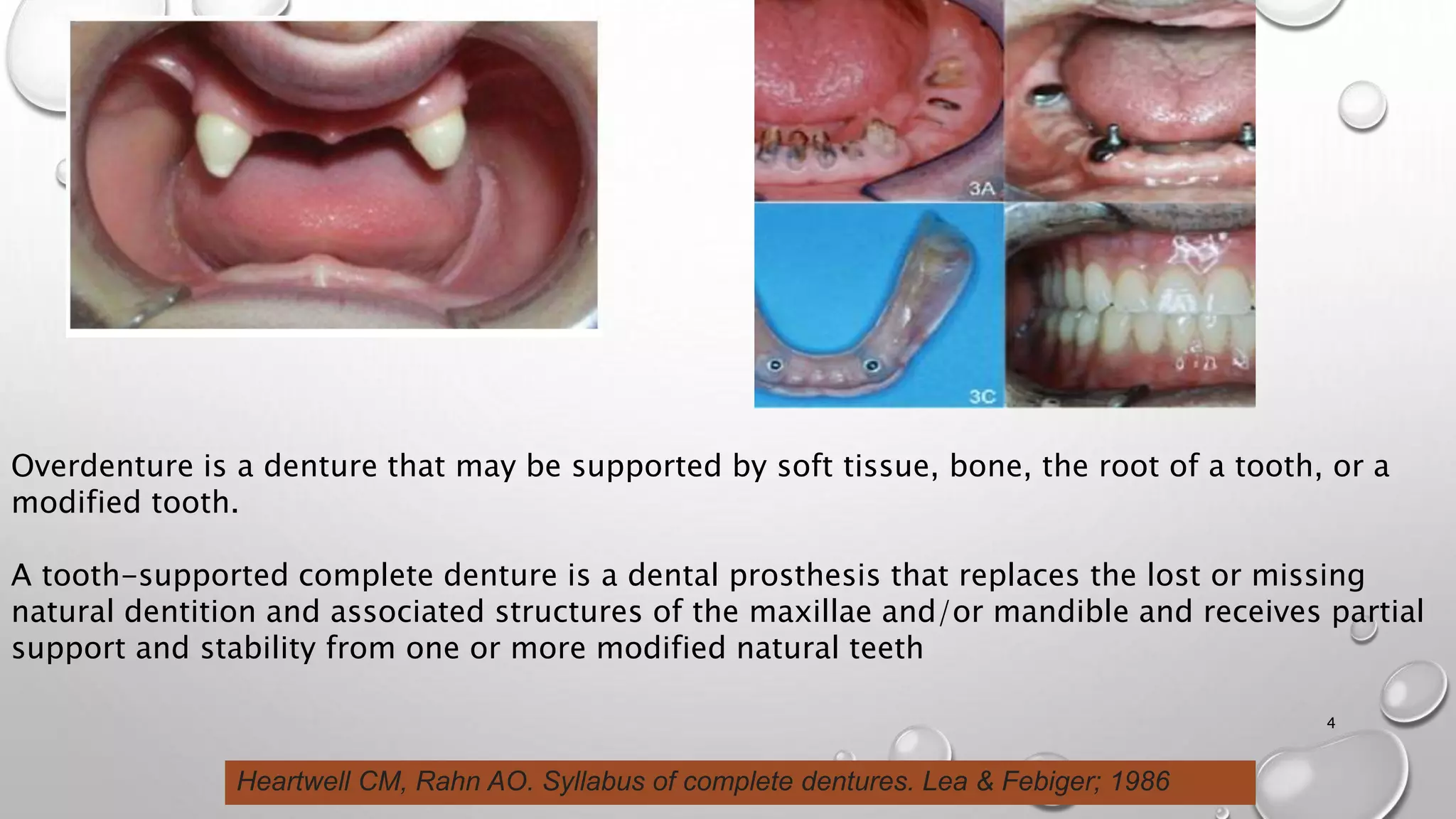
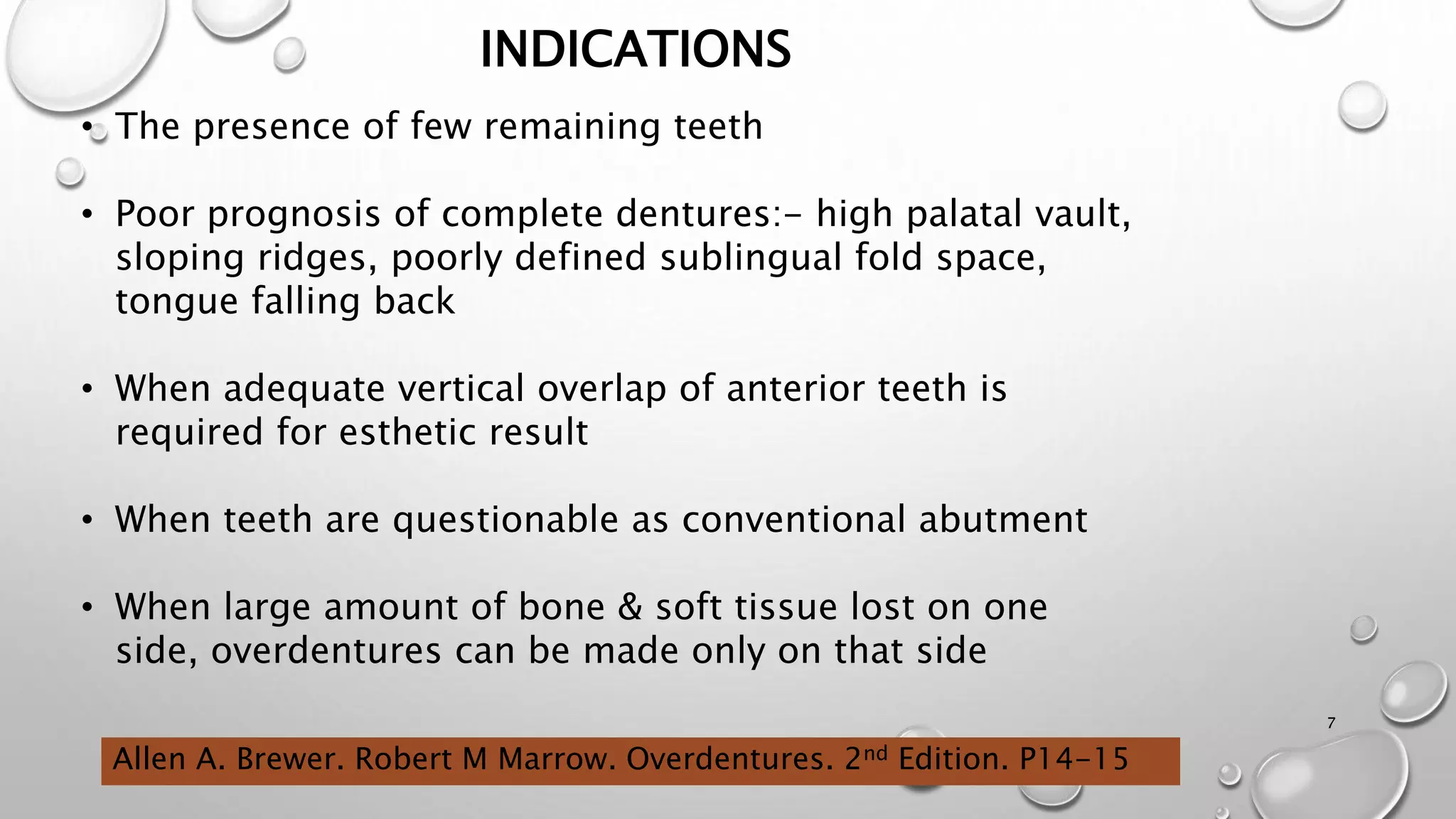
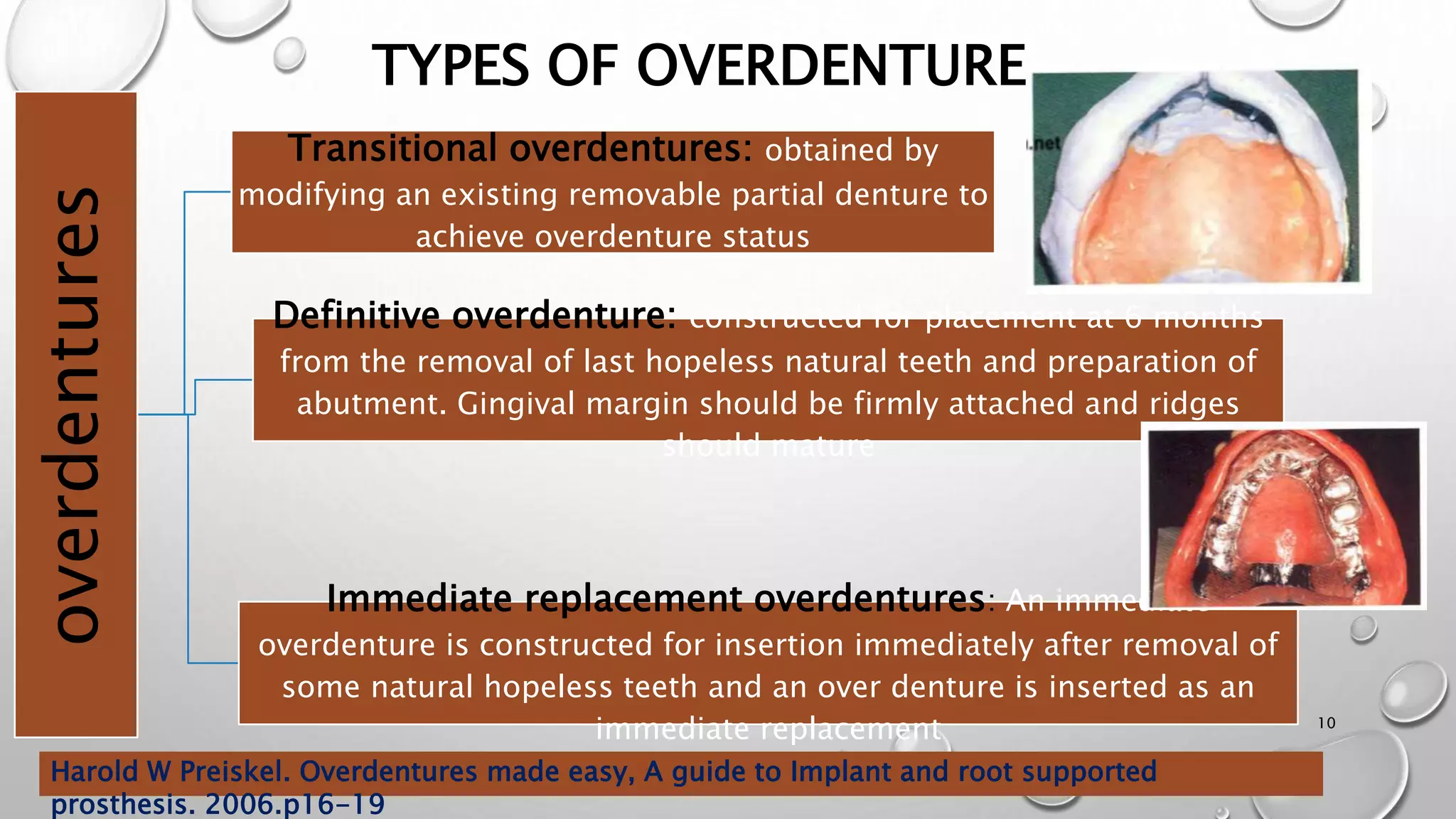
