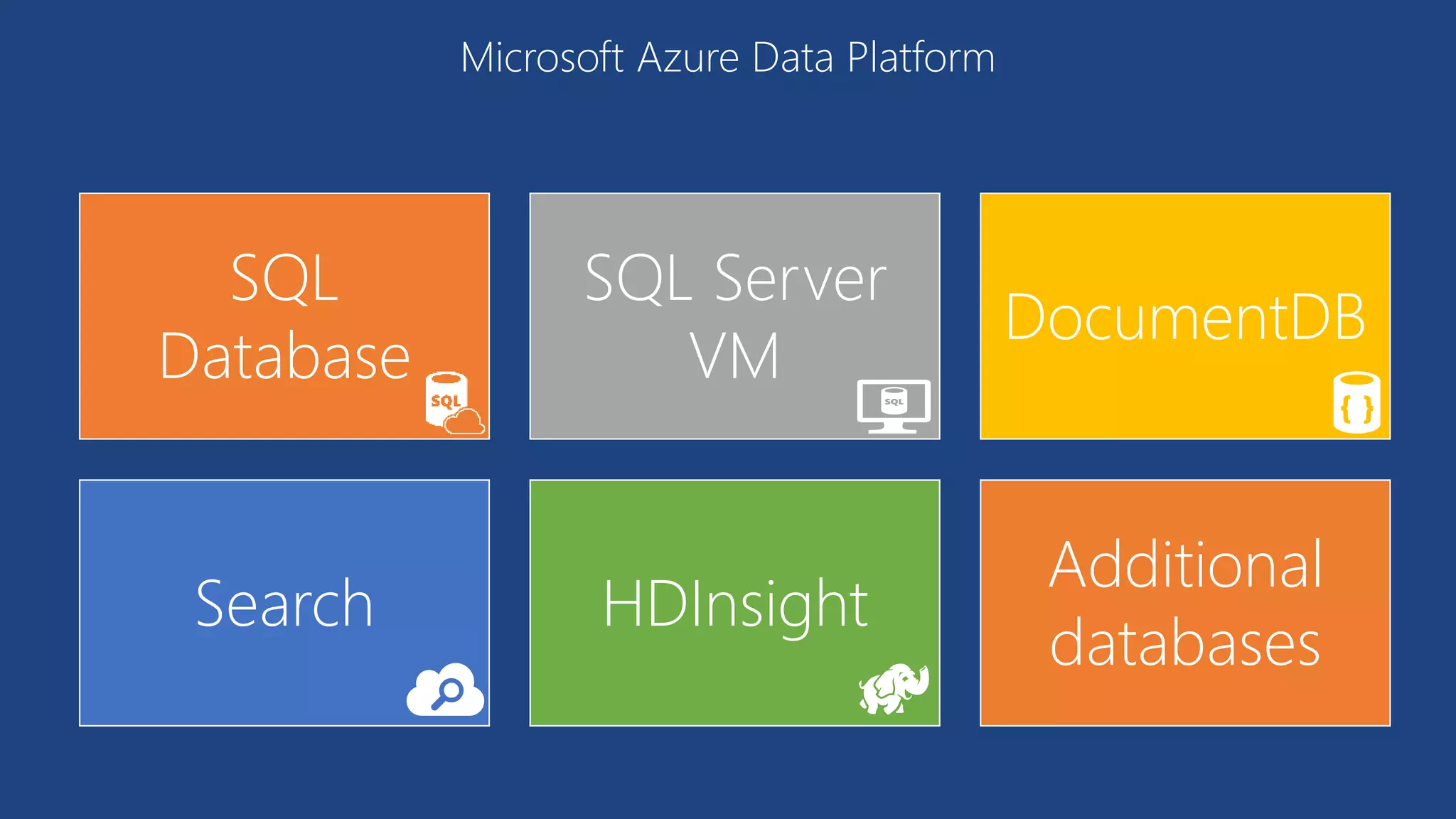
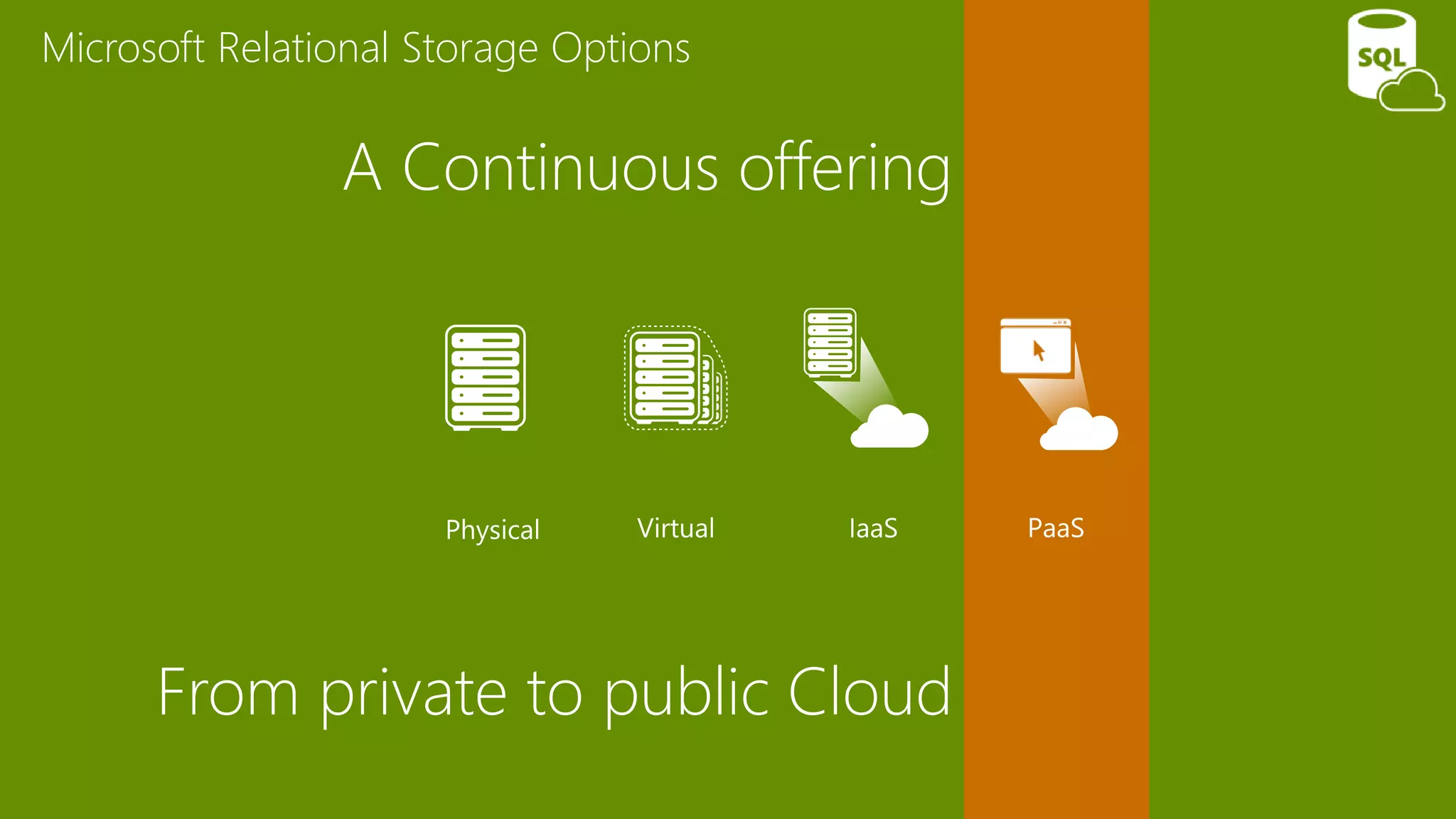
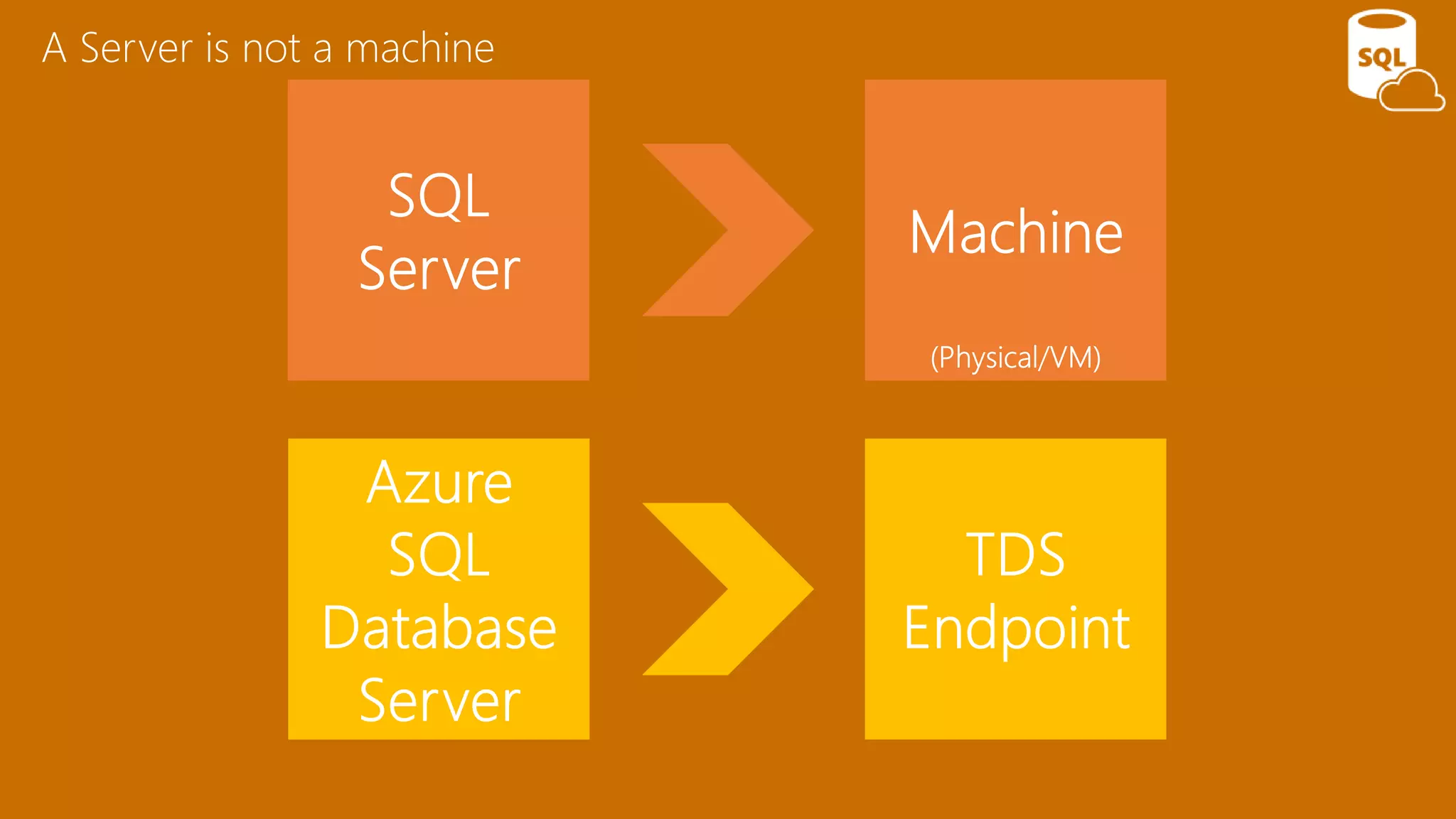
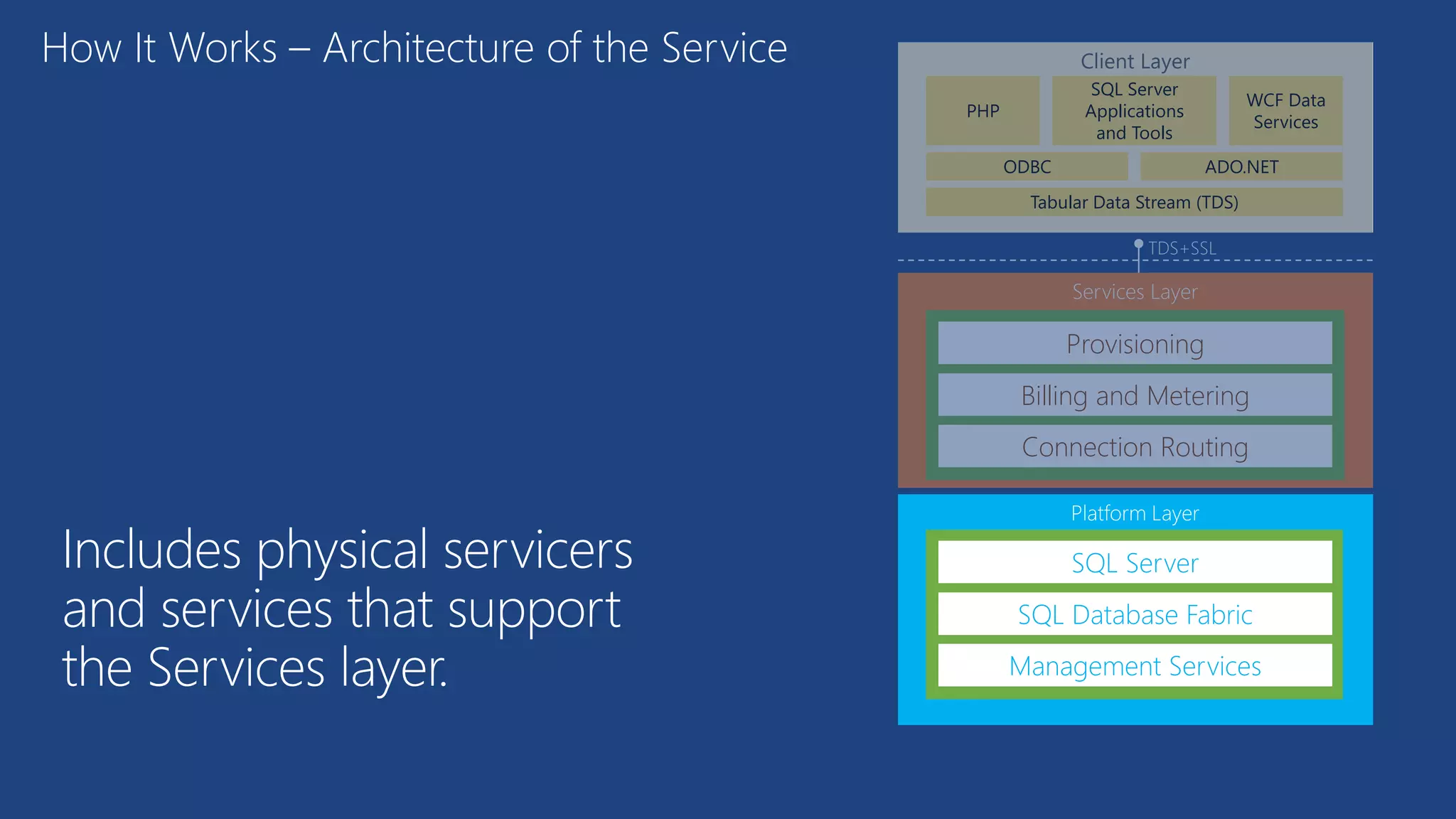
