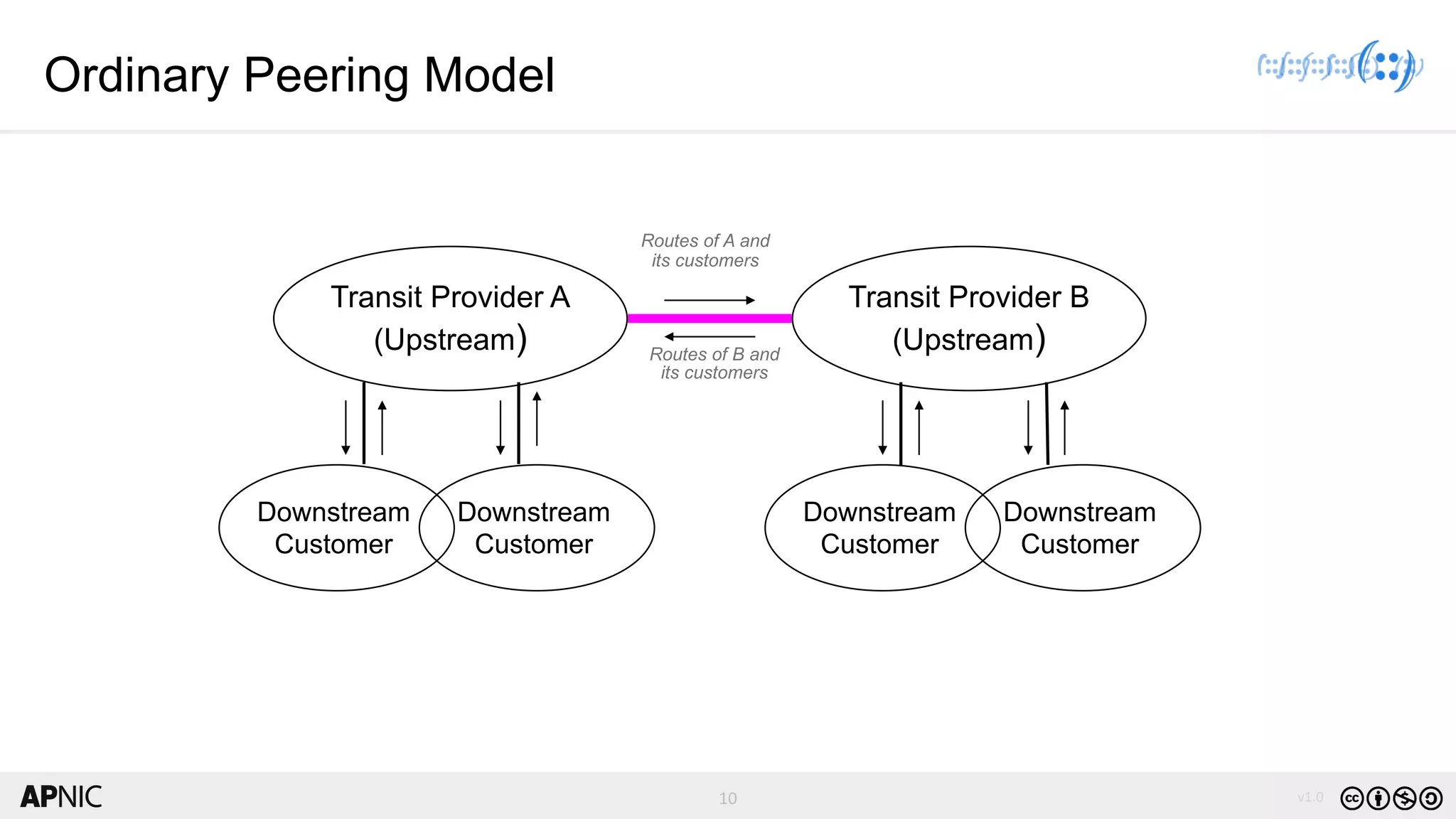
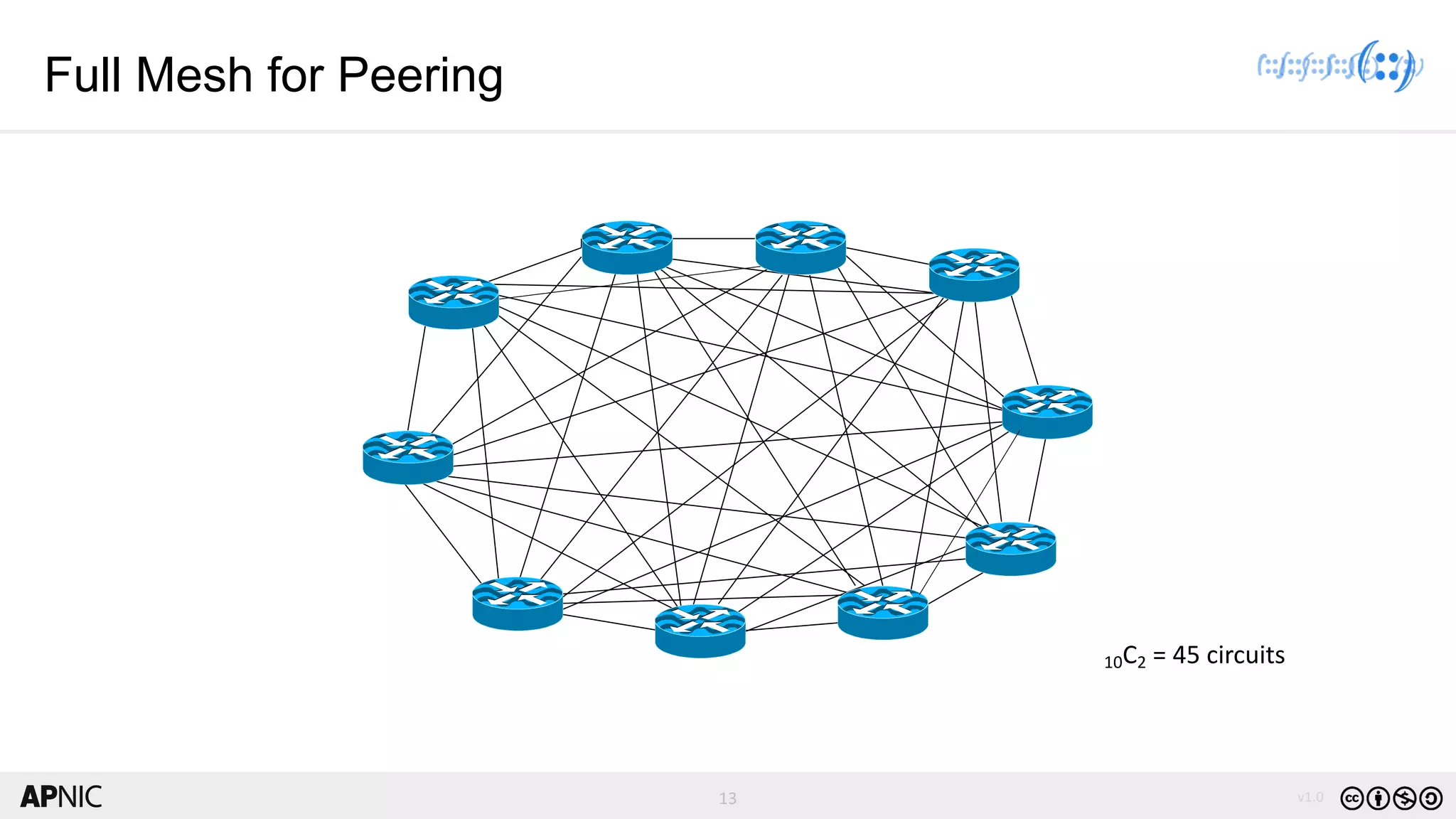
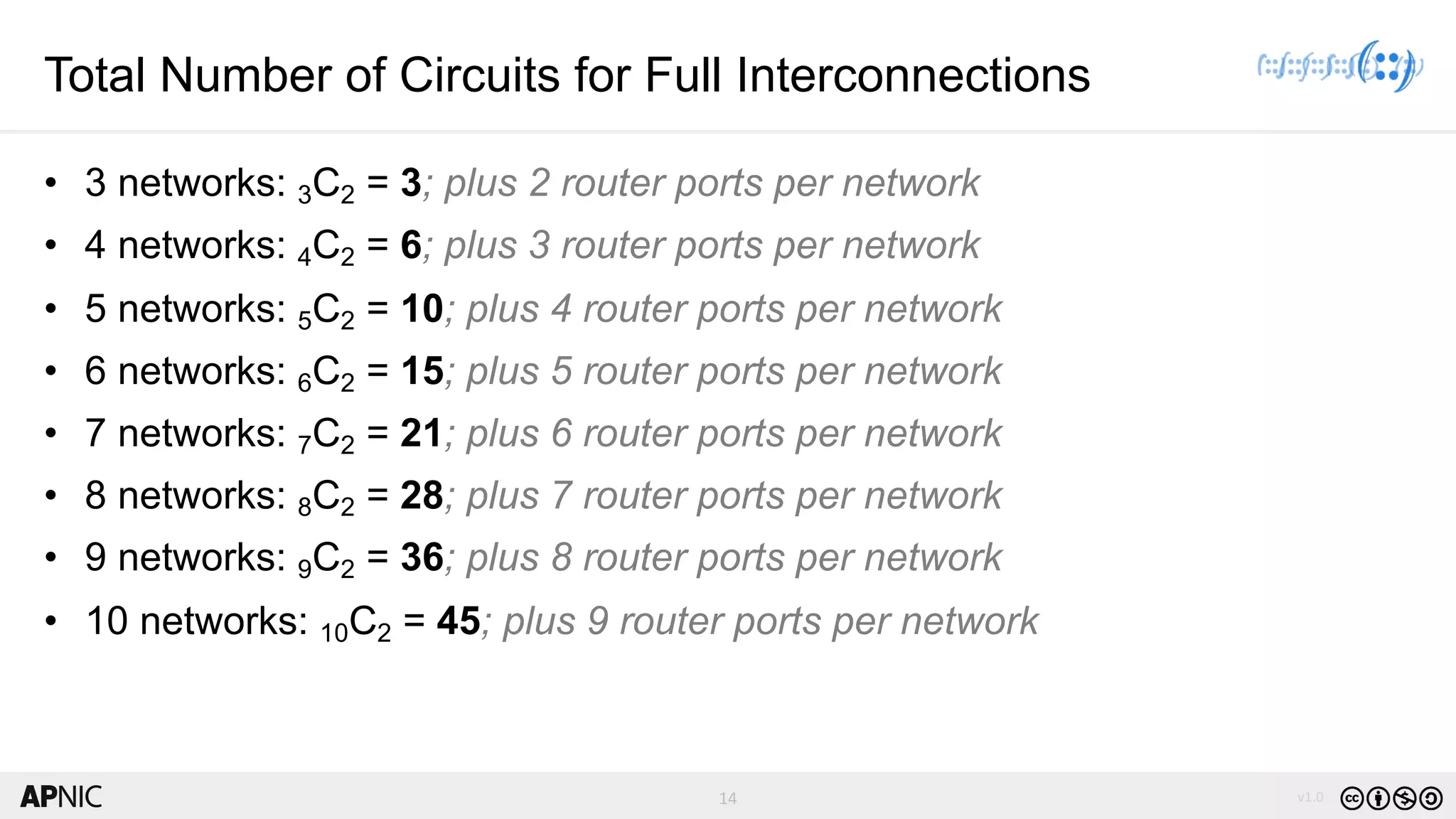
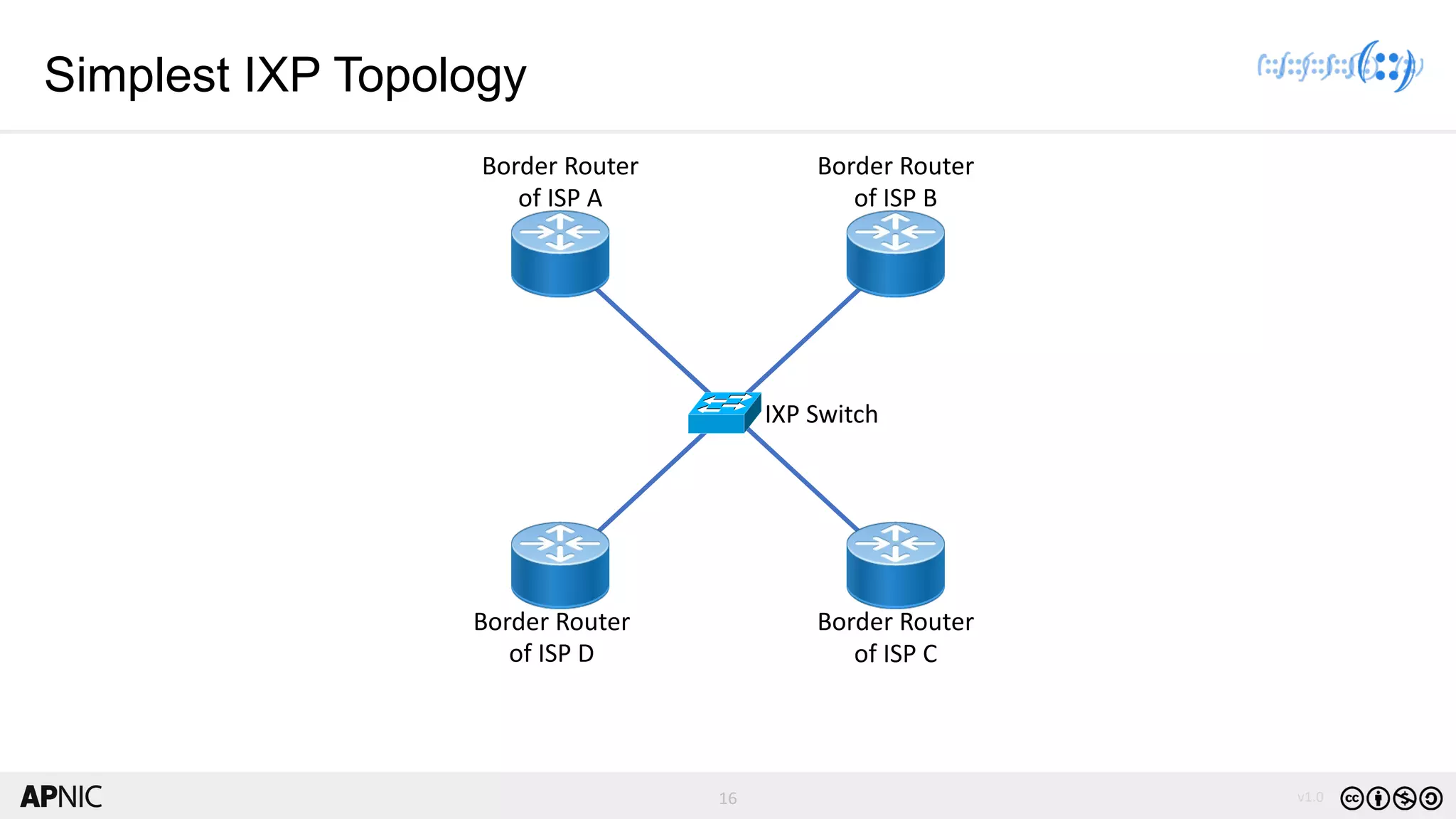
