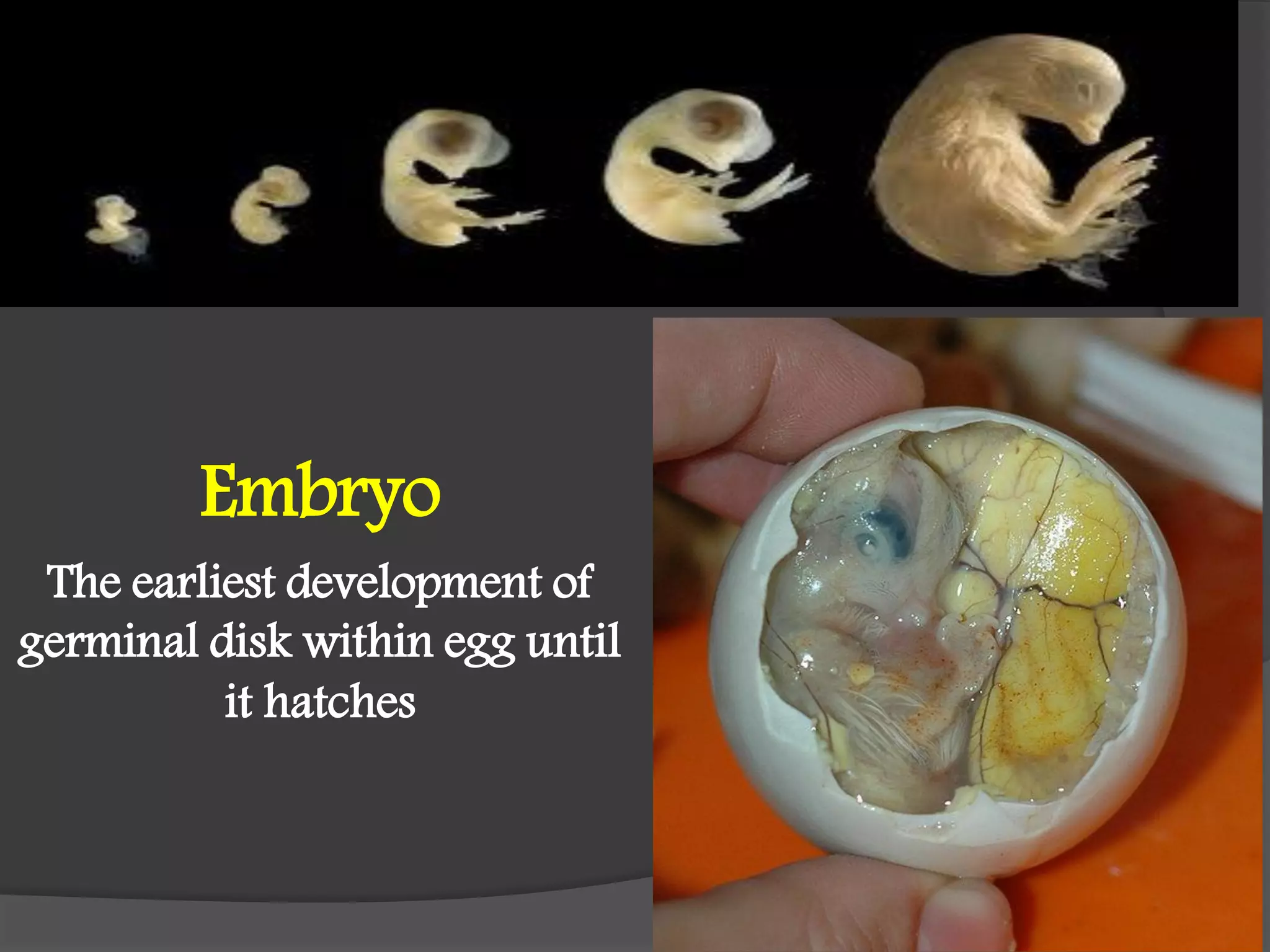
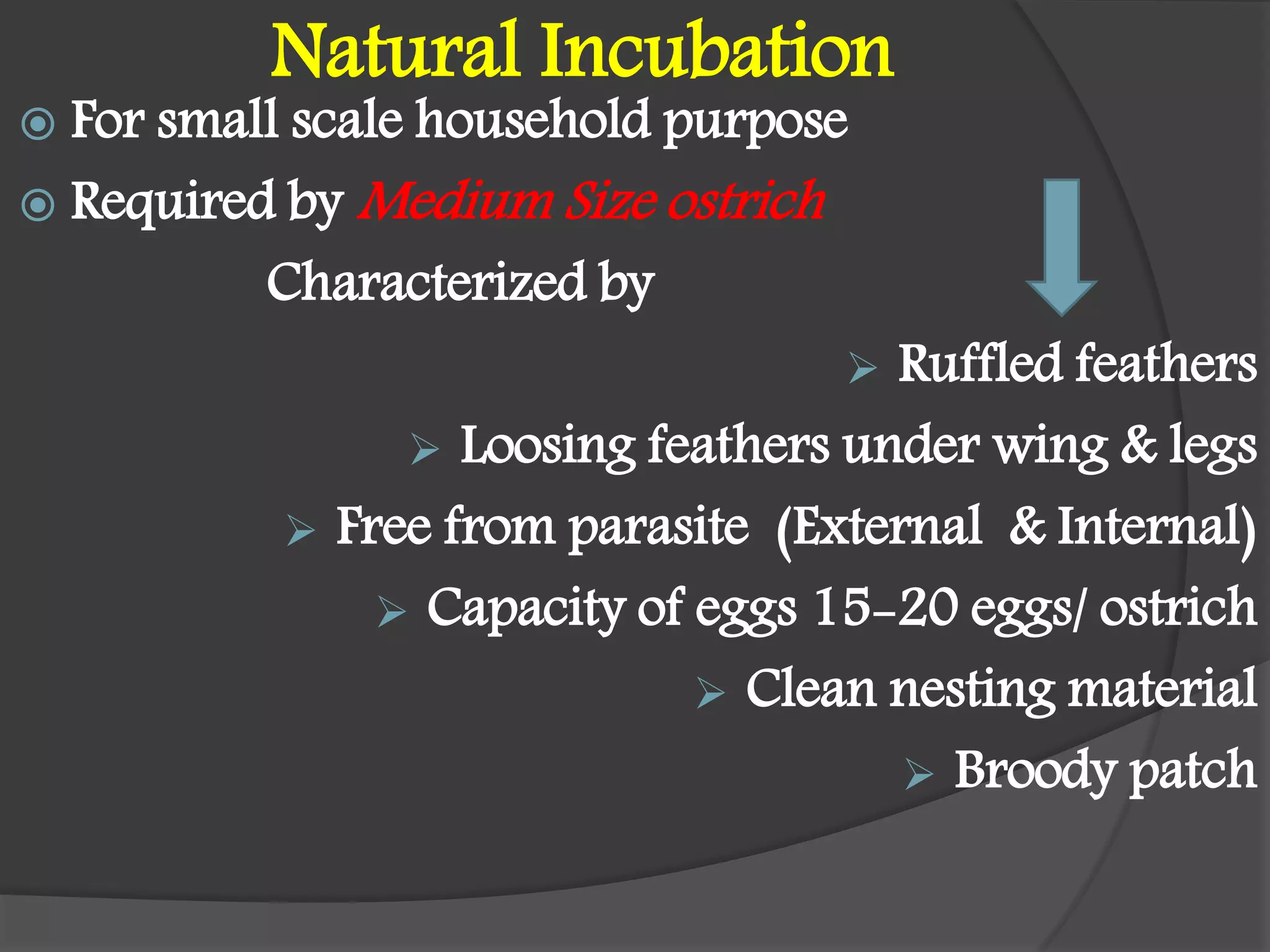
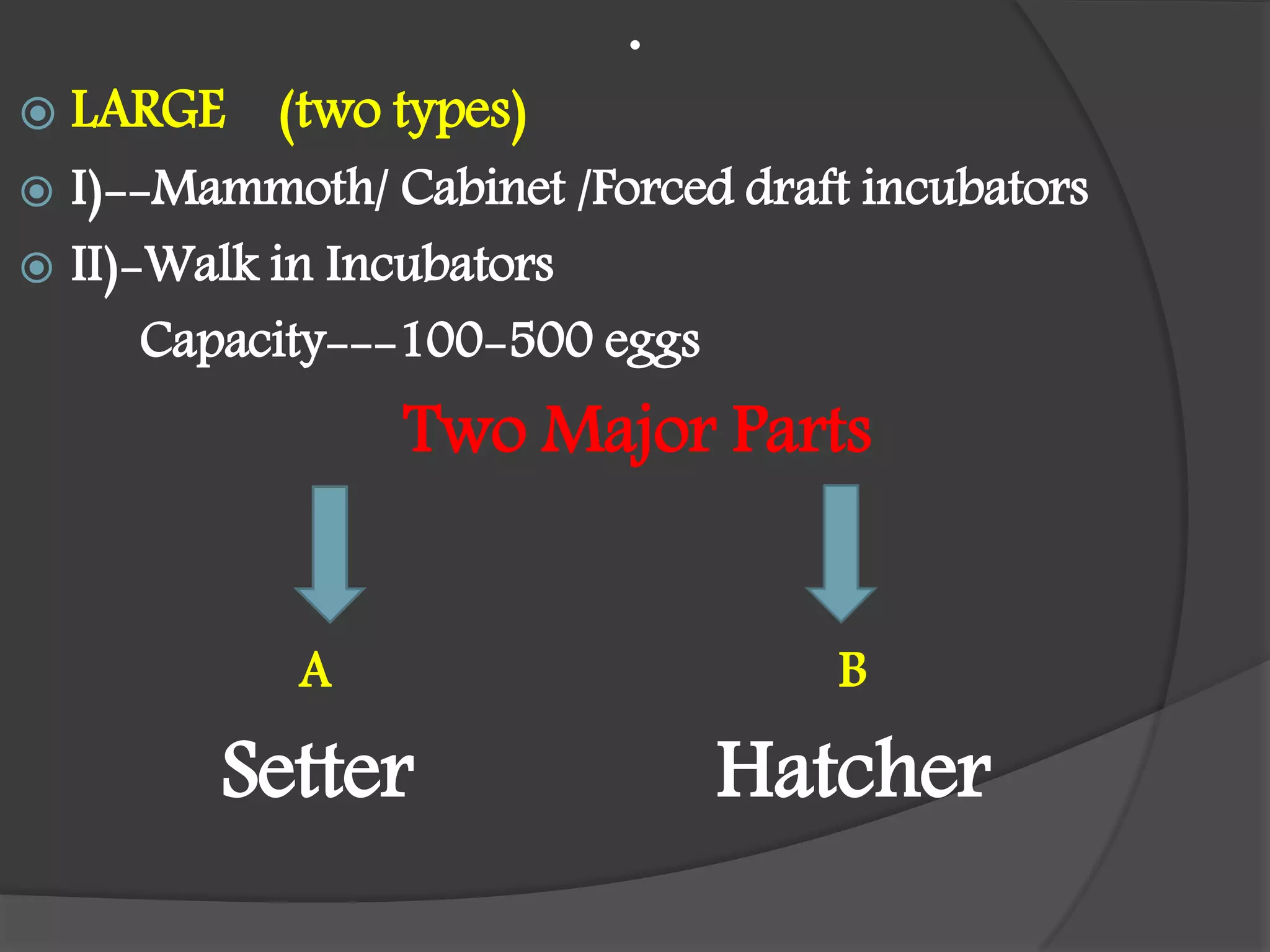