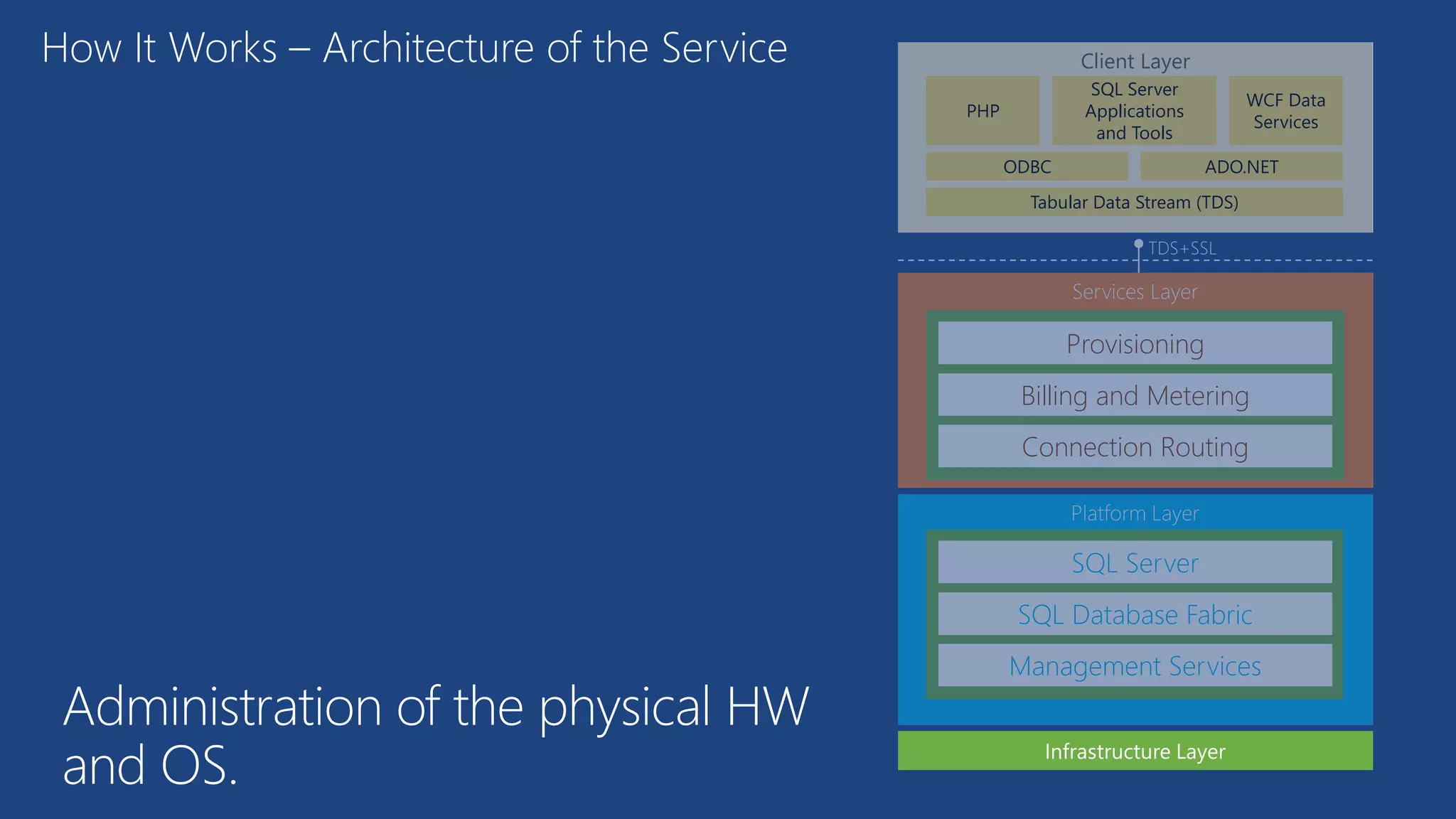
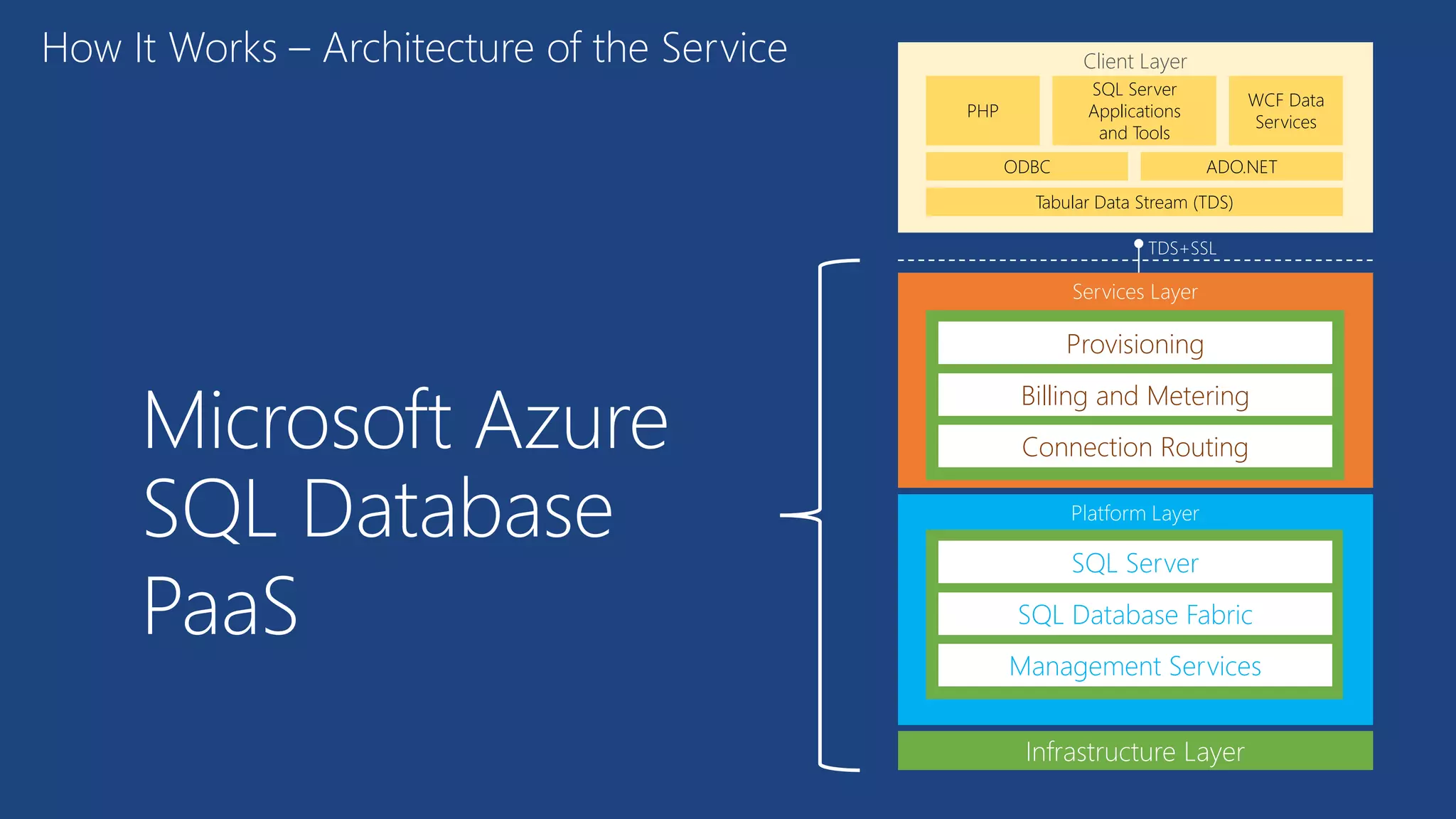
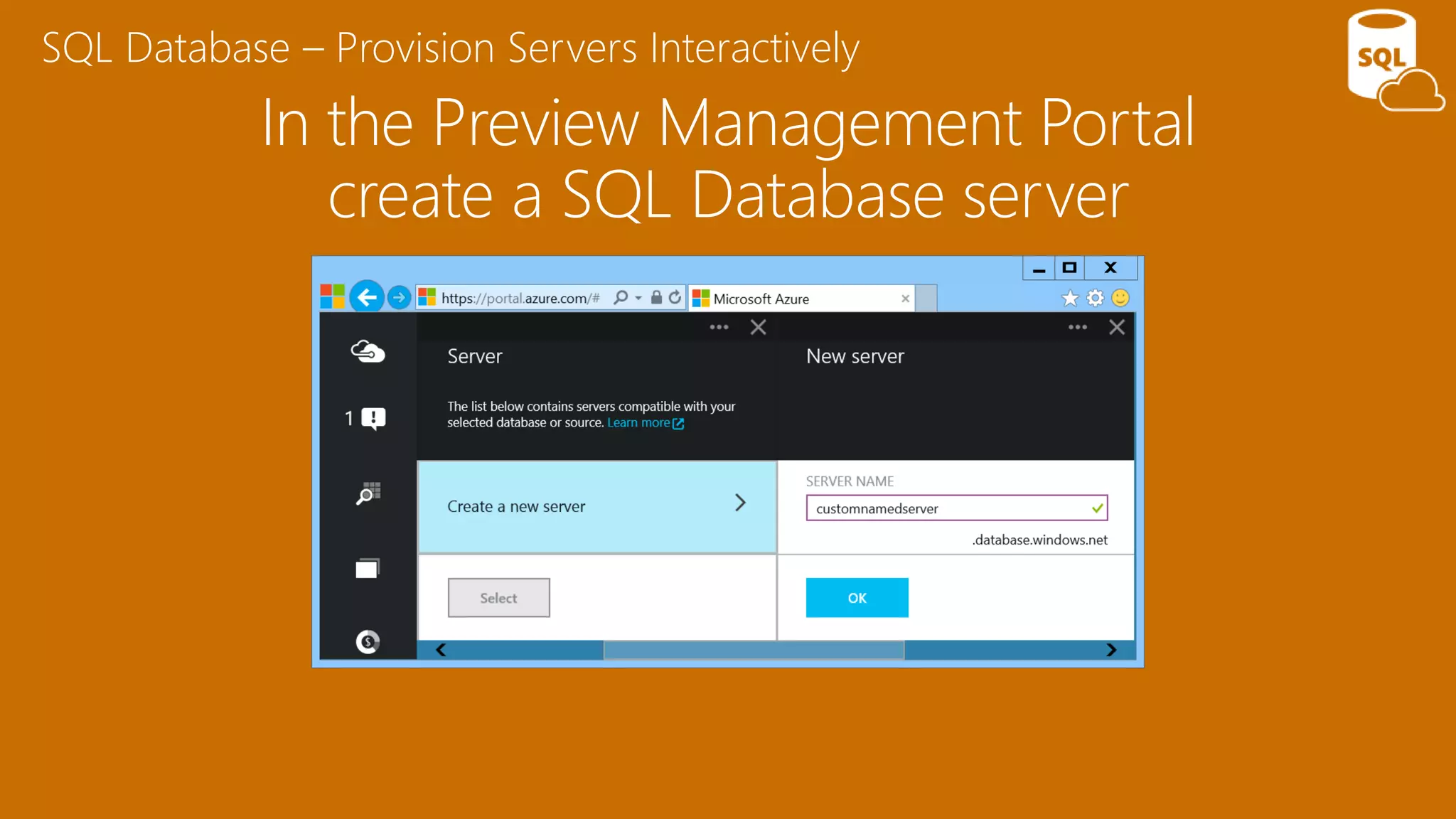
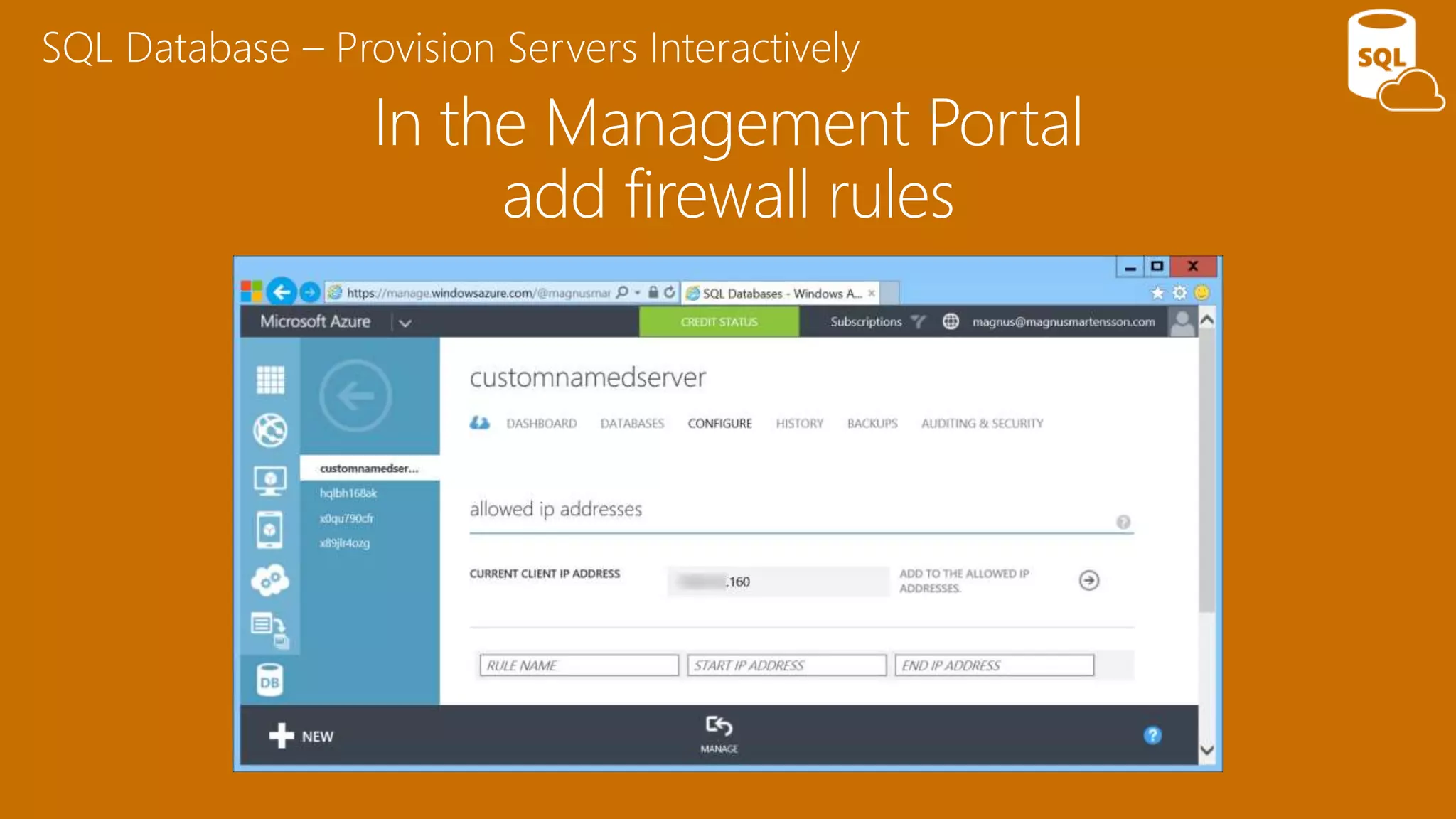
