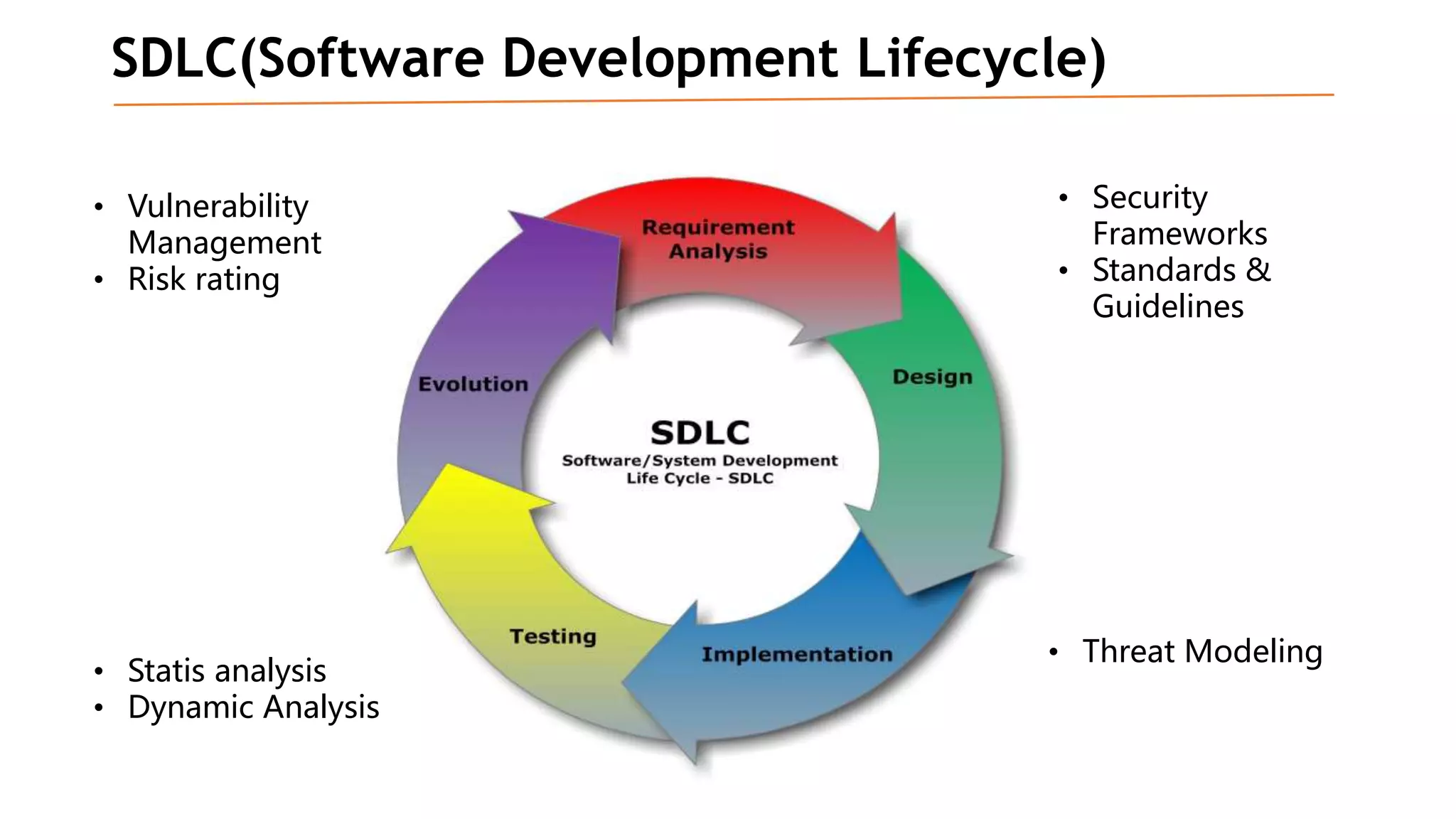
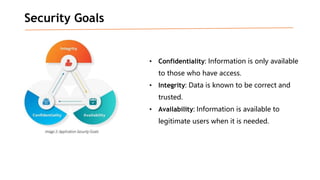
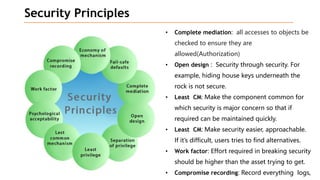
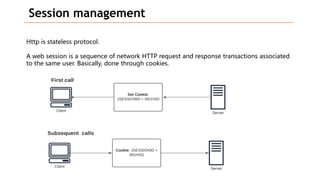
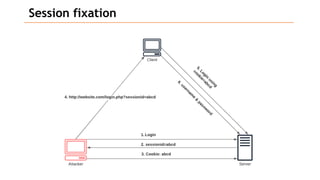
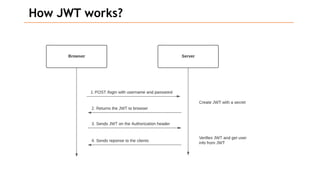
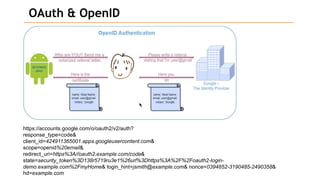
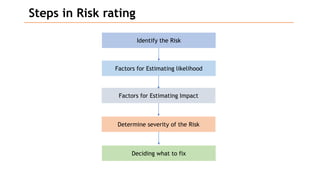
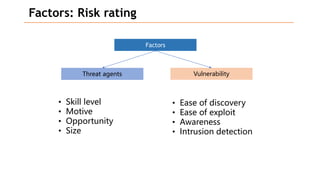
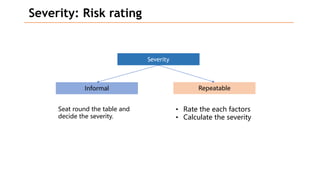
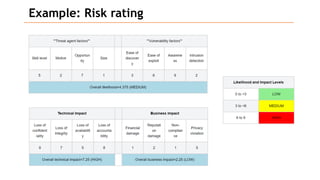
Based on the information provided, it is difficult to definitively say which risk is "bigger" without more context about the system and environment. Some factors to consider when comparing risks include:
- Likelihood of occurrence
- Potential impact of an exploit
- Existing controls and their effectiveness
- Cost to address
A structured approach like assigning ratings (e.g. high, medium, low) across these dimensions can help to systematically compare risks. Ultimately, the organization's priorities and risk tolerance also influence which risks should be addressed first. Regular re-evaluation is important as the environment changes over time. Addressing the highest priority risks based on a well-defined analysis process helps to strengthen security in a cost-effective manner.