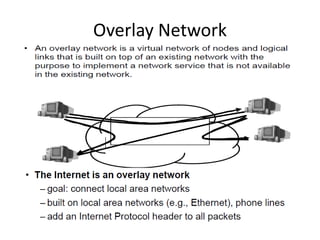
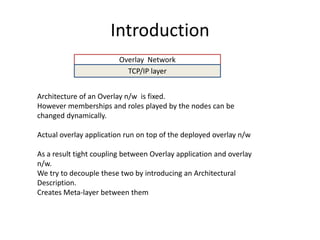
The document discusses architectural description based overlay networks. It proposes using architectural description documents that define the roles and relationships of nodes in an overlay network. These documents allow heterogeneous networks to work collaboratively by dynamically changing the roles nodes play and integrating multiple overlay networks. Nodes can switch between different overlays by exchanging and executing architectural description documents.