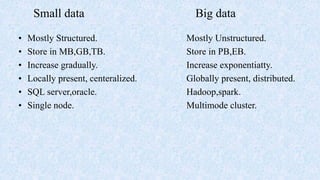
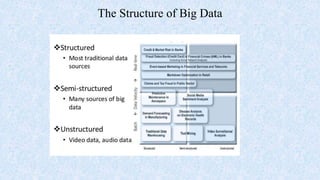
This document provides an overview of big data, including its definition, characteristics, sources, tools used, applications, risks, benefits, and future. It defines big data as large, diverse, and growing datasets that require new processing techniques. The key characteristics are volume, velocity, and variety. Common sources include user data, sensors, social media, and system logs. Tools used include Hadoop, Spark, MongoDB and cloud platforms. Applications span customer analytics, business intelligence and scientific research. Risks include privacy and escalating costs, while benefits are improved decision making, customer insights and new business opportunities. The future of big data is projected to be a multi-billion dollar industry with growing demand for data scientists and analysts.