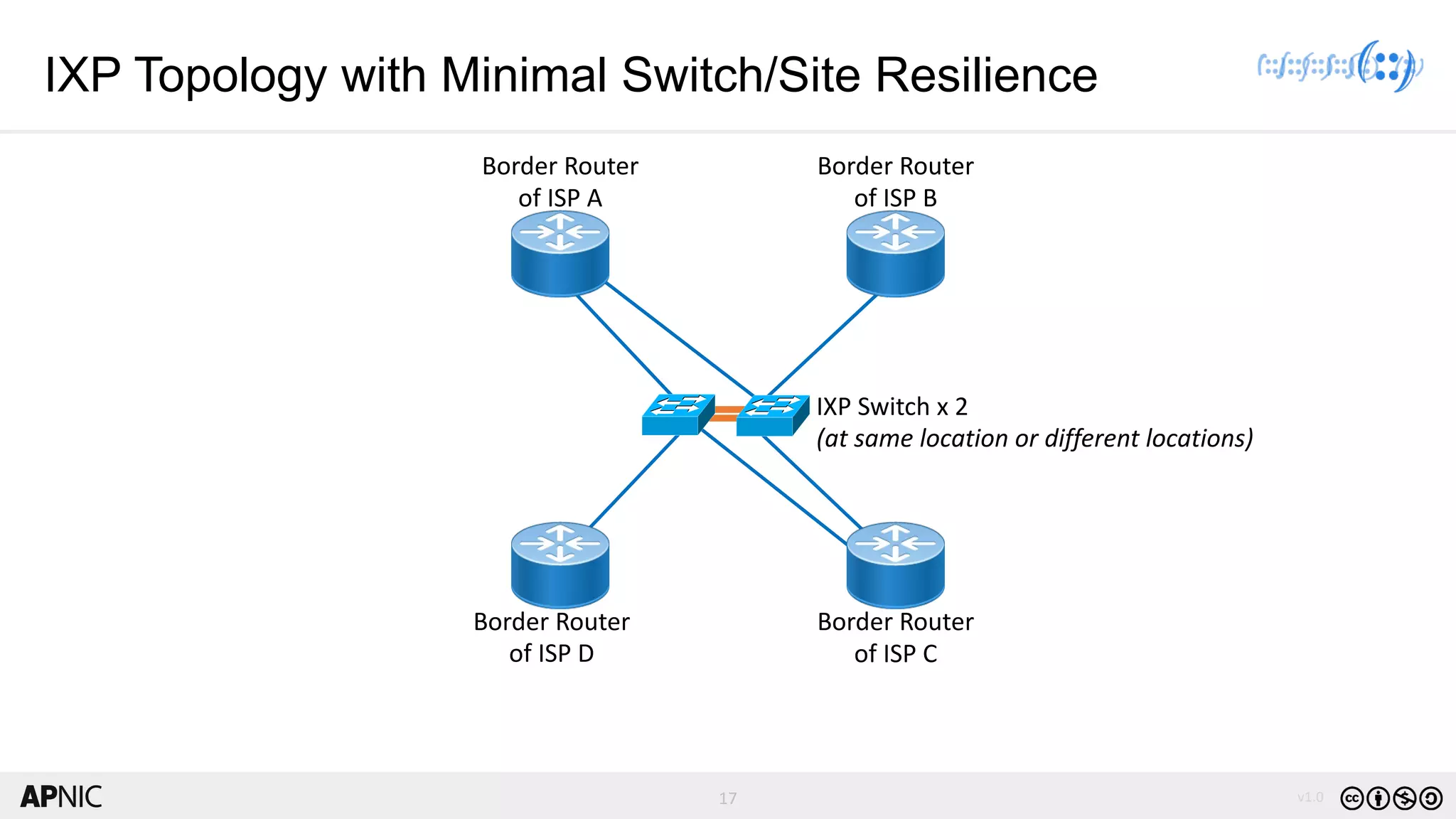
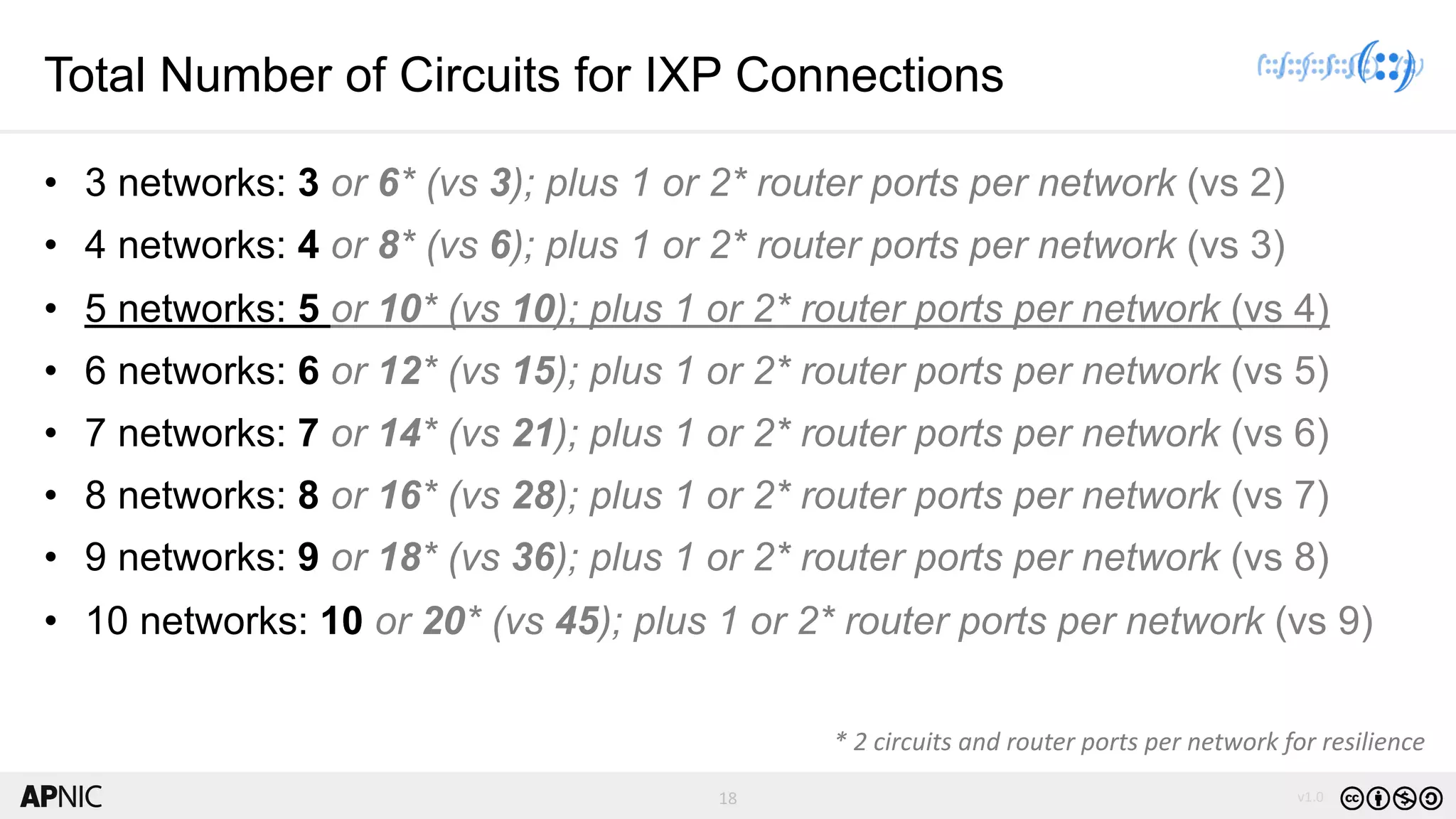
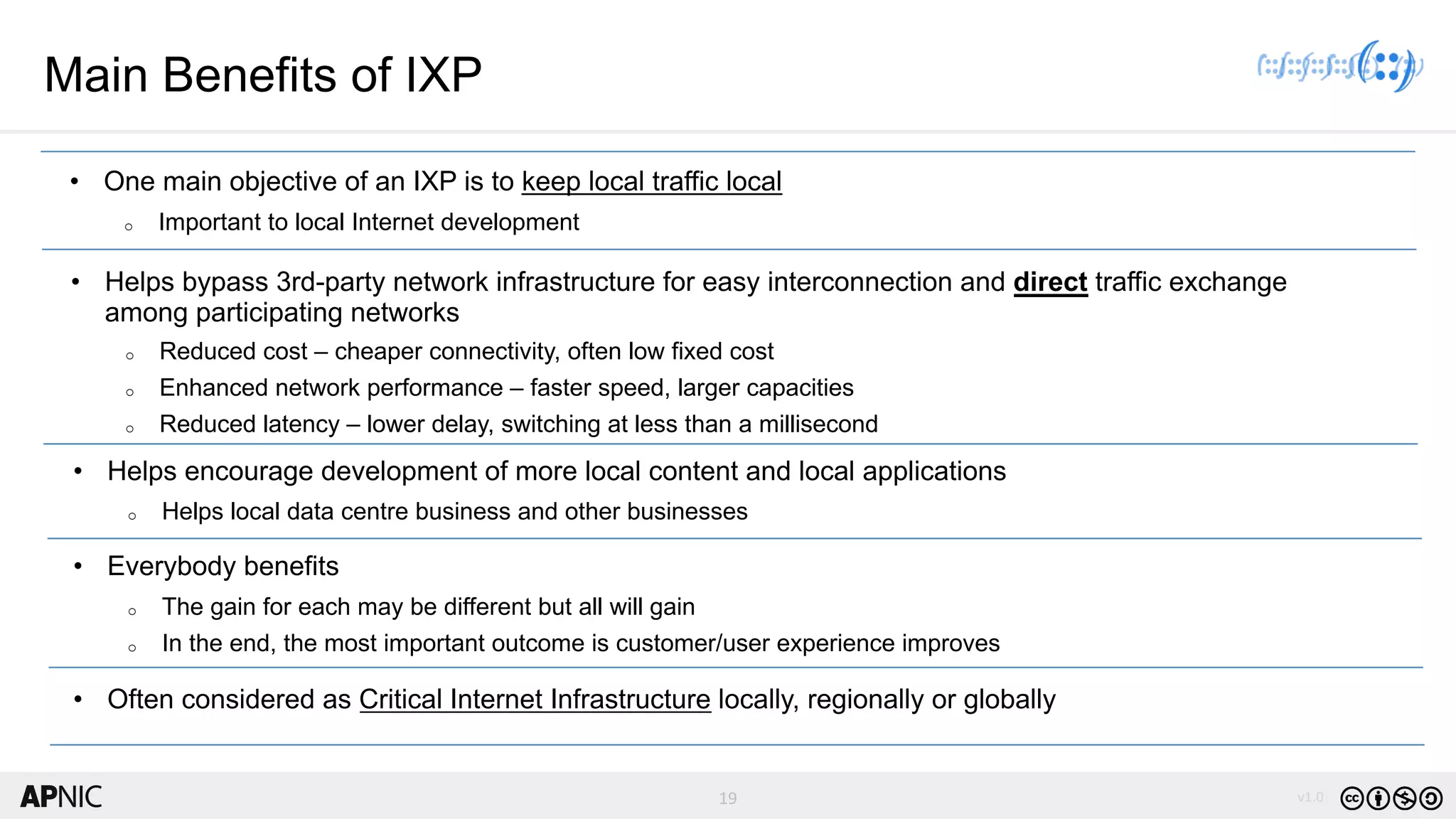
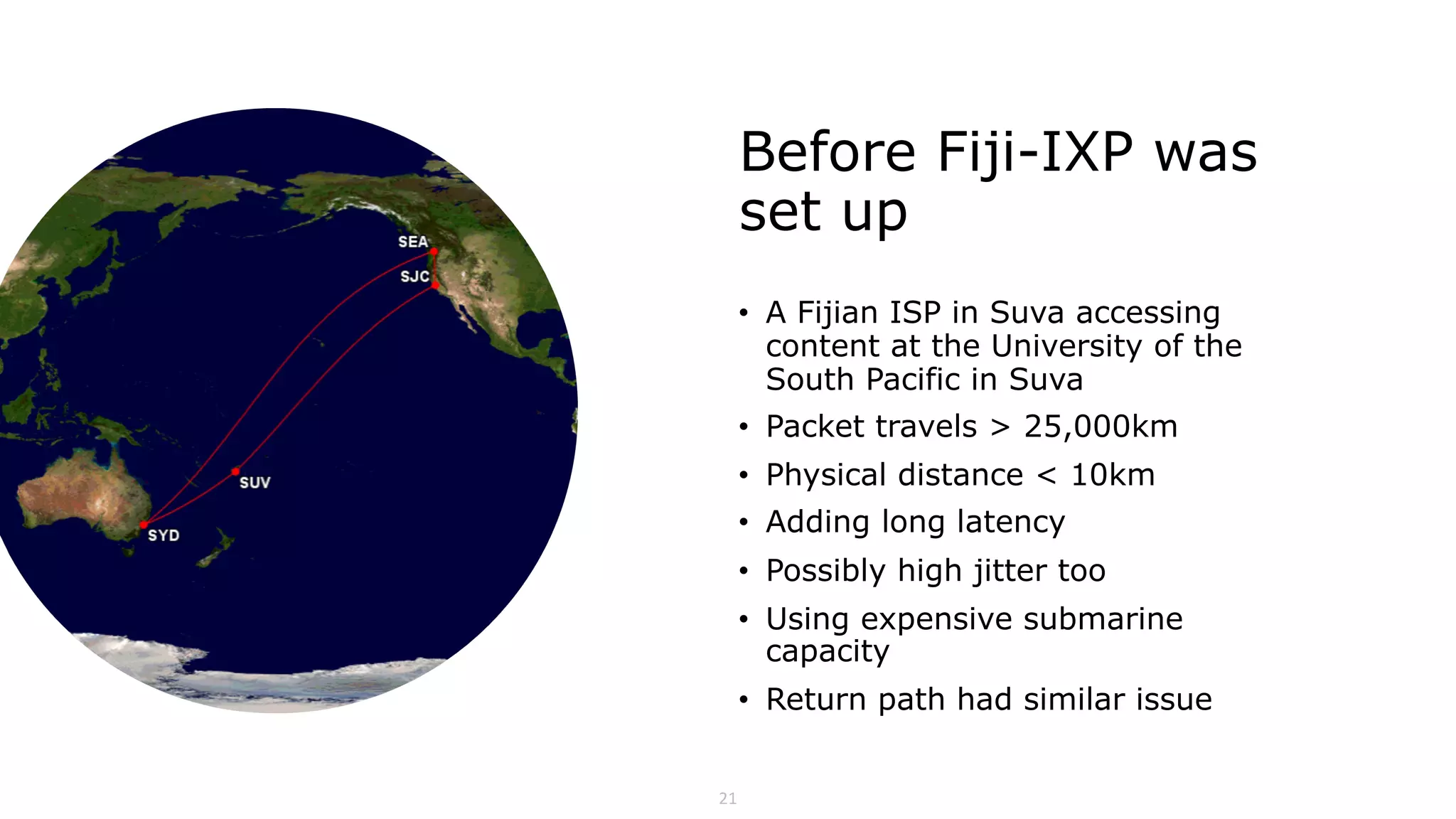
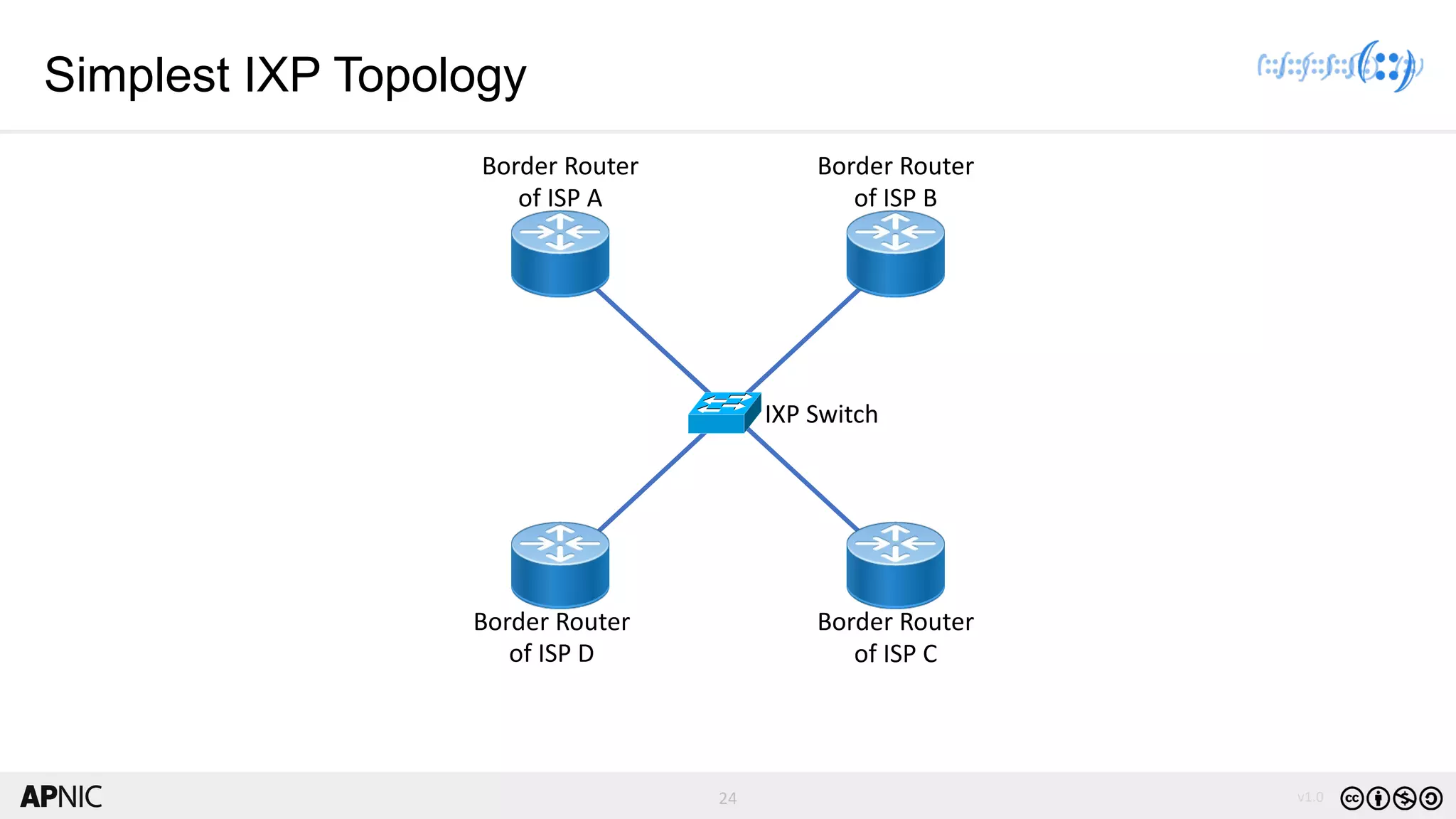
