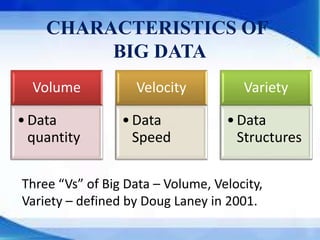
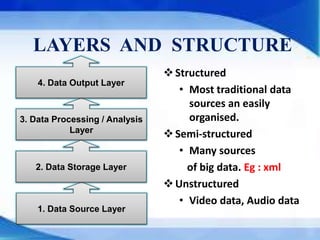
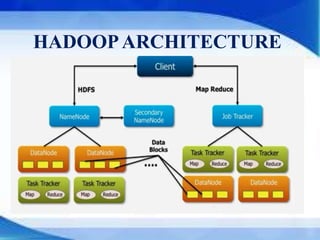
This document provides an introduction to big data, including its characteristics, layers and structures, tools and technologies used, applications, and benefits. Big data refers to large datasets that are beyond the processing capabilities of typical database software. It has the key characteristics of volume, velocity, and variety. Common tools for big data include Hadoop, MapReduce, and NoSQL databases. Big data has many applications and benefits across industries like retail, healthcare, and banking through improved decision making, cost reduction, and innovation.