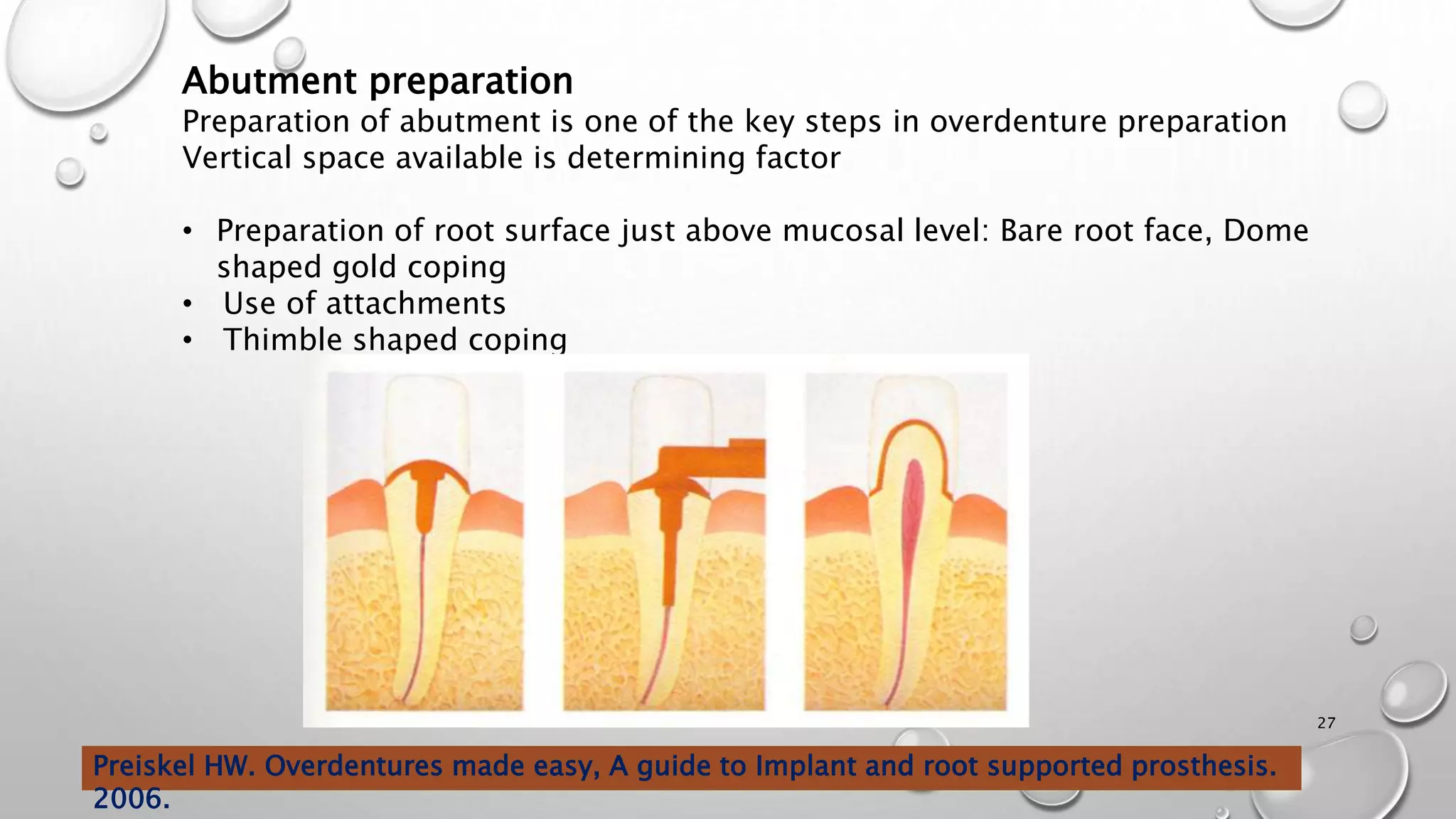
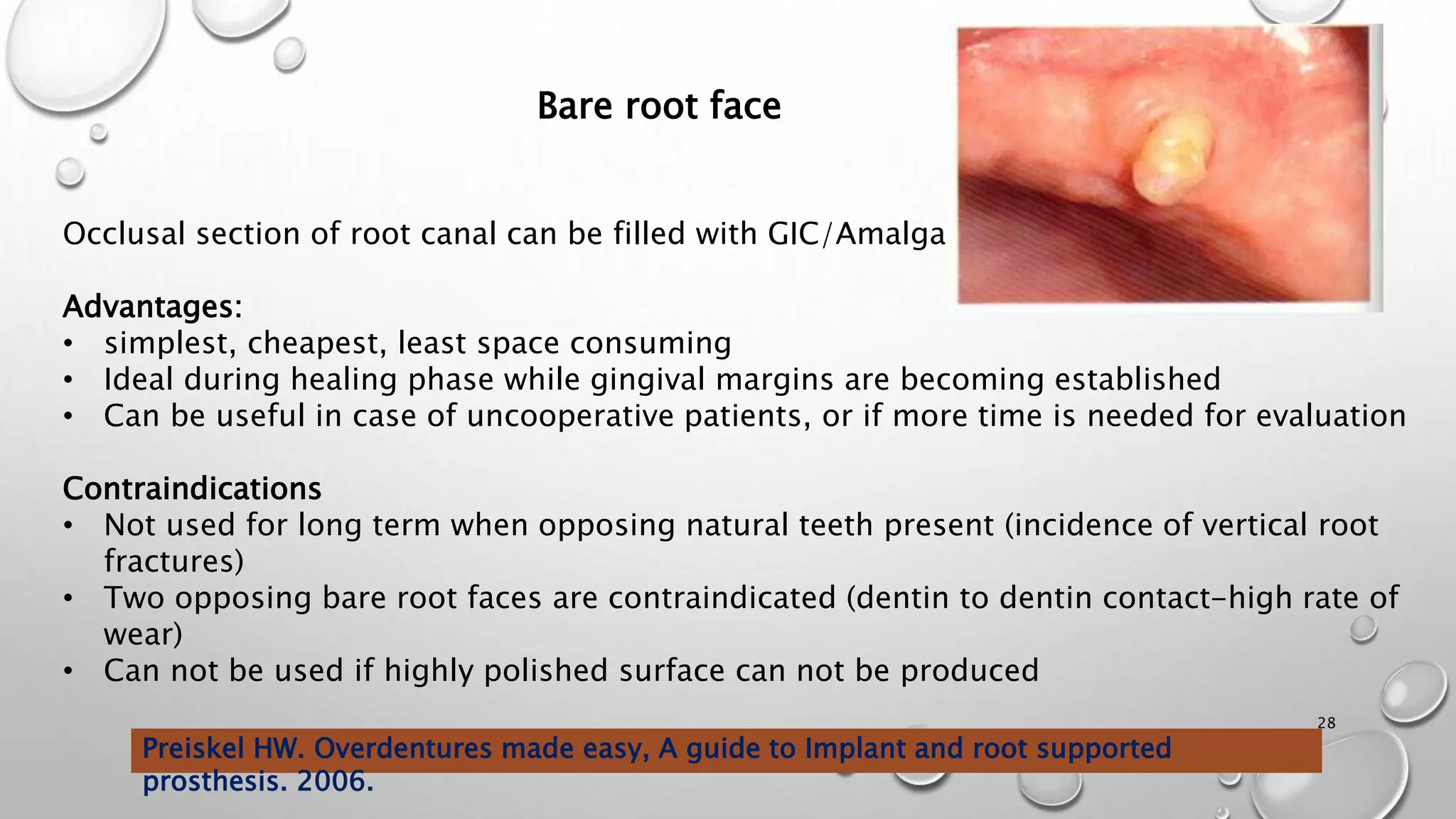