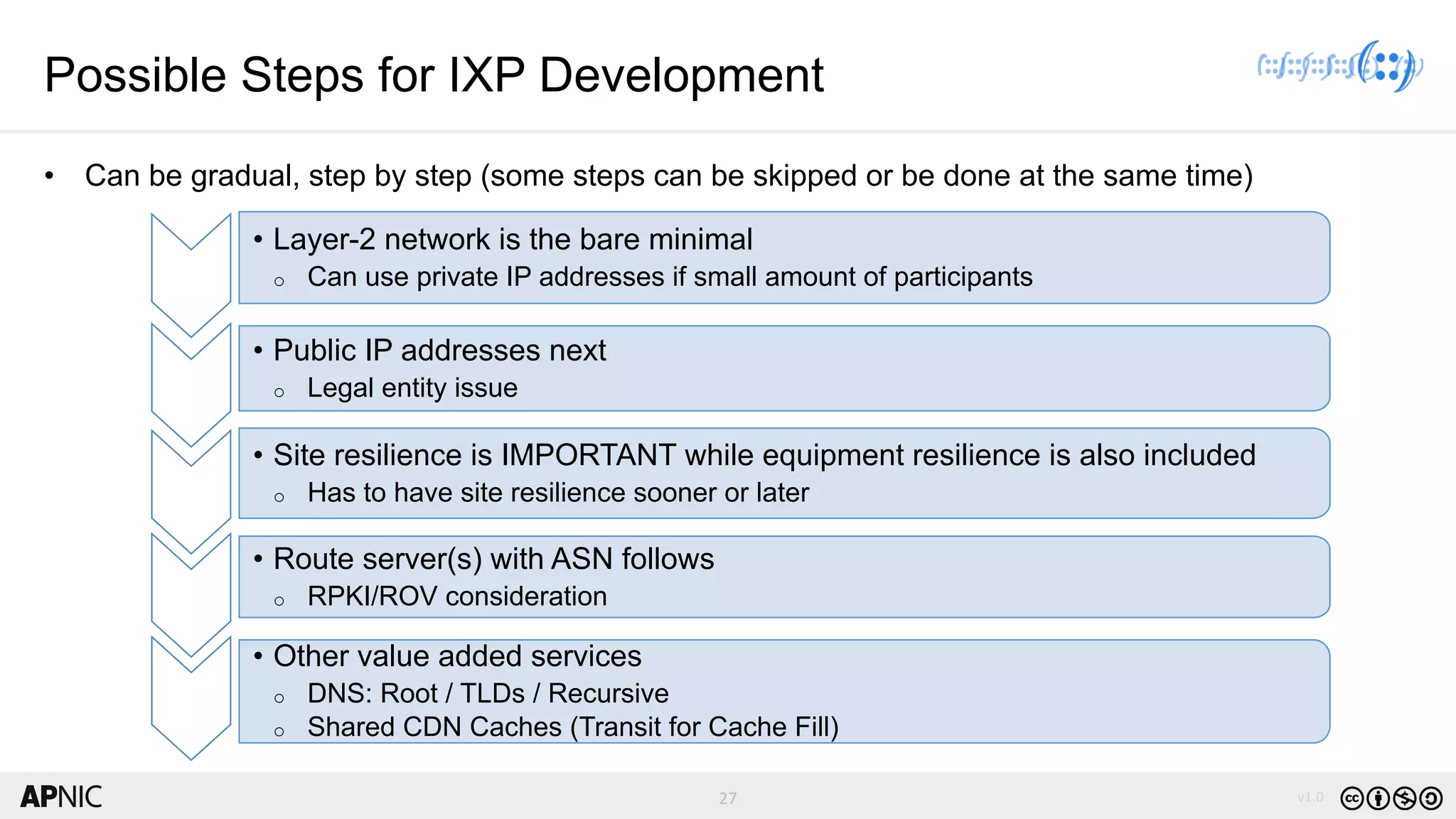
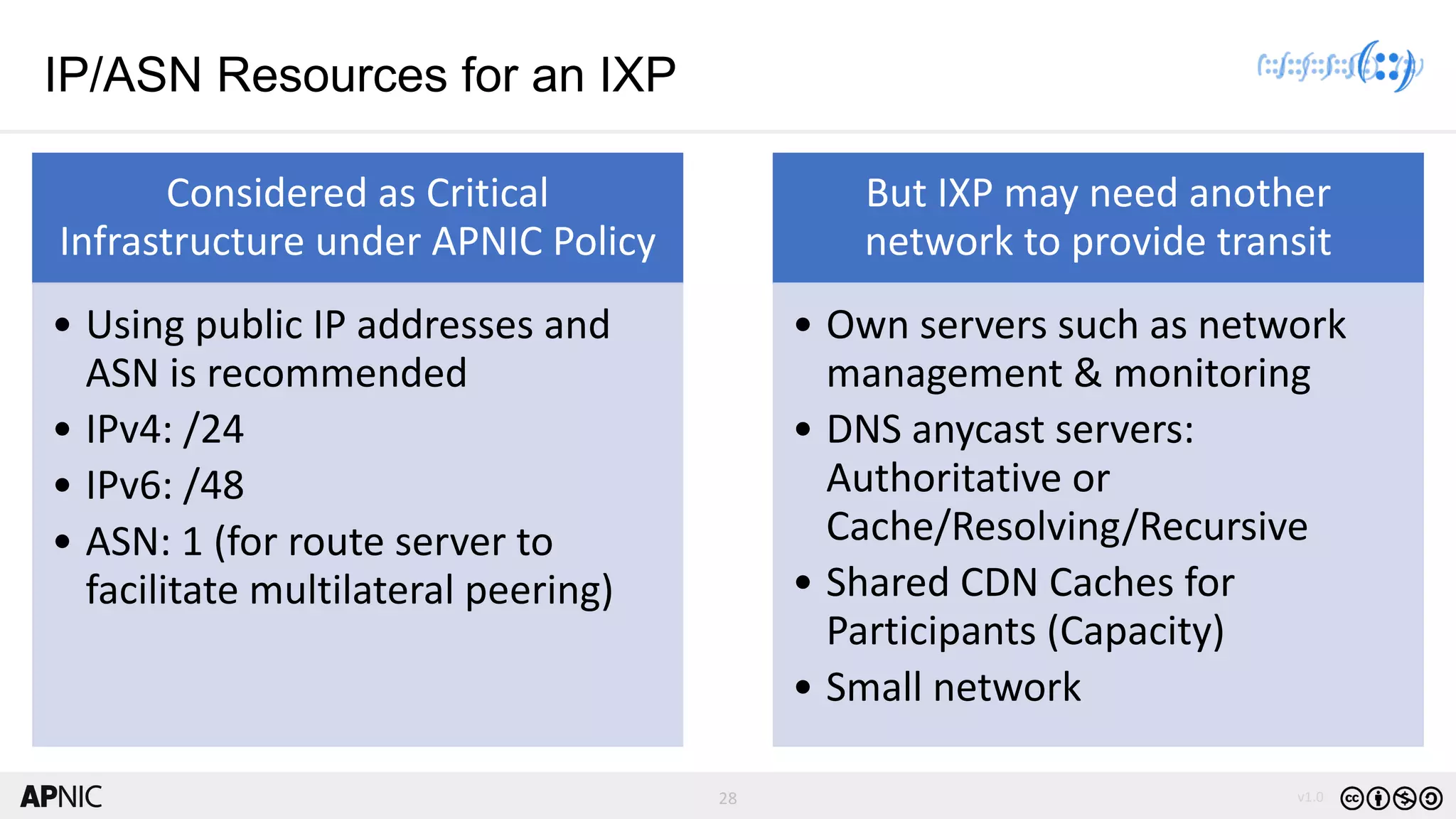
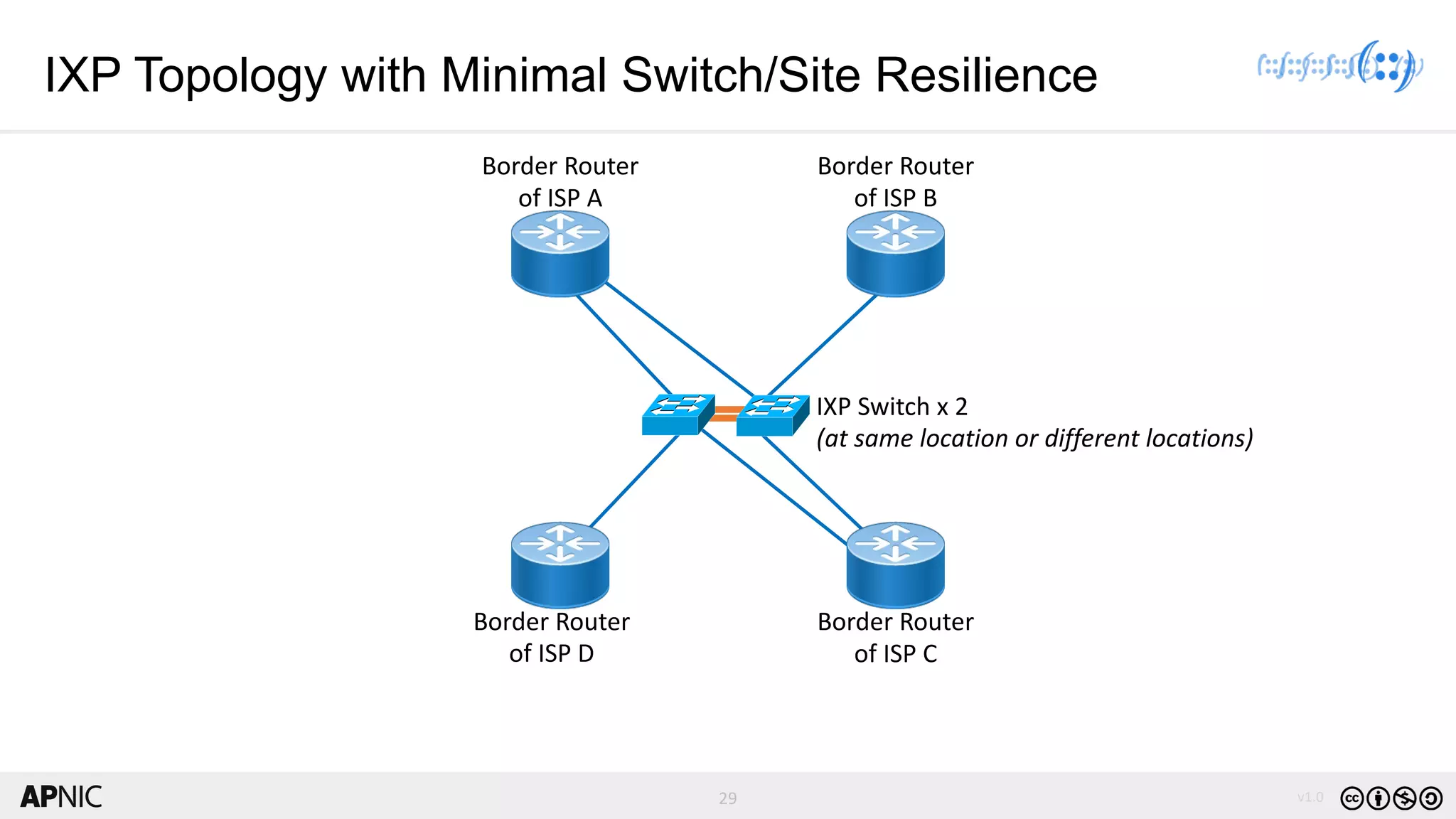
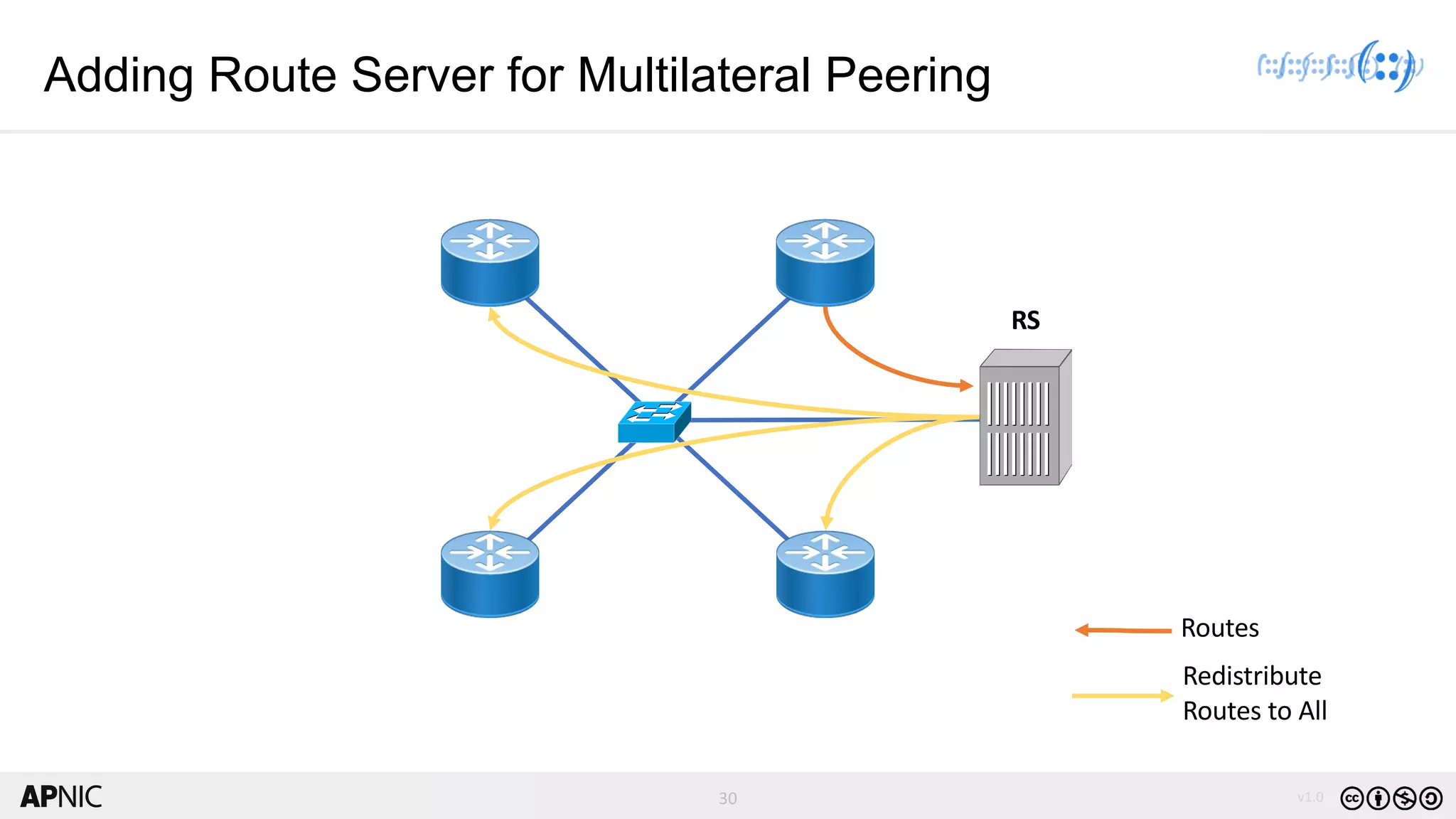