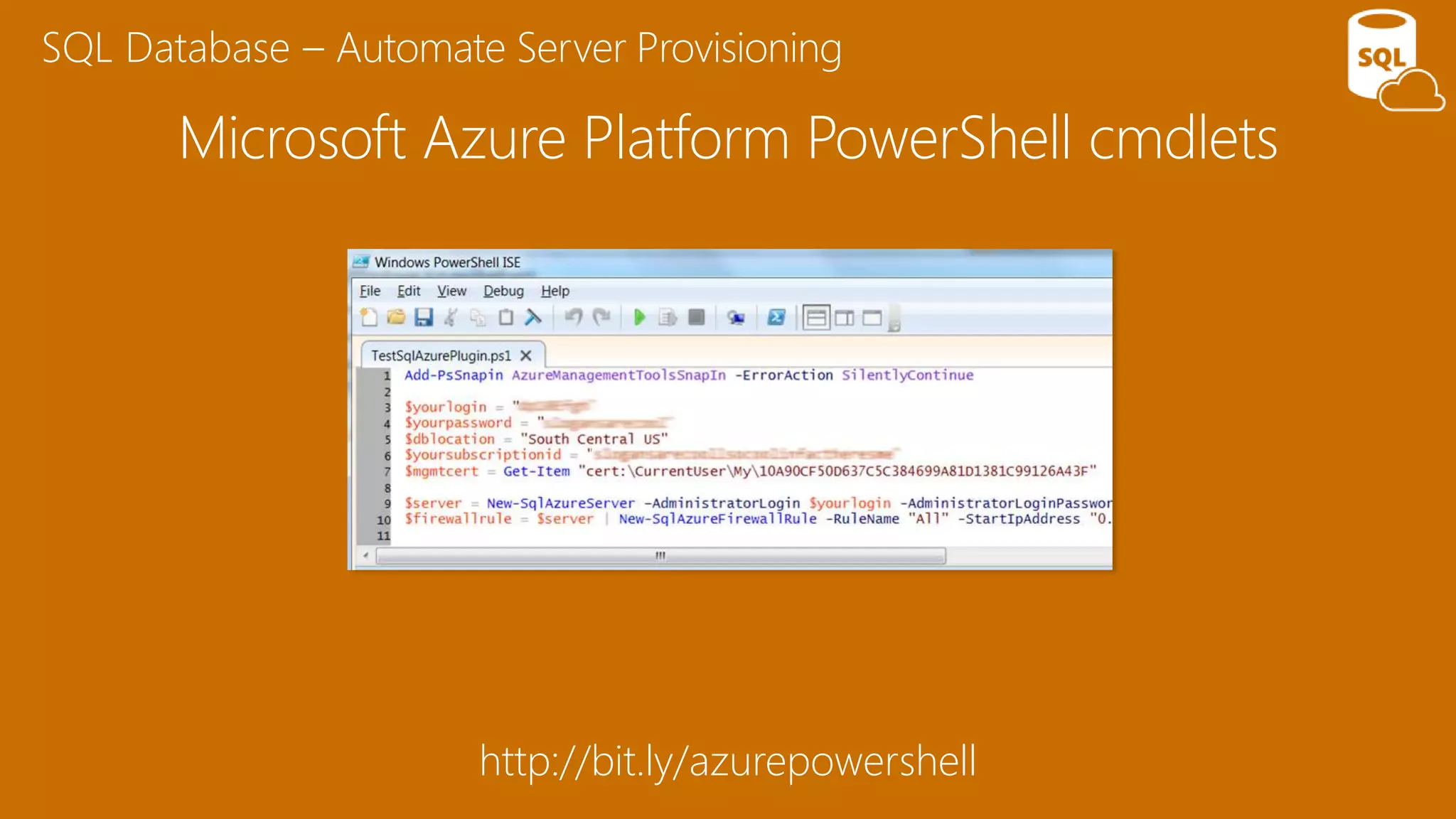
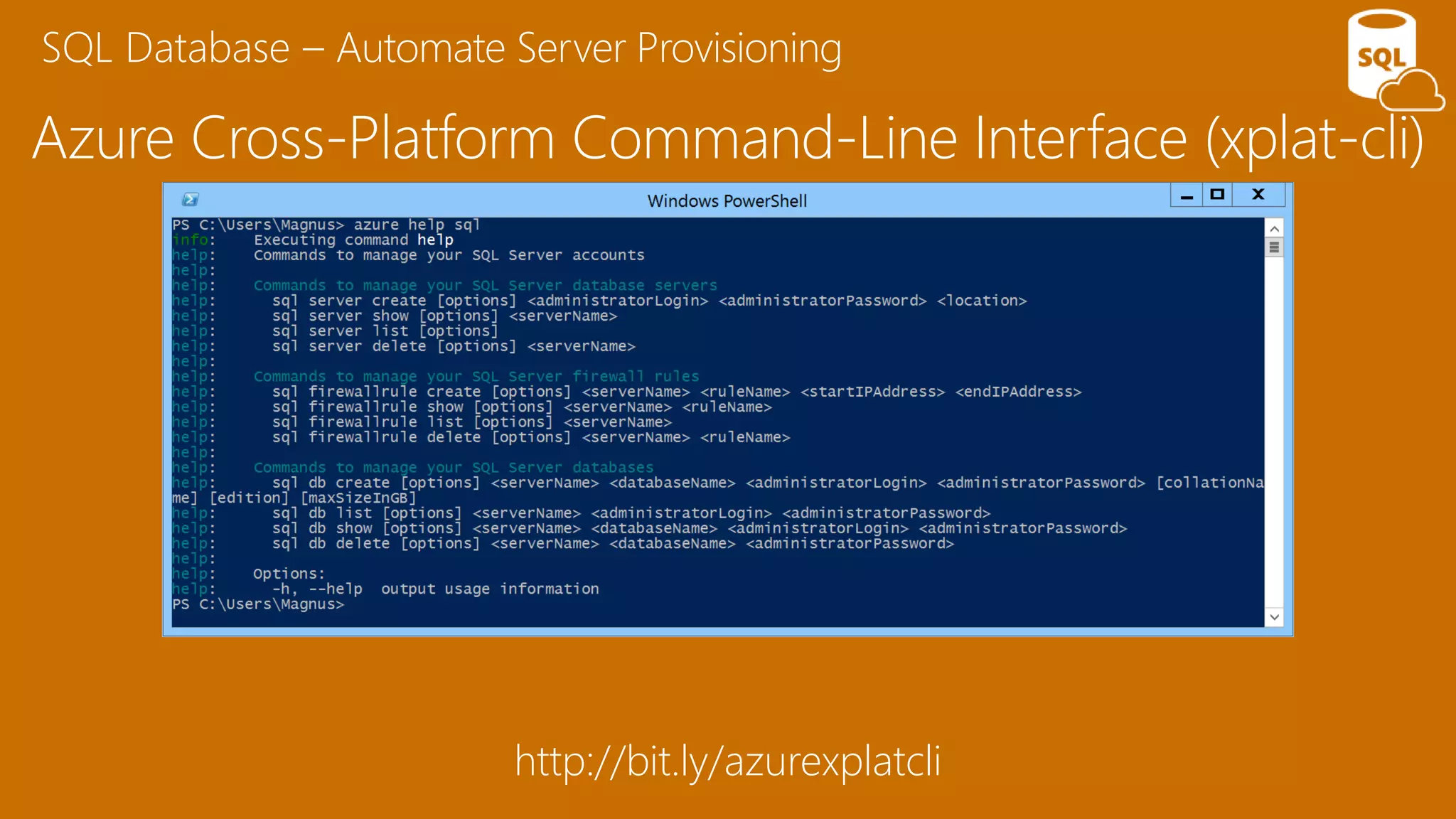
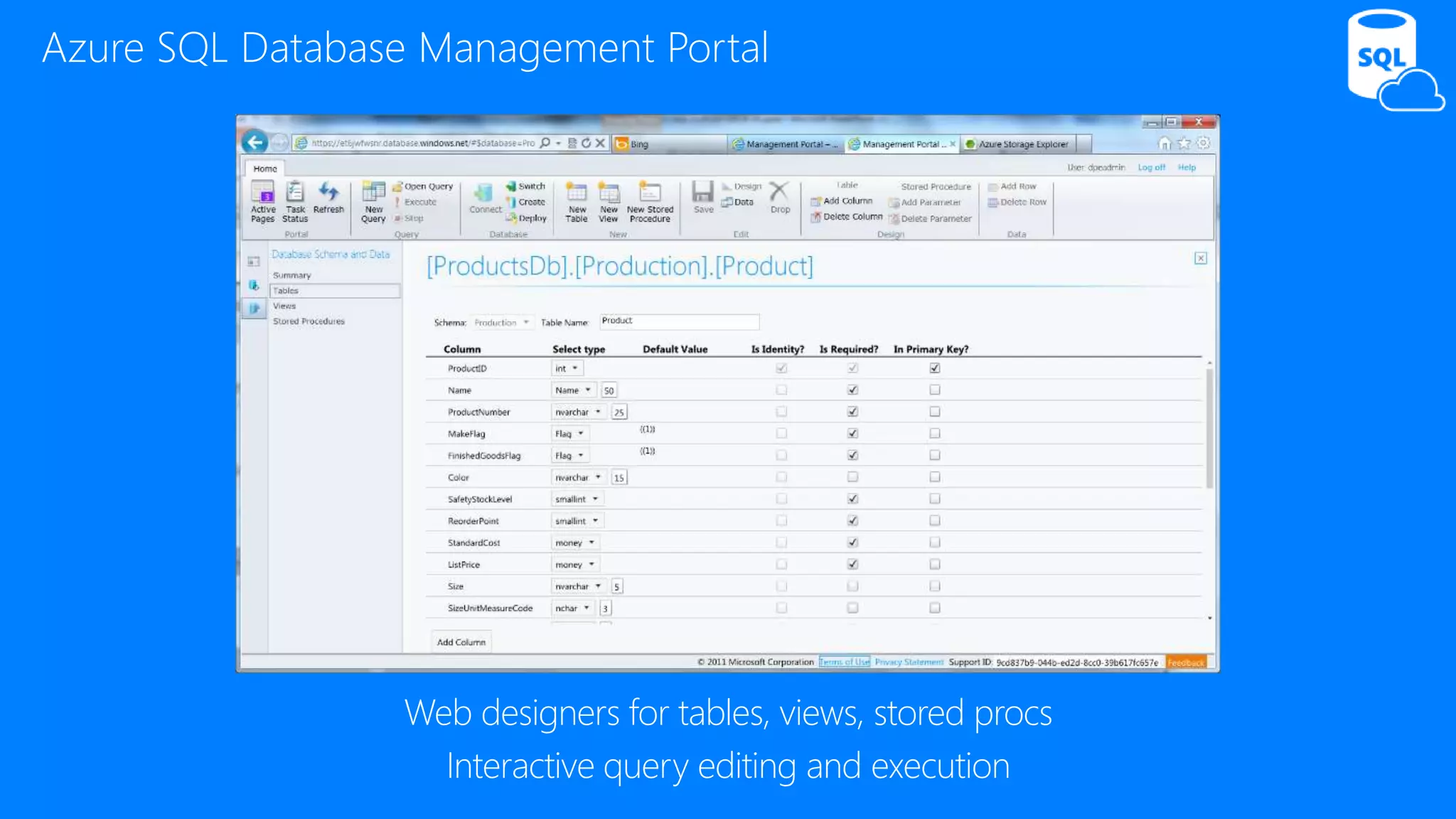
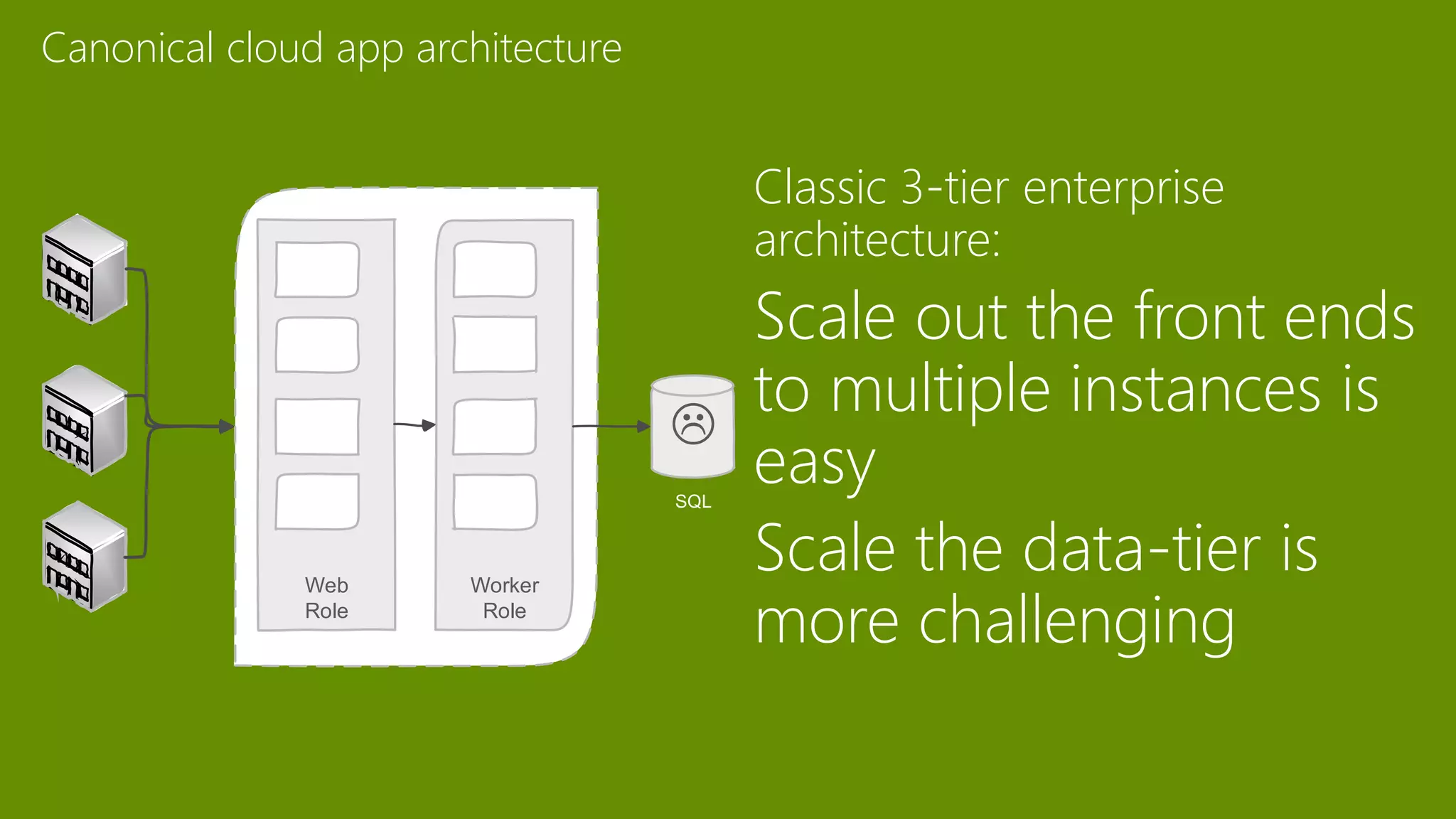