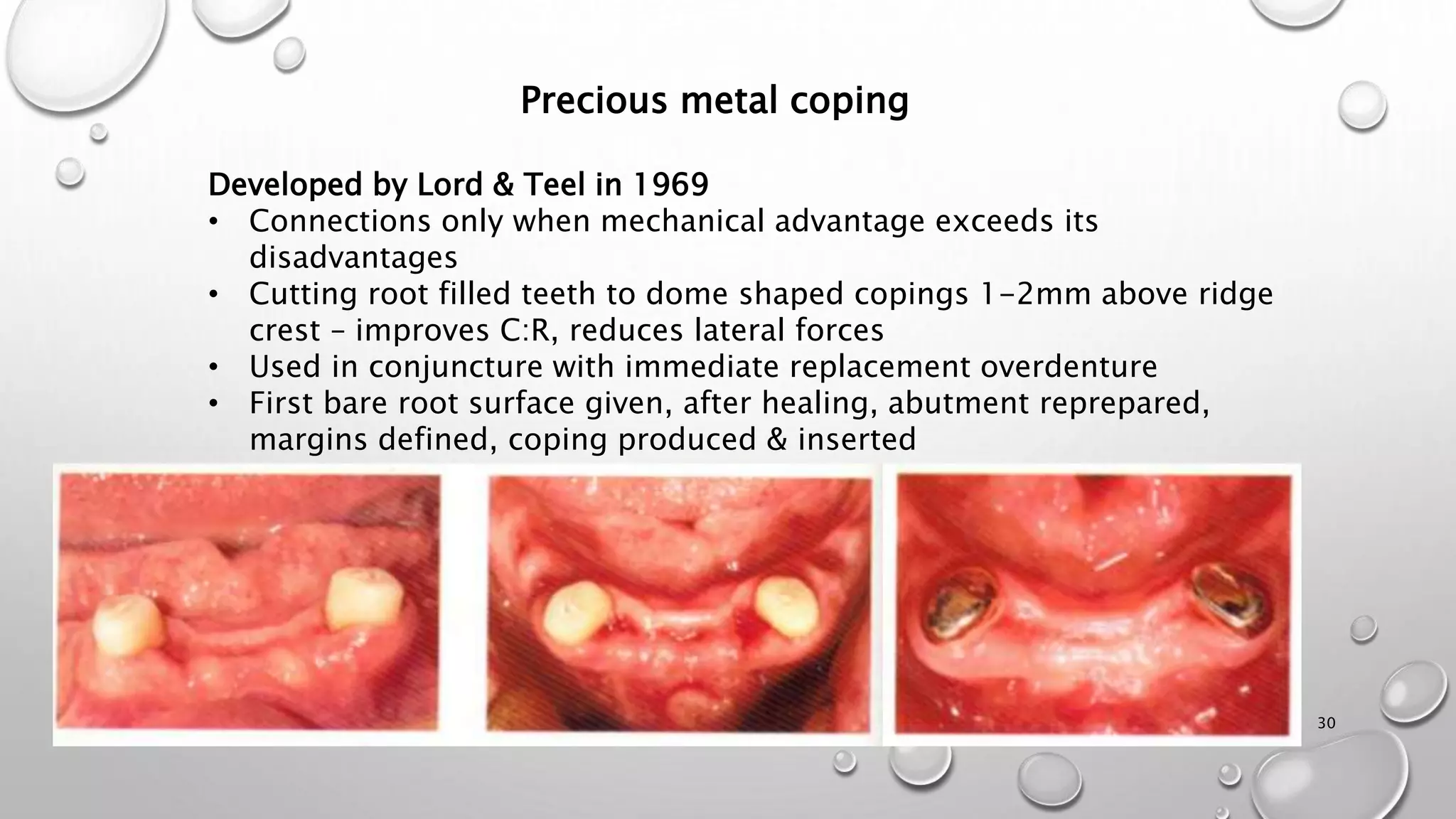
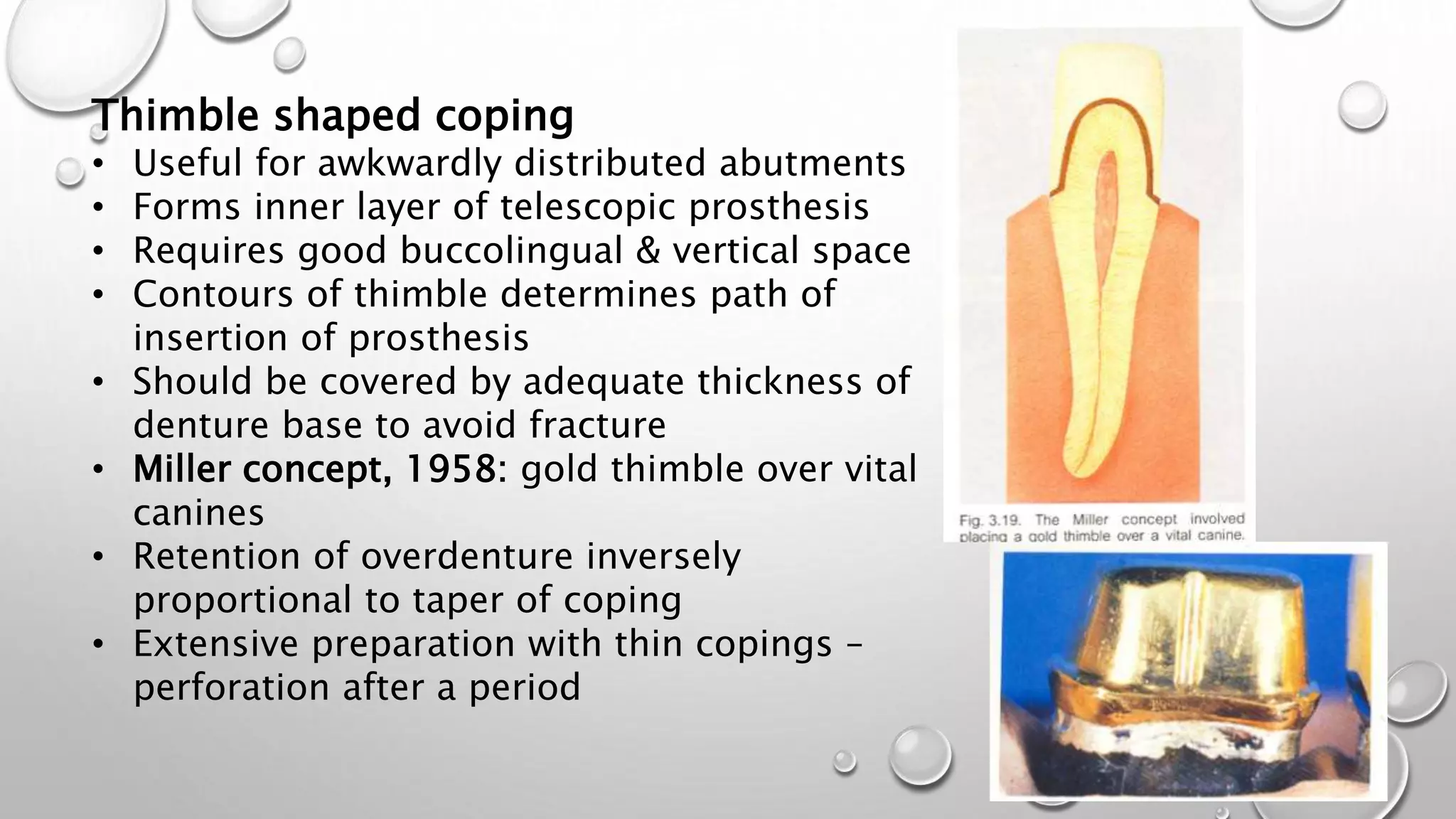
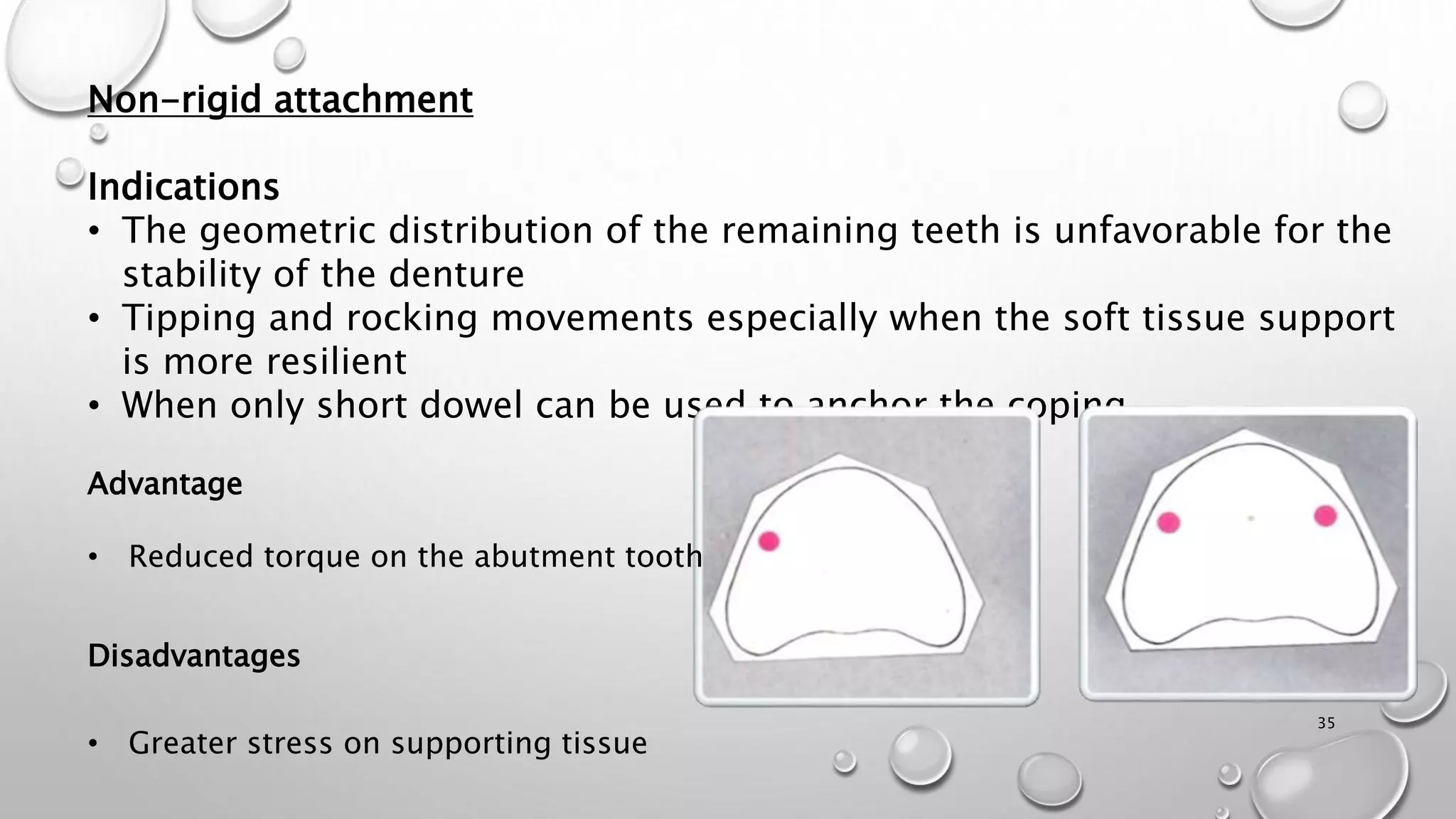