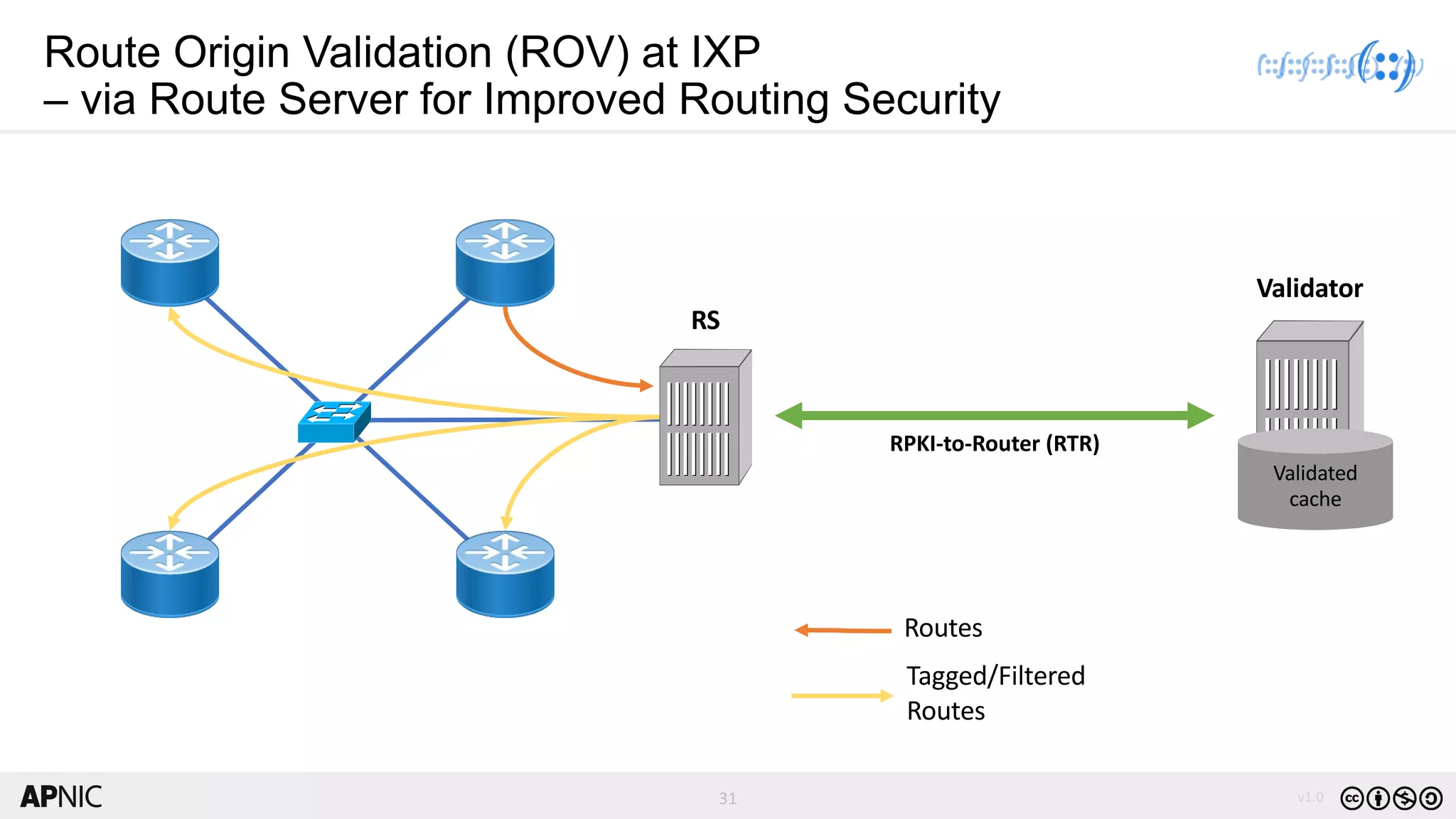
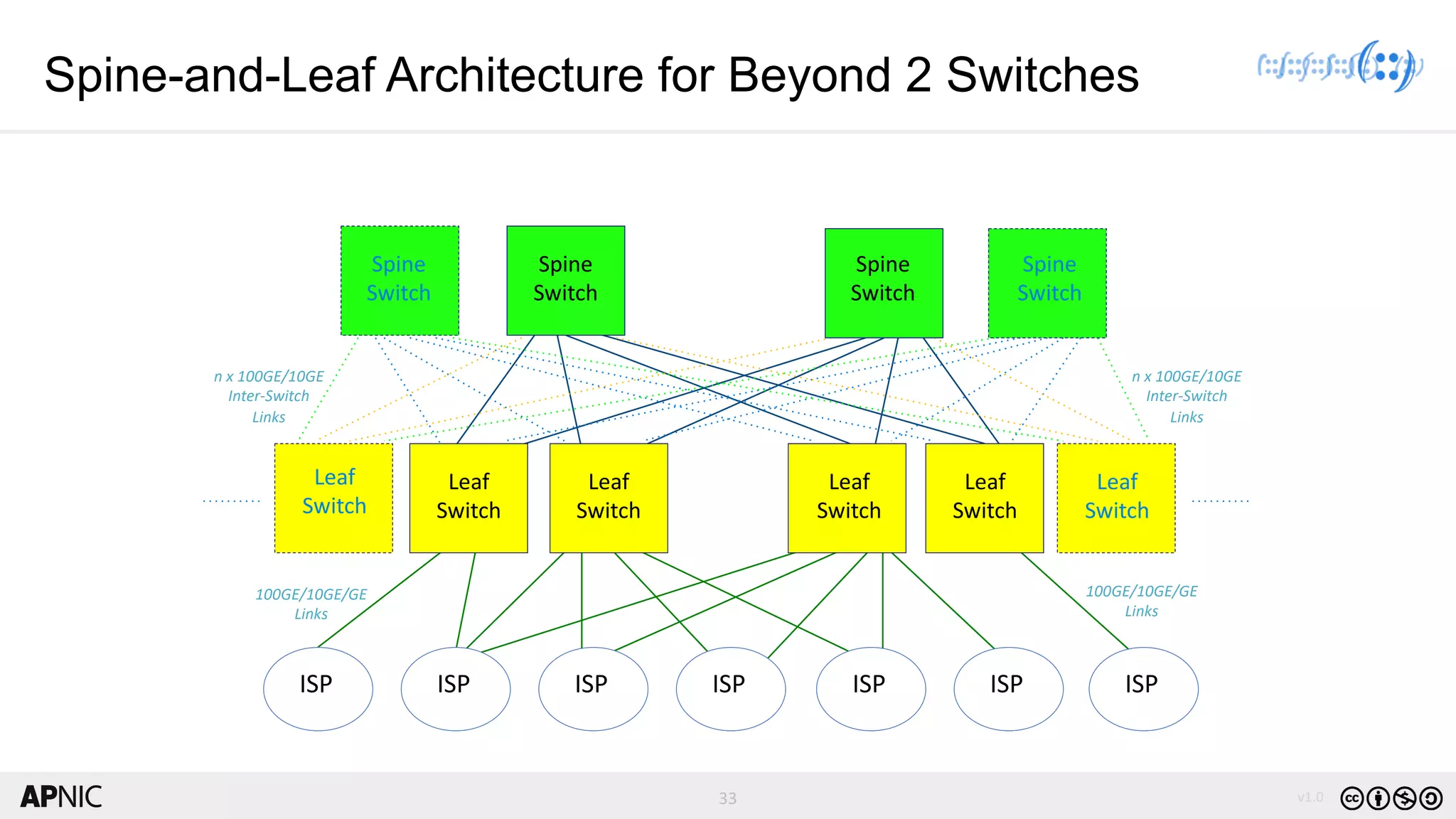
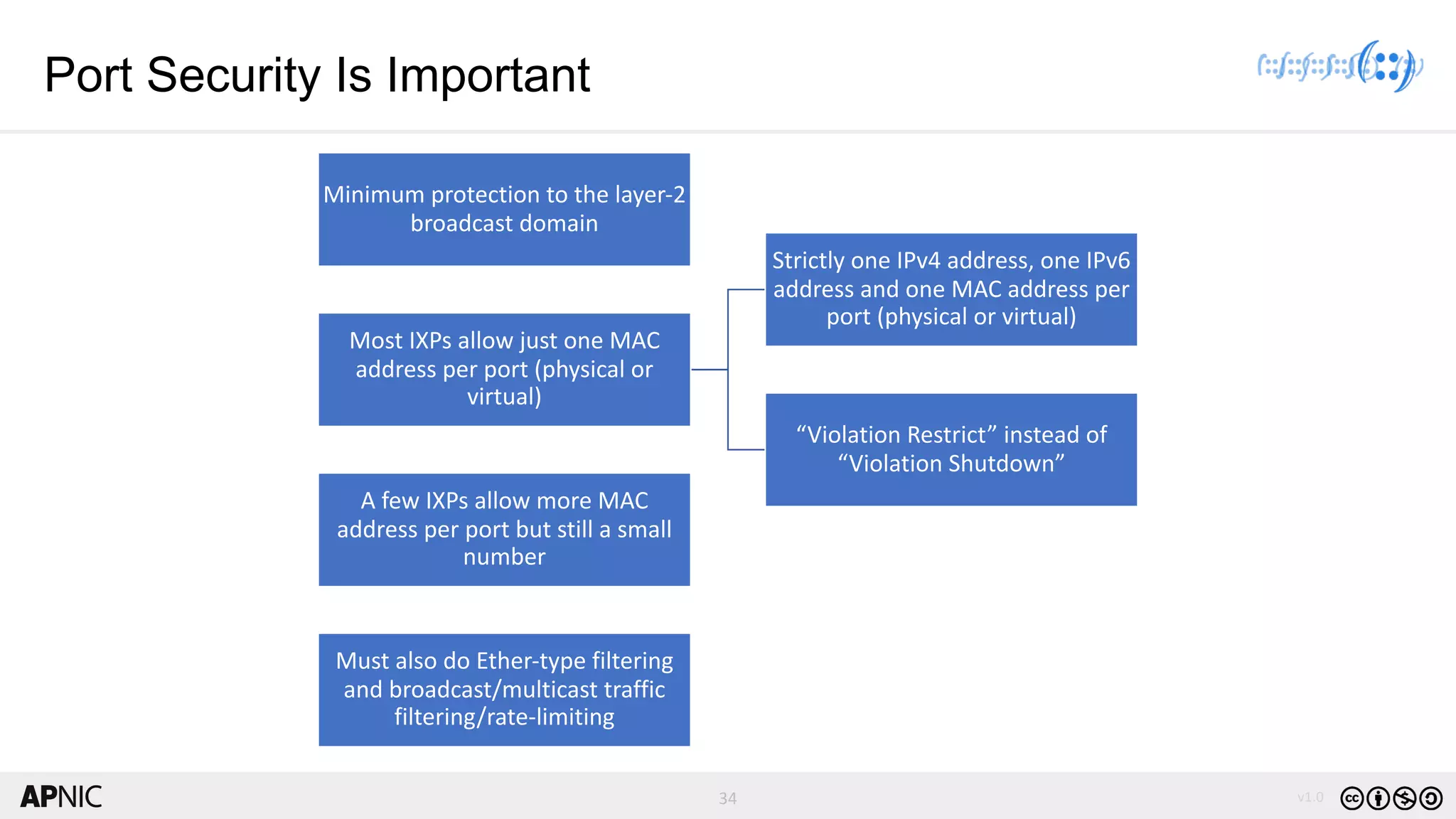
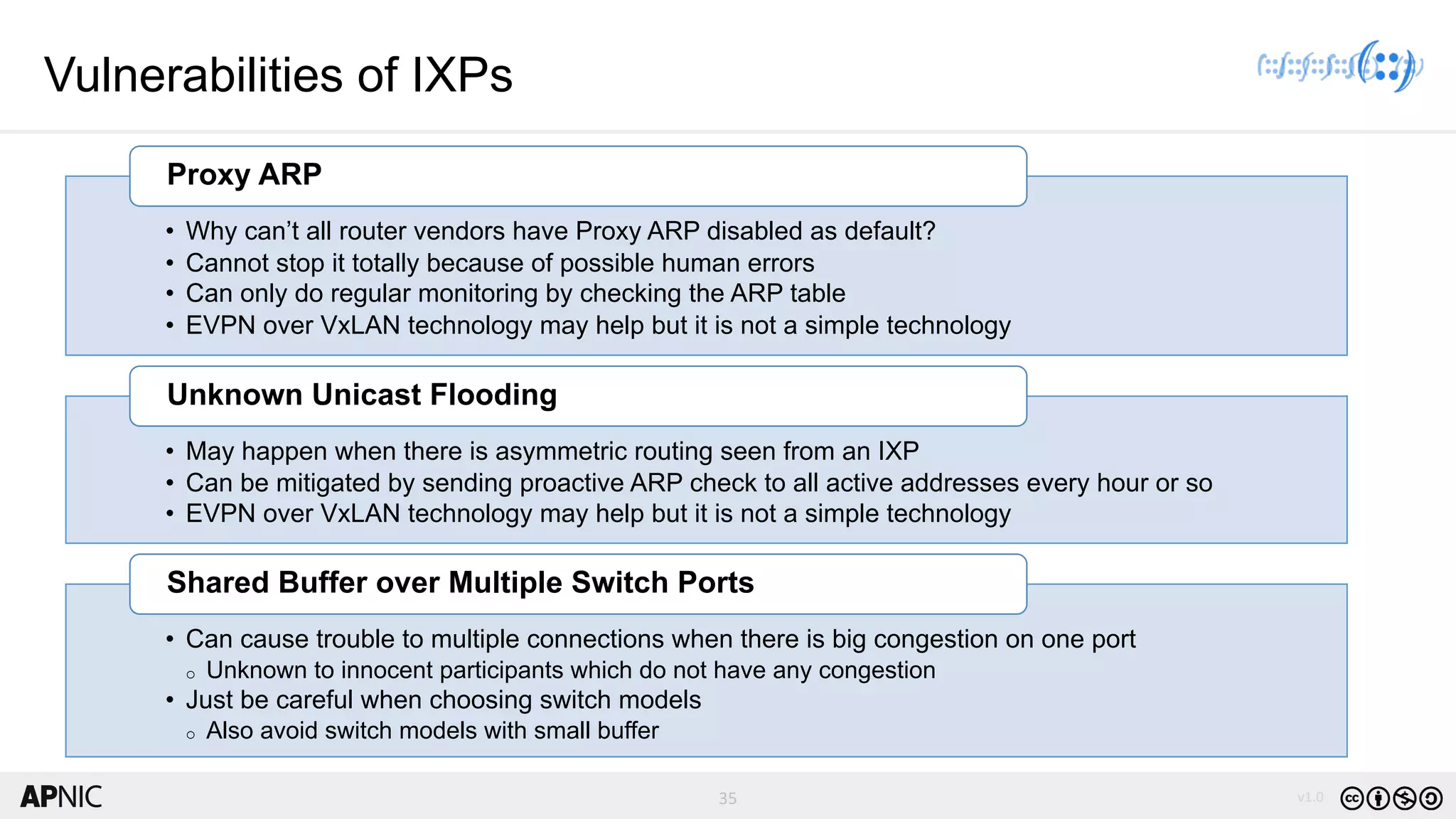
