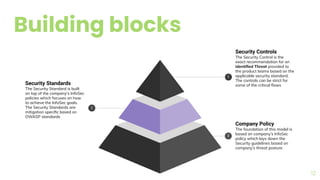
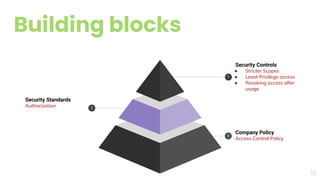
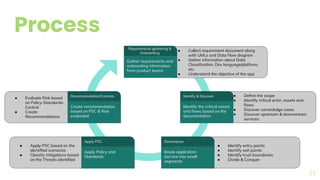
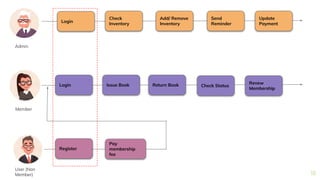
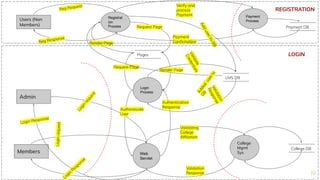
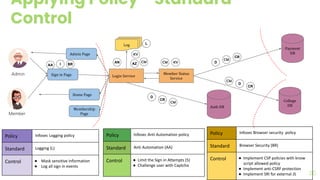
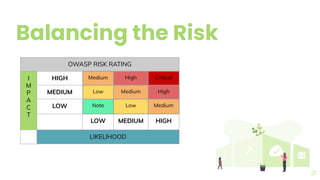
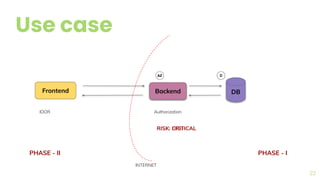
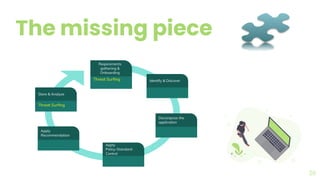
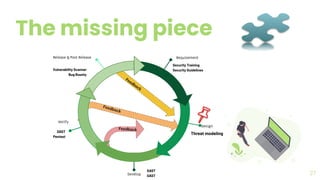
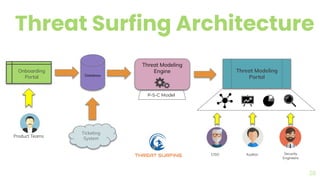
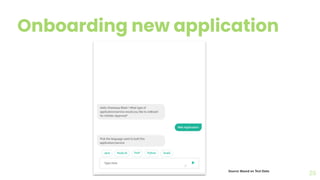
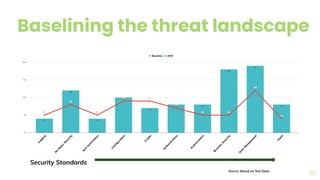
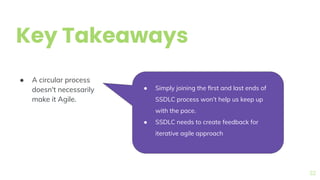
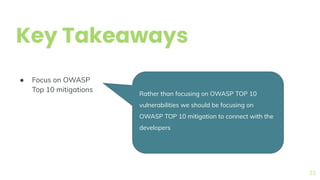
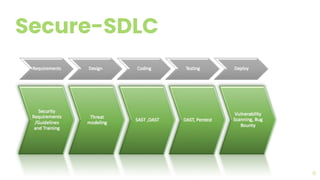
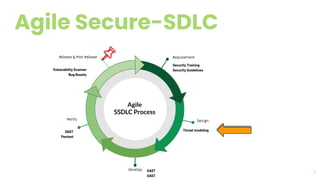
The document presents a comprehensive overview of threat modeling within an agile environment, emphasizing the importance of early threat identification to enhance application security. It introduces the P-S-C model, which is grounded in company-specific infosec policies and provides a systematic approach for identifying and mitigating threats. Key takeaways highlight the necessity of a circular, feedback-driven threat modeling process that adapts to evolving threat landscapes while facilitating developer engagement.






![Some of the commonly used
frameworks
STRIDE
● Spoofing
● Tampering
● Repudiation
● Information disclosure
● Denial of service
● Elevation of privilege
DREAD
● Subjective Rating based on
5 Qs of each threats
● Categories:
○ Damage [potential]
○ Reproducibility
○ Exploitability
○ Affected users
○ Discoverability
PASTA
● Process for Attack
Simulation & Threat
Analysis
● Risk Centric
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalthreatmodelingowasp-210319194038/85/OWASP-based-Threat-Modeling-Framework-9-320.jpg)