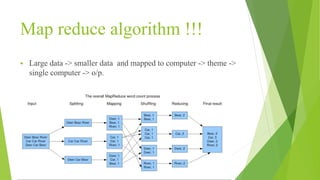
The document presents an overview of Hadoop as a solution for processing big data, detailing its significance due to the explosive growth of data and the limitations of traditional systems. It explains the Hadoop framework's components such as HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN, while also addressing challenges and considerations for implementation. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting appropriate projects and preparing for necessary skills and resources.