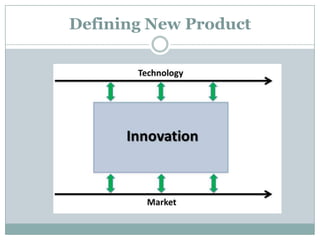
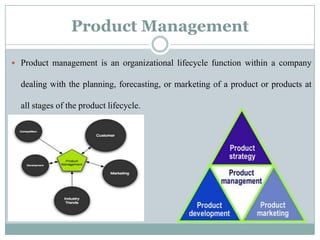
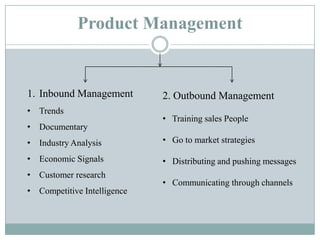
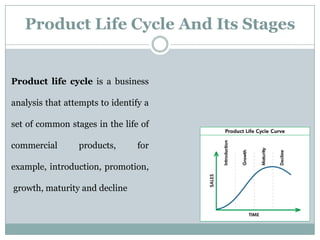
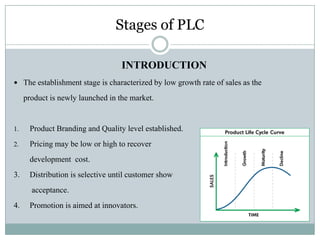
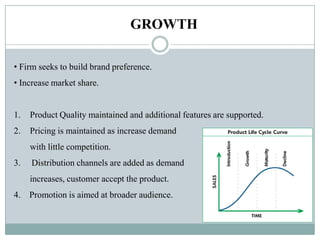
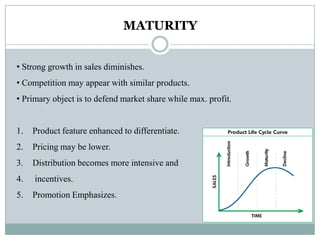
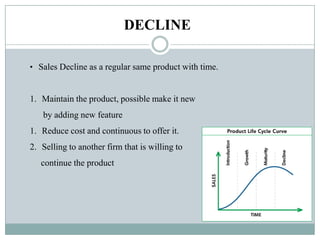
This document summarizes key concepts related to product management. It defines a product, classifies products as goods, services, or ideas. It describes defining new products based on business needs and constraints. Product management is defined as dealing with planning, forecasting, and marketing a product throughout its lifecycle stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. The roles of product management include analyzing markets, defining product features, driving new products, and activities from strategic to tactical levels.