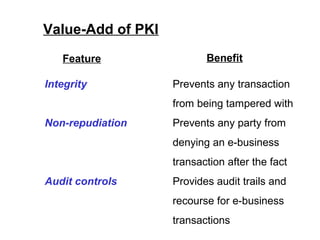
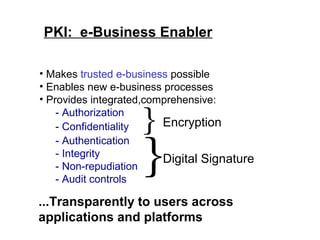
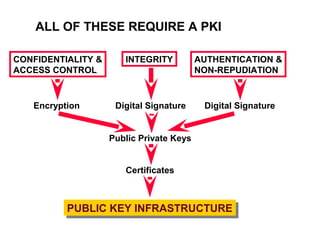
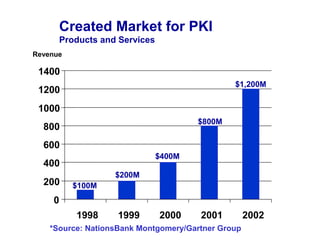
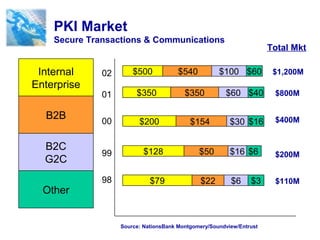
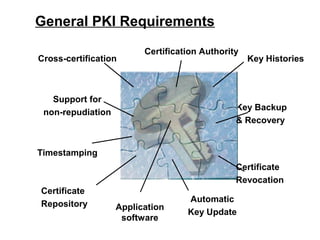
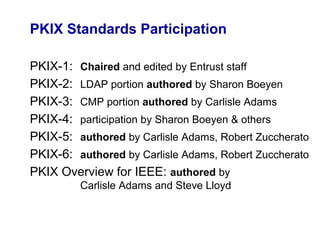
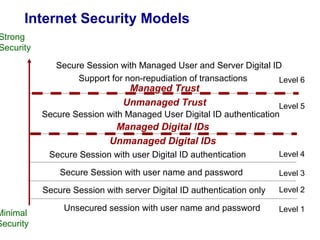
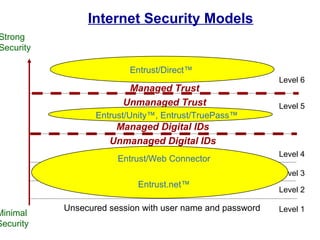
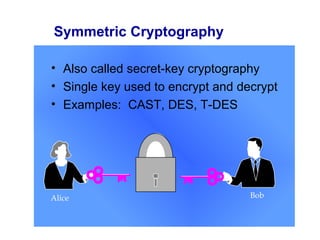
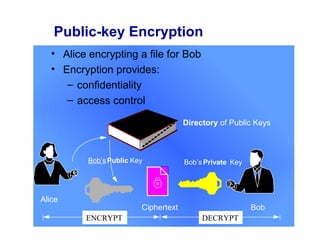
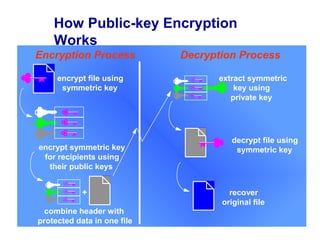
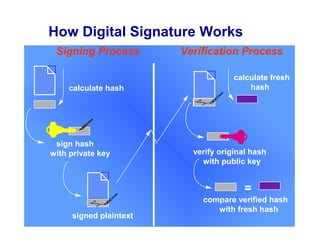
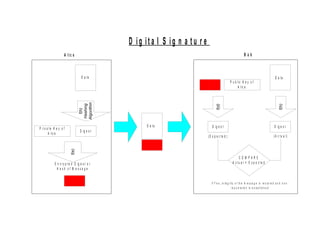
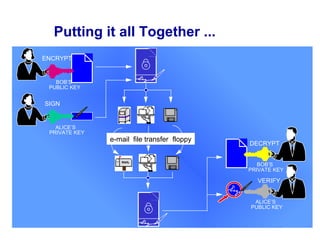
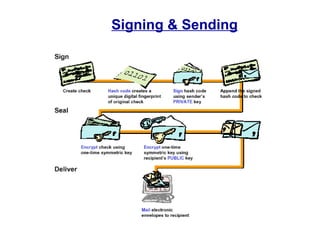
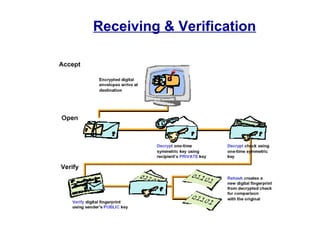
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) allows for trusted electronic business by establishing trust through the generation and distribution of public keys and certificates. A PKI consists of components that work together to publish, manage, and use public keys seamlessly. It provides capabilities for authentication, authorization, confidentiality, integrity, non-repudiation, and audit controls through the use of public key cryptography and digital signatures. The PKI market has grown significantly since the late 1990s as PKI enables new e-business processes and transactions. Common cryptographic algorithms used in PKI include symmetric algorithms like DES and public key algorithms like RSA.