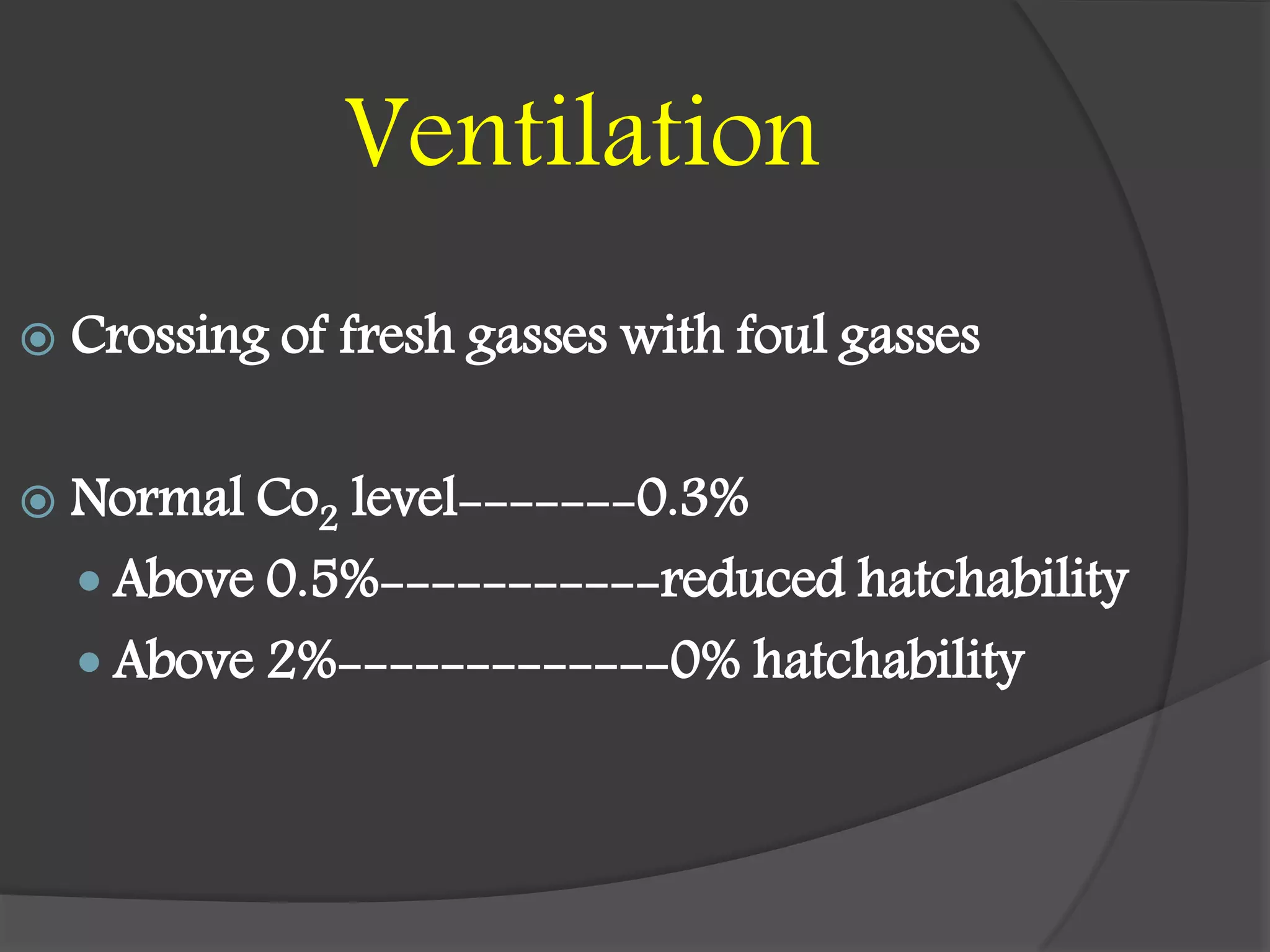
This document details the requirements and processes for ostrich hatcheries, including natural and artificial incubation methods. It covers essential aspects such as incubation periods for various bird species, temperature and humidity needs, egg positioning, and turning frequency to maximize hatchability. It also discusses the impact of altitude and ventilation on hatching success.