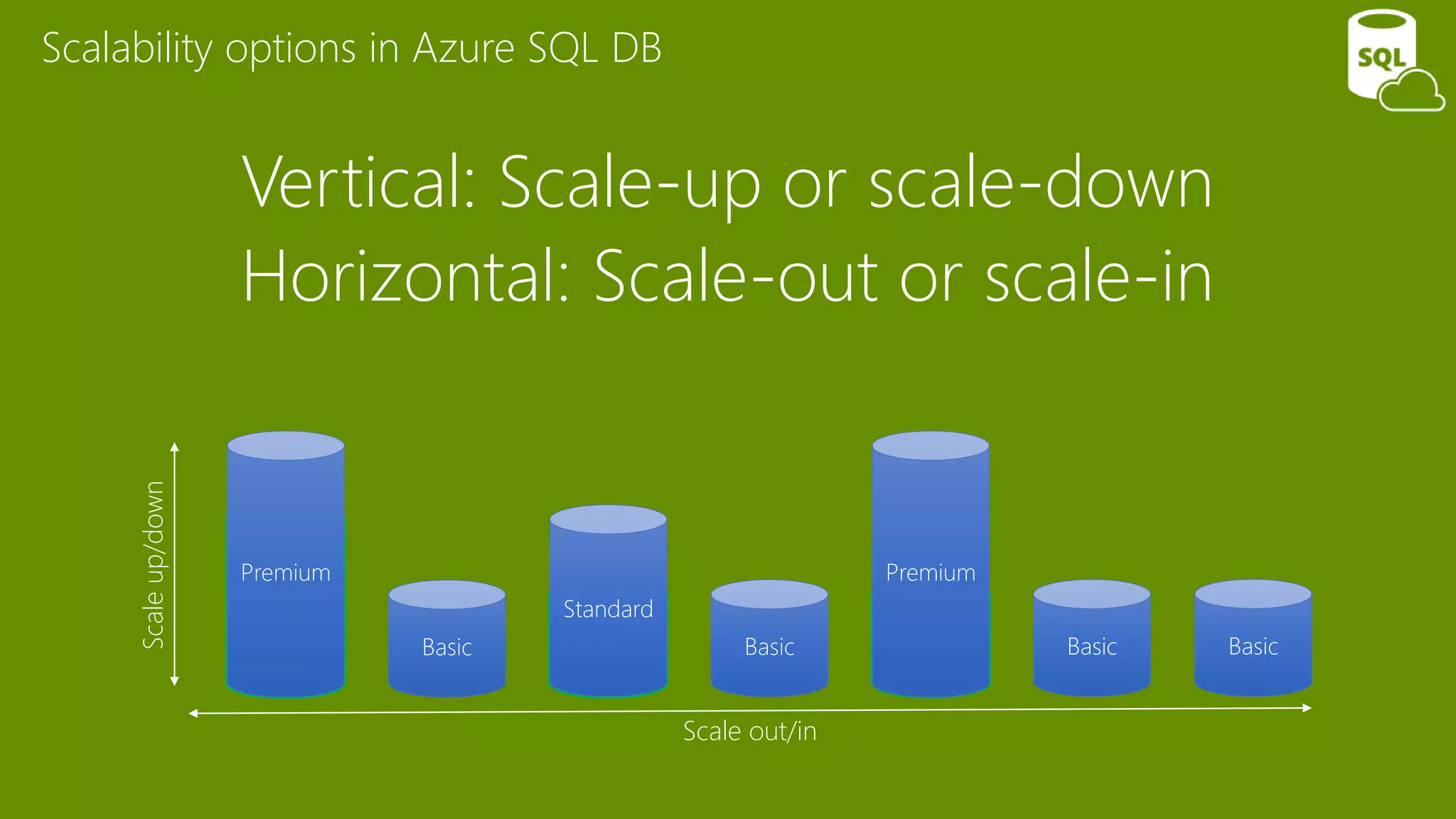
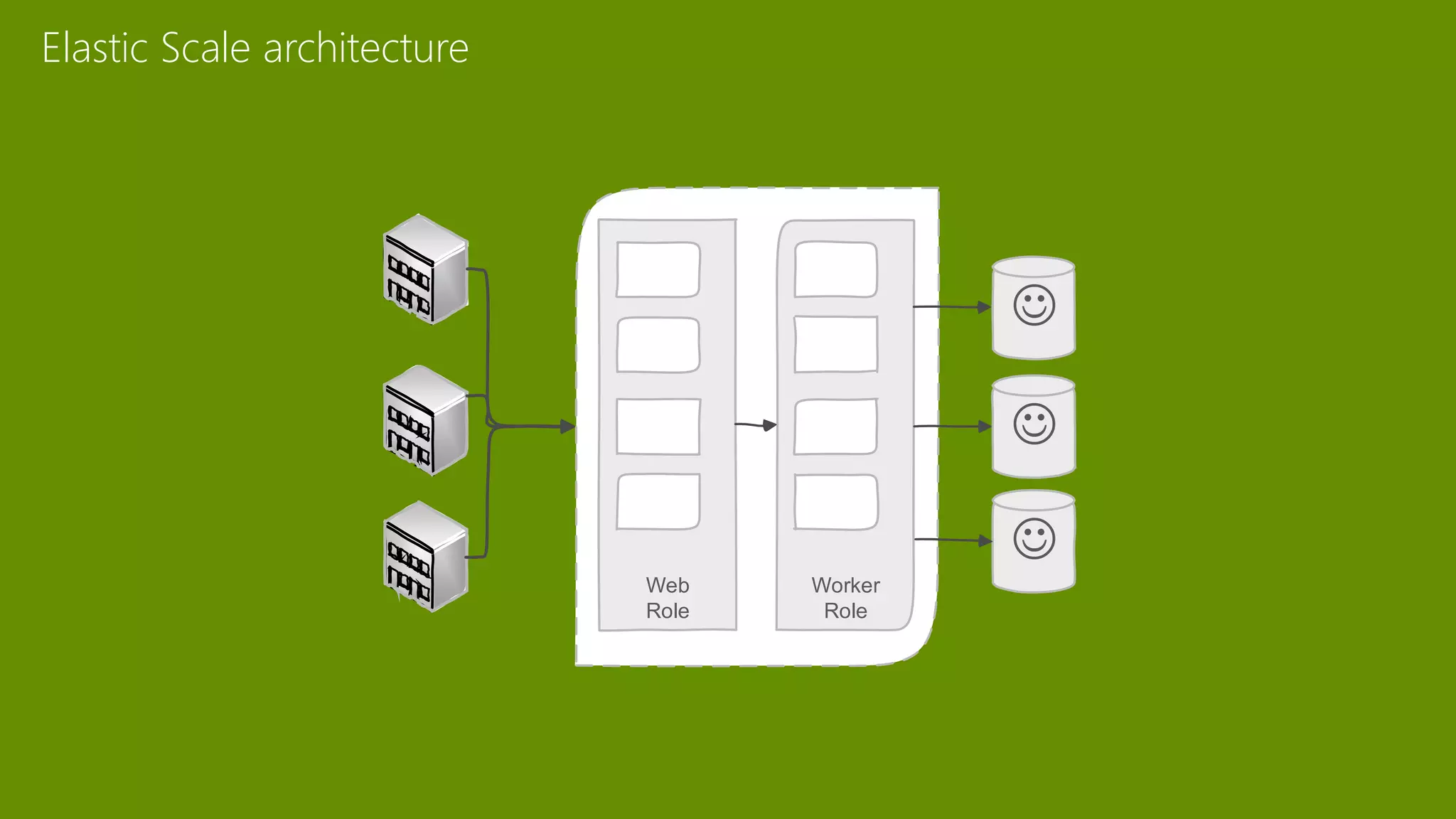
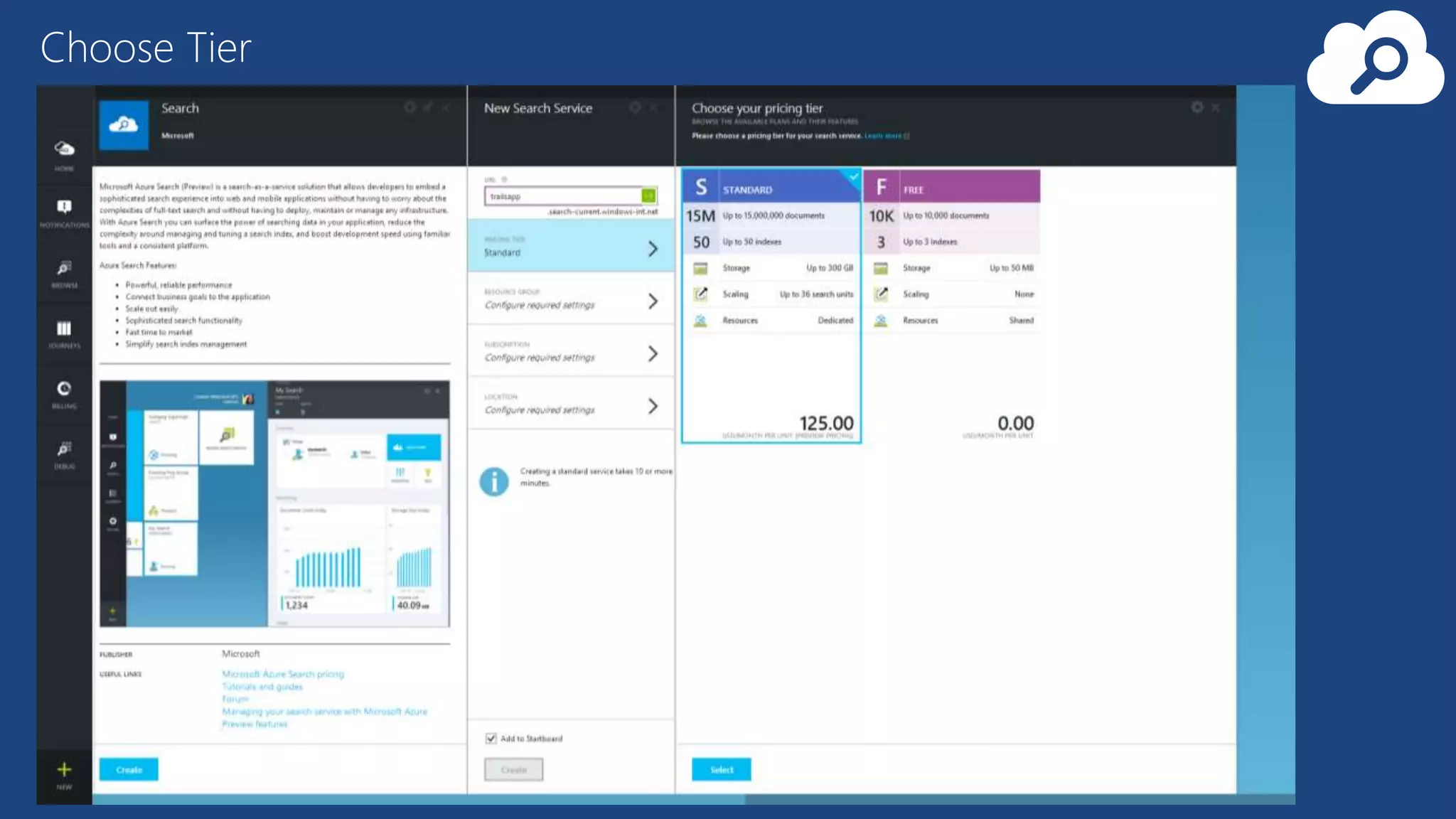
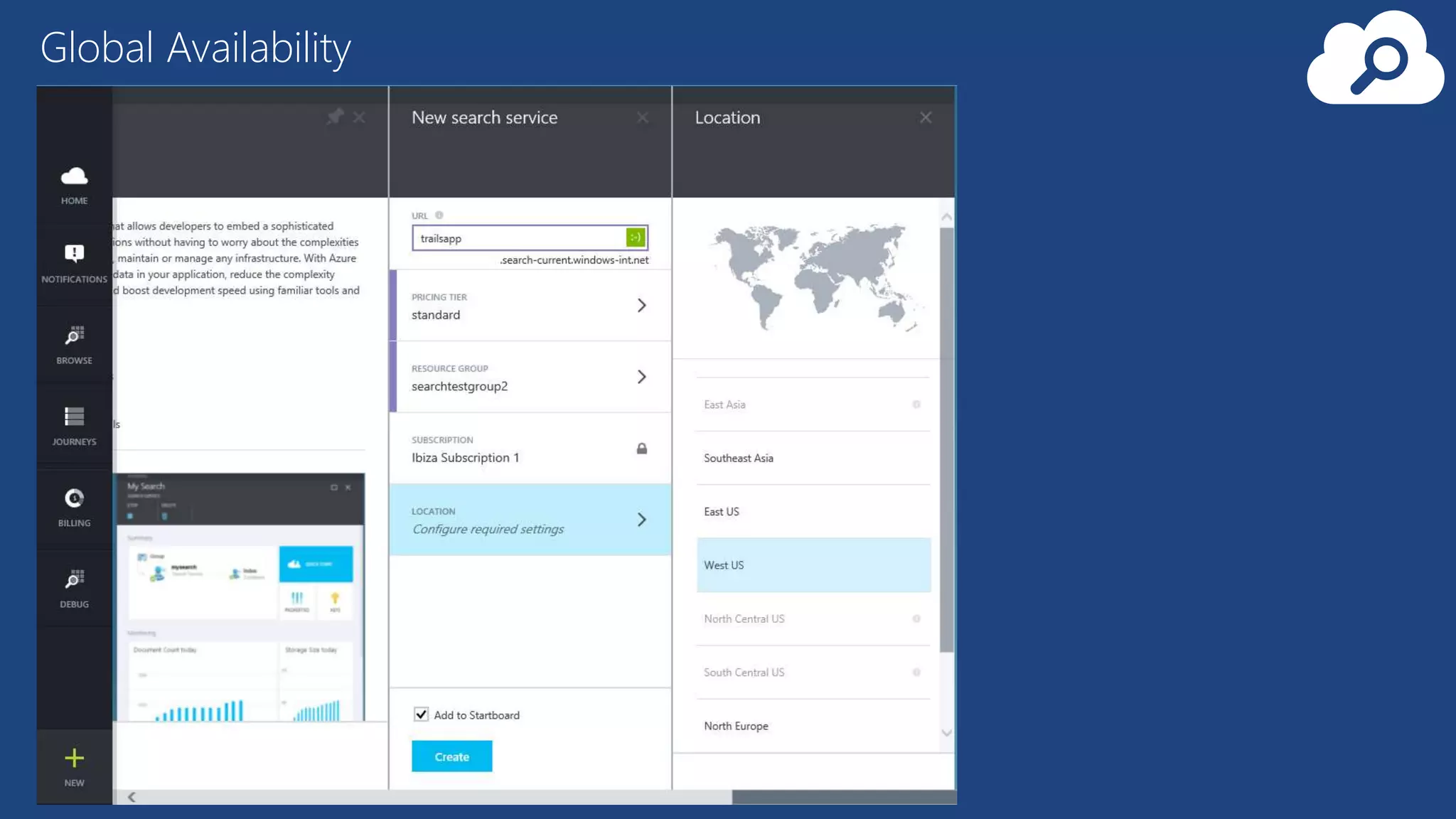
