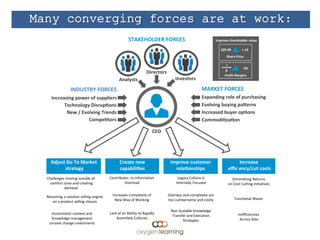
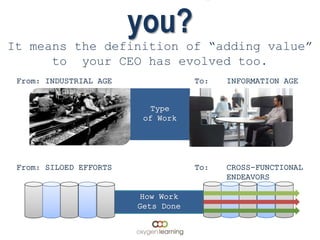
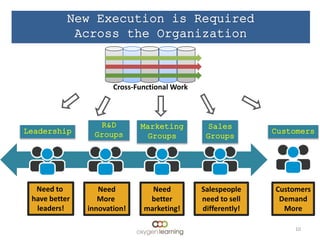
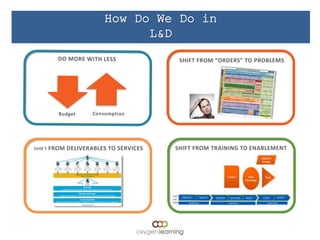
The document discusses challenges facing companies as work changes from the industrial age to the information age and from siloed efforts to cross-functional endeavors. It notes that while work has changed, how employees are taught has not changed much and still uses outdated teaching methods like chalkboards and topic-based teaching rather than problem-centric learning. This "industrialization" of learning has cost companies millions in lost productivity by not teaching important skills like cross-functional teaming. It calls for leadership development, marketing, sales, and other groups to work together across functions to address customer needs in new ways, and for learning and development to shift from training to enablement to help elevate its value contribution.