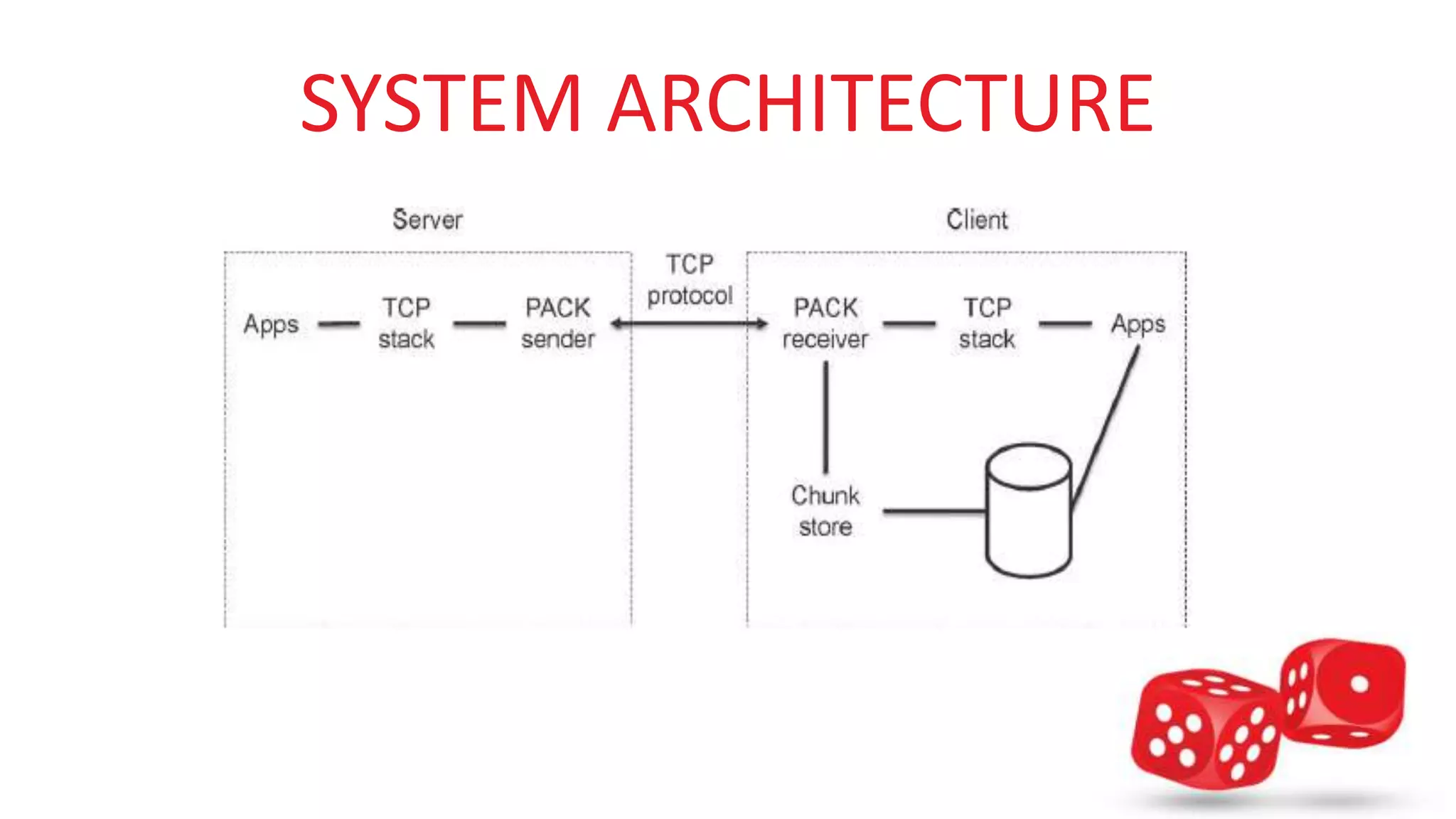
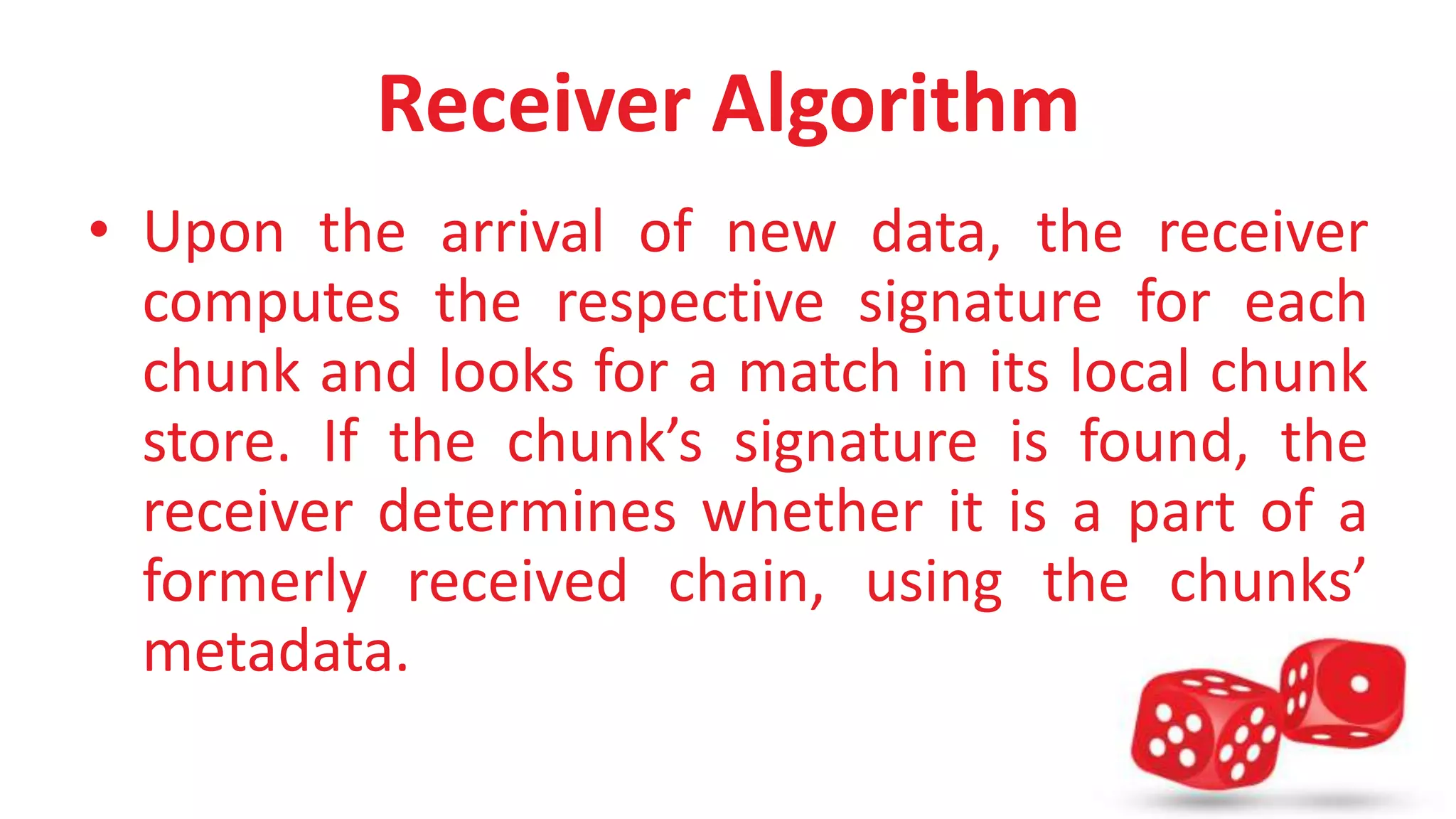
The document presents PACK, a predictive traffic redundancy elimination system designed for optimizing bandwidth costs in cloud computing by offloading processing to end clients. It utilizes a new chunking scheme that enhances data processing speeds and addresses challenges of mobility and cloud elasticity. The proposed system's architecture includes modules for chunk storage, algorithms for receivers and senders, and a wire protocol for efficient communication.