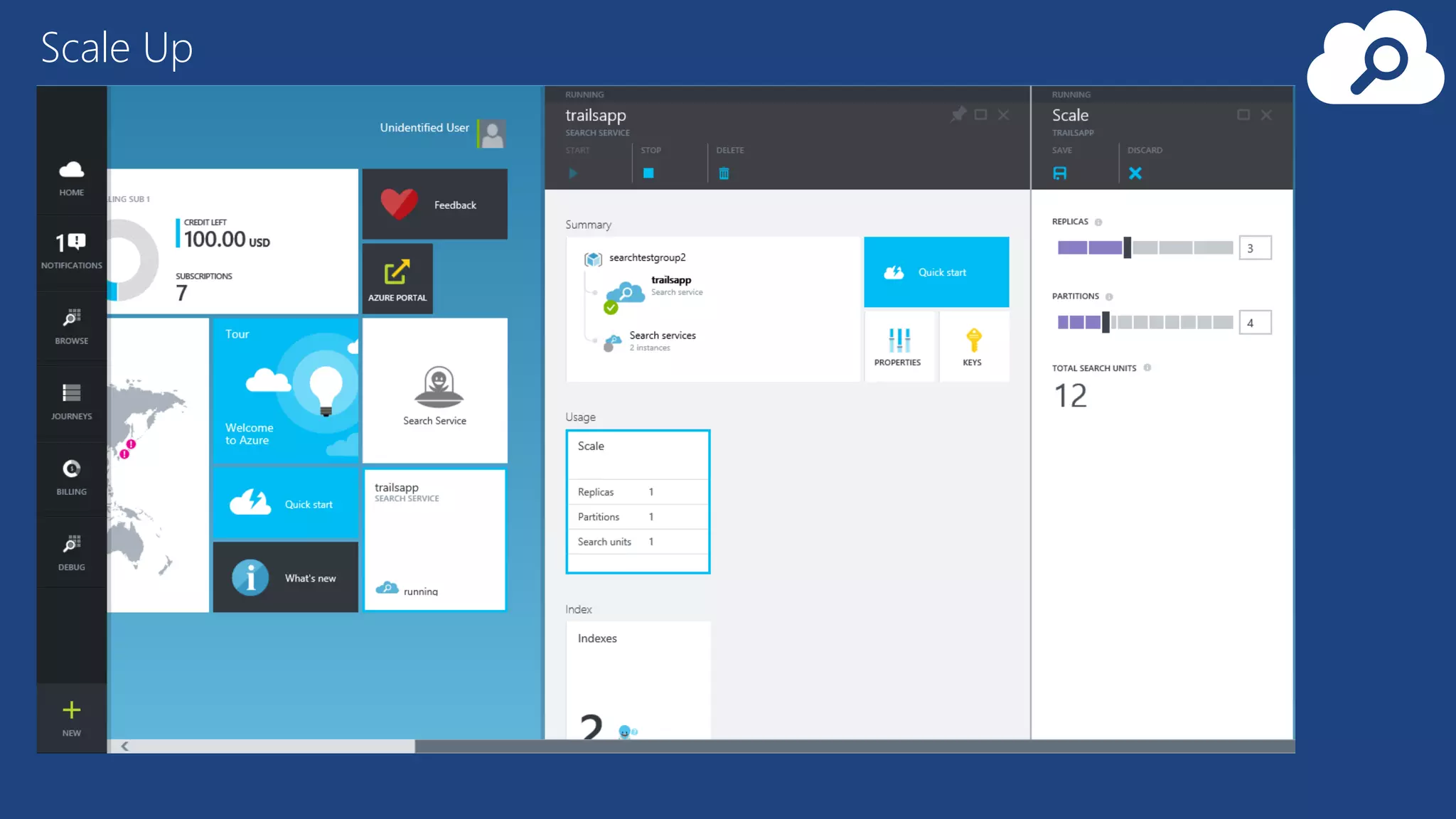
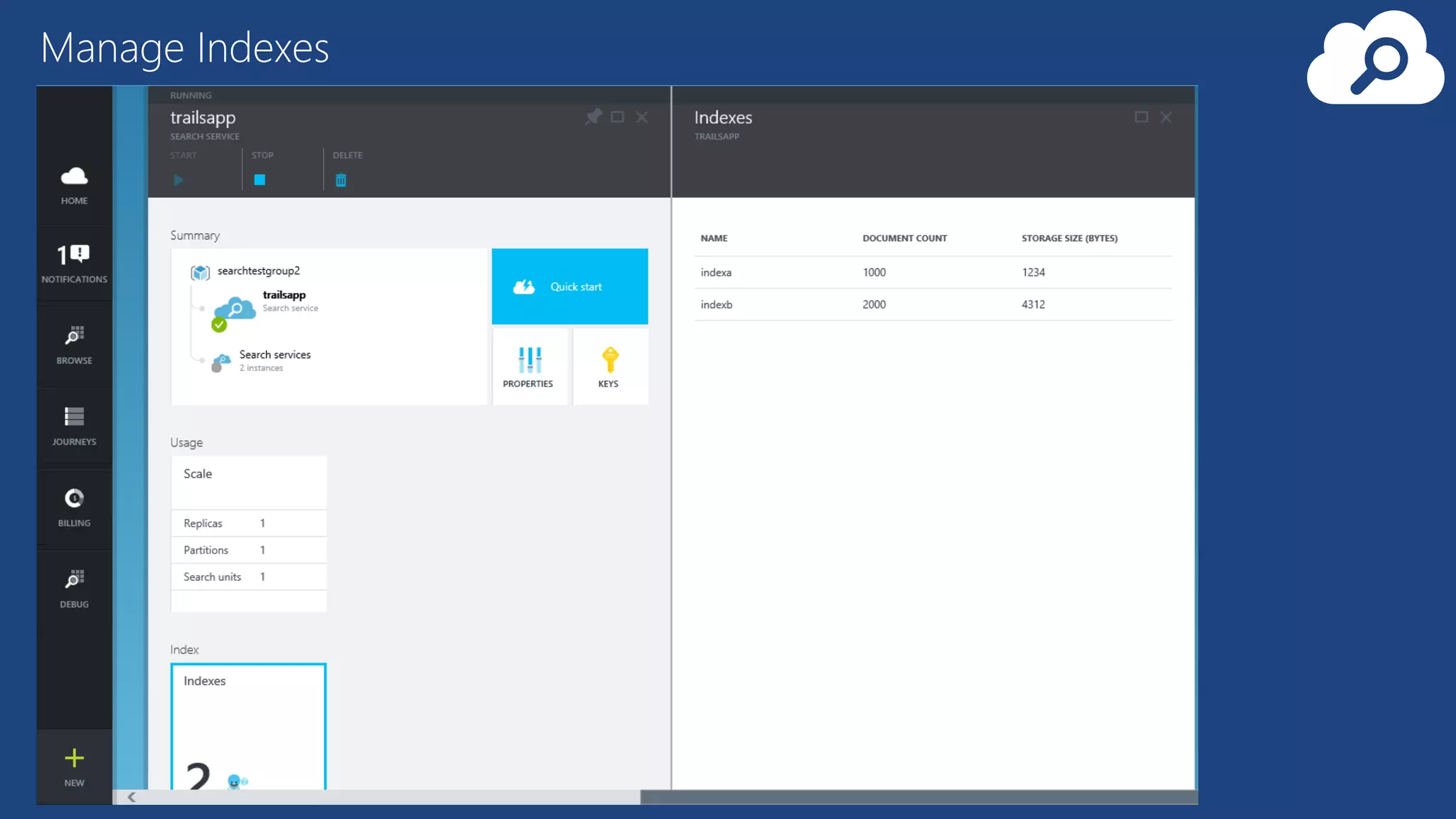
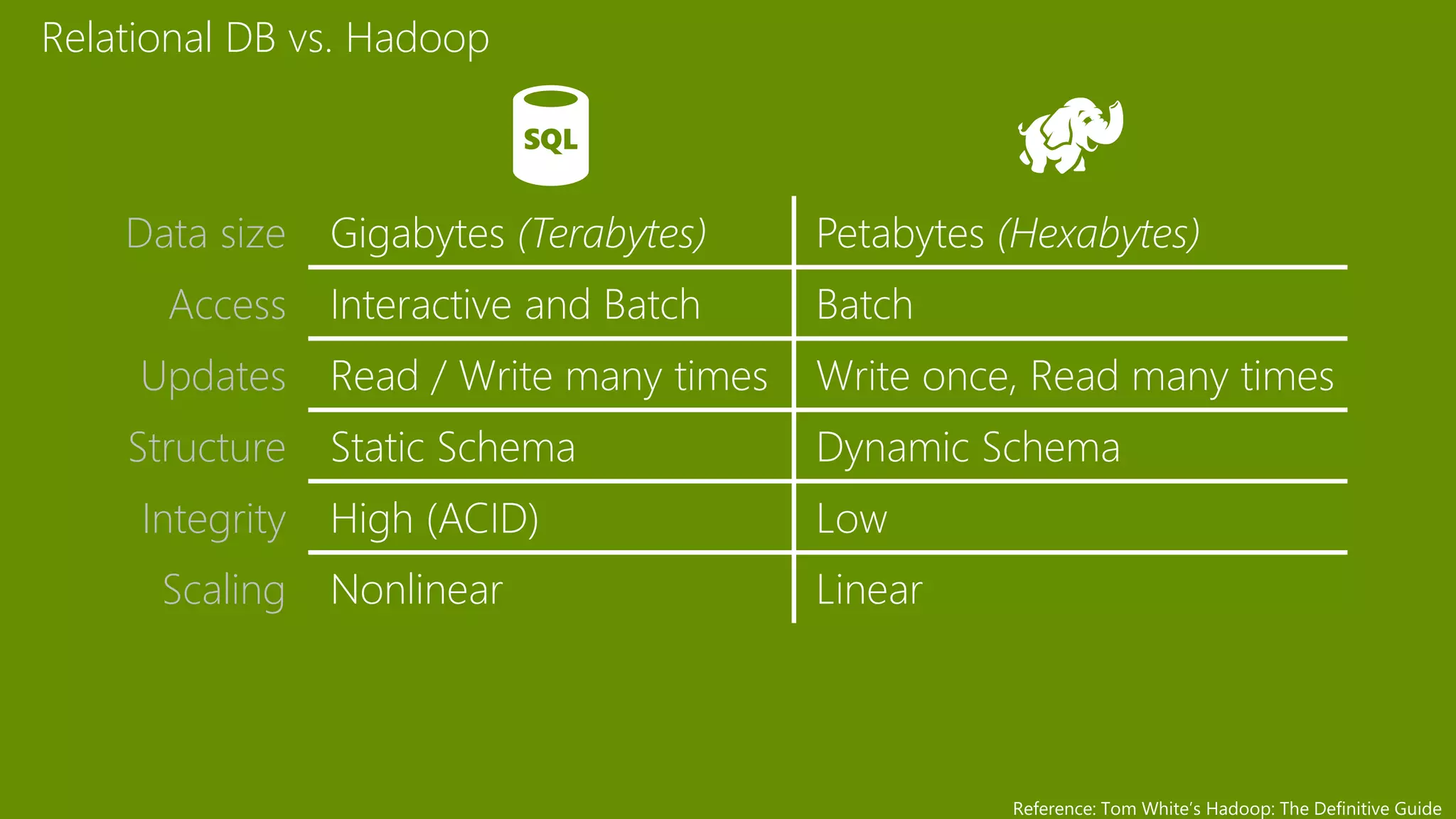
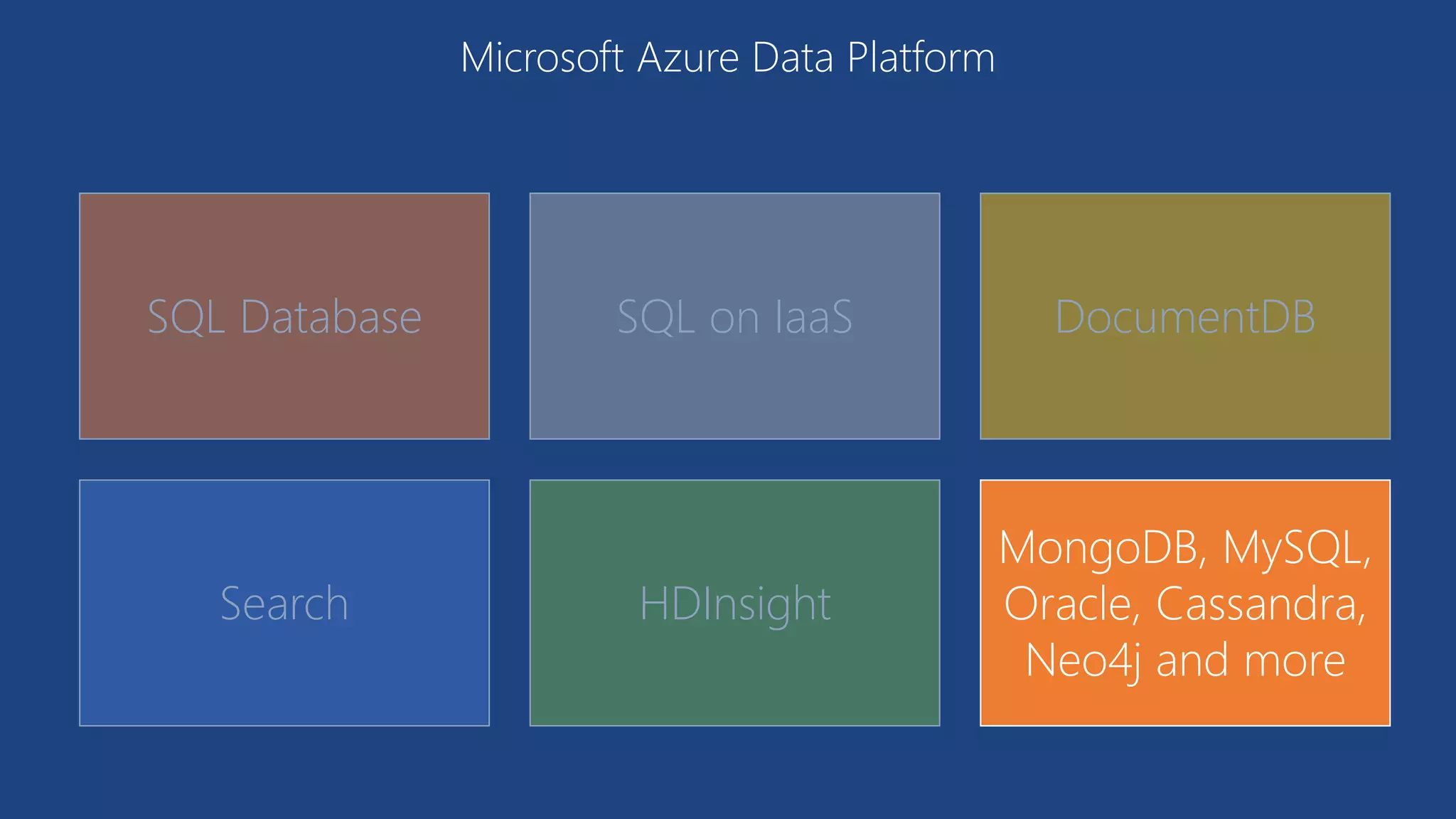
The document provides an overview of Microsoft Azure's data platform and various database options, including SQL Database, SQL Server VMs, DocumentDB, HDInsight, and Azure Search. It discusses the architecture and features of these services, how to provision and manage databases, and includes demos of interacting with the databases. The key services covered allow for relational, non-relational, and search databases hosted on Azure infrastructure at varying levels of management and control.