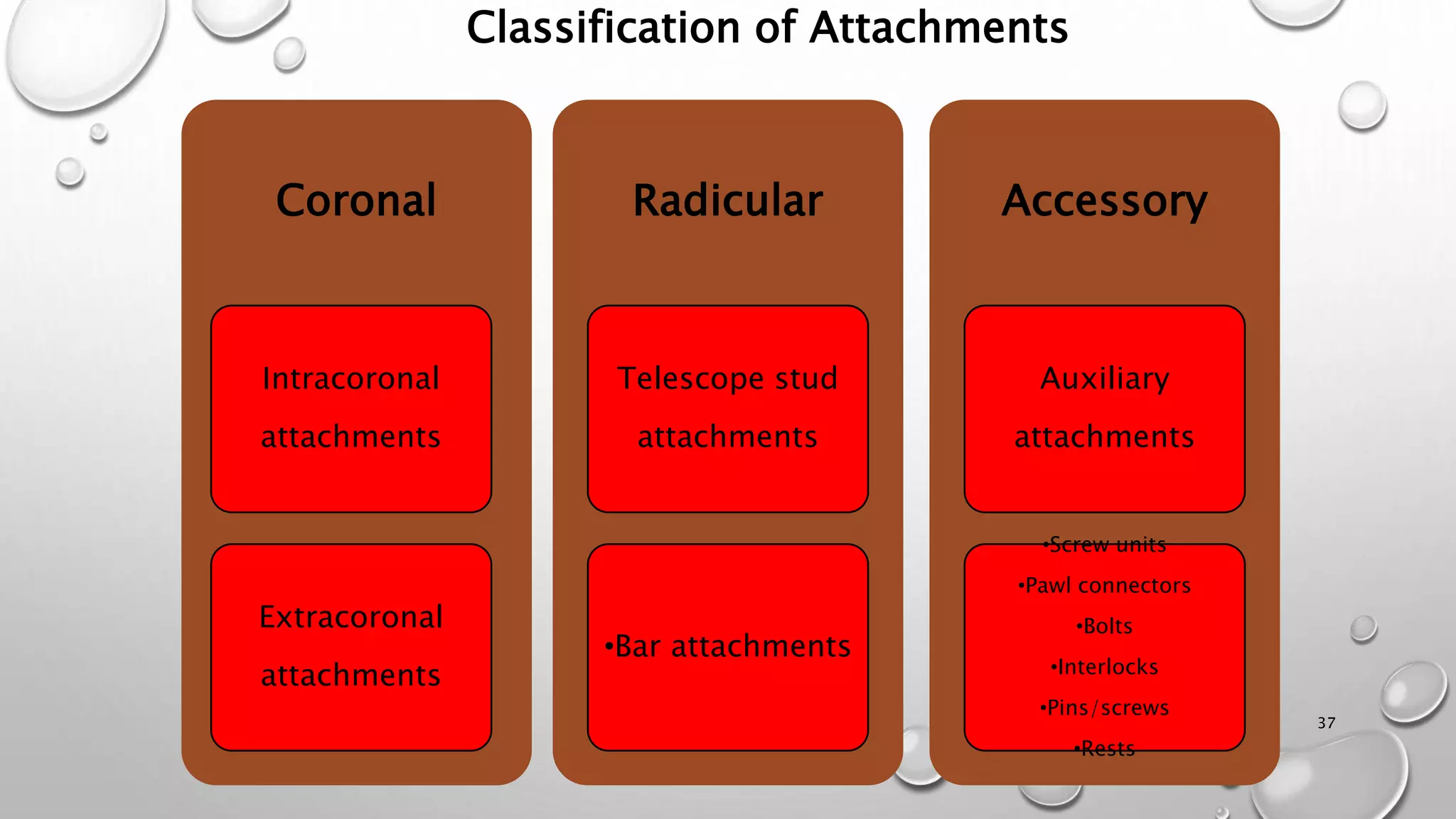
The document provides an overview of overdentures, which are removable dental prostheses supported by natural teeth, roots, or implants. It details the indications, advantages, and disadvantages of overdentures, outlines treatment planning steps, and describes techniques for selecting and preparing abutment teeth. The document emphasizes the importance of careful planning and various methodologies for the effective use of overdentures in dental prosthetics.