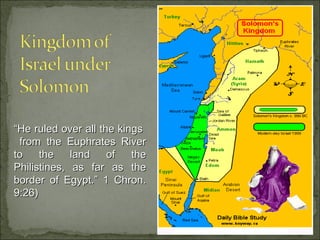
The document discusses the historical books of the Old Testament, particularly focusing on the books of Samuel, Kings, and Chronicles, which convey the themes of covenant and salvation history. It details the roles of prophets, priests, and kings, highlighting their responsibilities and the expectations set forth in the scriptures, along with key historical events and figures during the monarchy period. The text also emphasizes the theological perspectives underlying these histories and their implications for understanding God’s covenant relationship with His people.