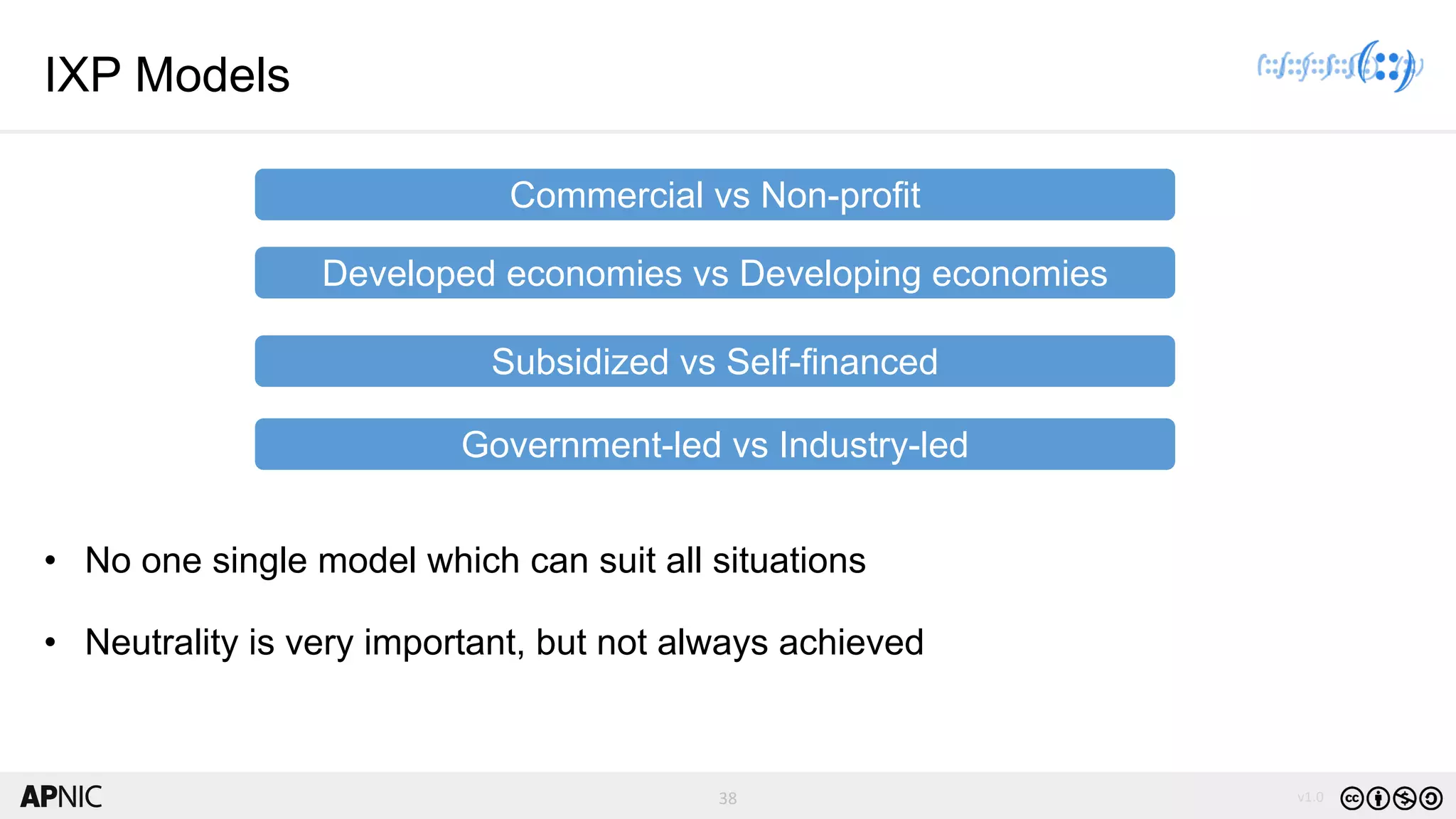
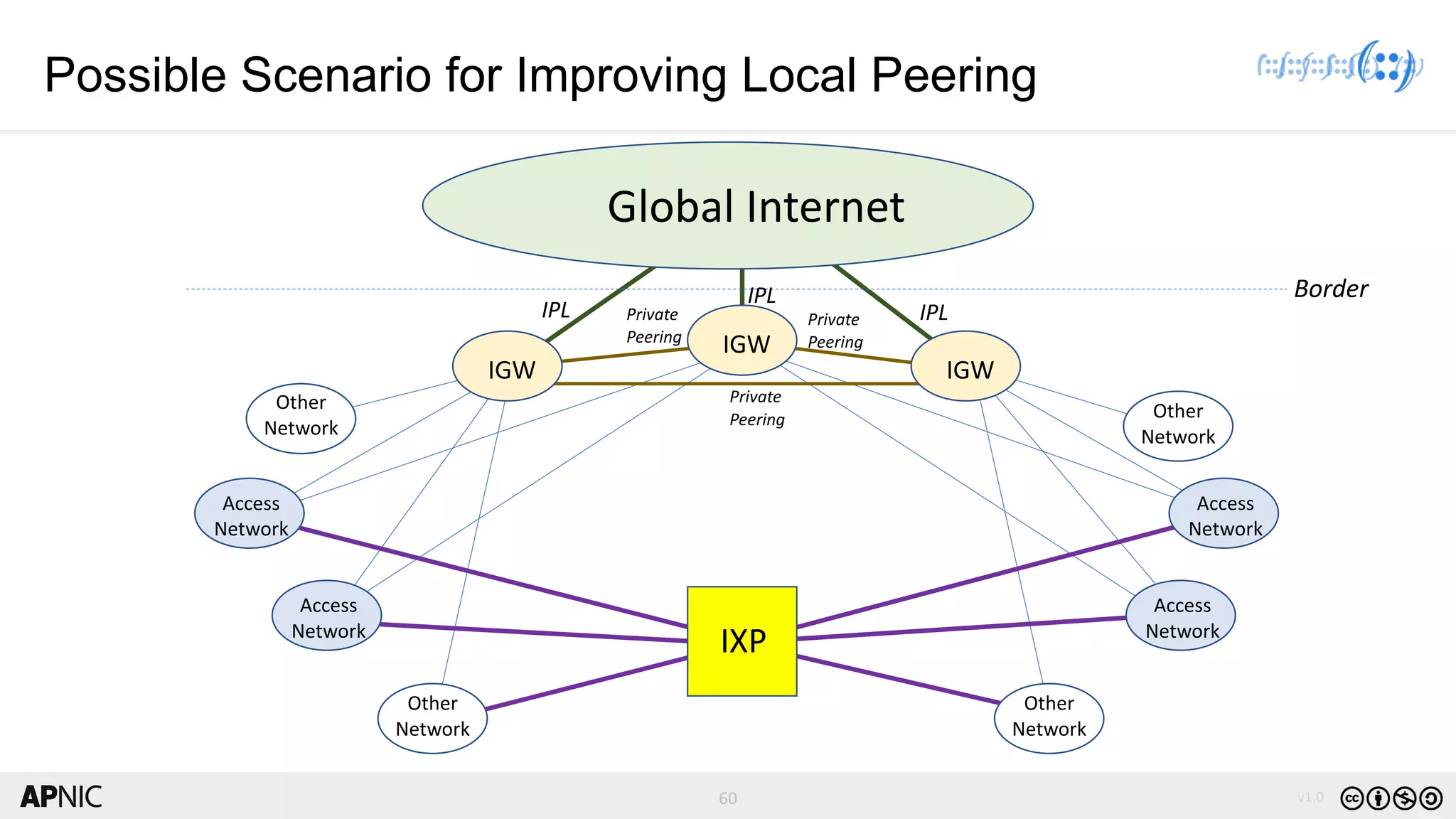
The document discusses the structure, operation, and benefits of Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) in the context of regional internet development, particularly for the Pacific Islands. It highlights the importance of IXPs in facilitating direct peering among autonomous systems, reducing latency, and enhancing network performance while addressing various operational and governance models for both developed and developing economies. The document emphasizes that local IXPs are crucial for improving local internet infrastructure and fostering better connectivity among Internet Service Providers (ISPs).