This document discusses several key topics related to measuring economic activity and growth:
1. Total output in an economy (gross domestic product or GDP) can be measured in three equivalent ways: by total output, total income, or total expenditure in the economy.
2. GDP is used to measure the total value of goods and services produced, but nominal GDP does not account for inflation - real GDP adjusts for inflation to show the actual growth in output.
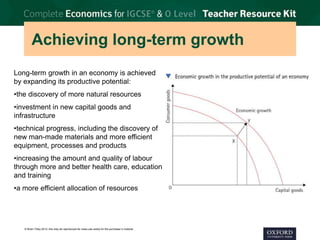
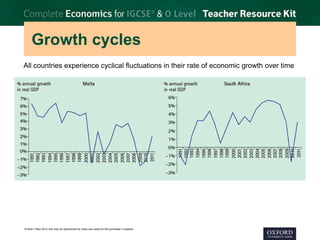
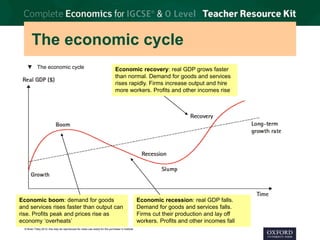
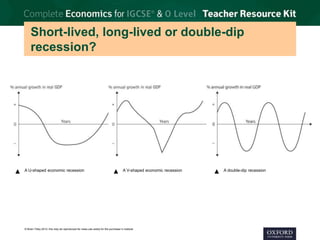
3. Economic growth is defined as the increase in real GDP from one period to the next. Long-term growth comes from expanding an economy's productive potential through factors like new resources, technology, education, and efficient allocation of resources.
4.