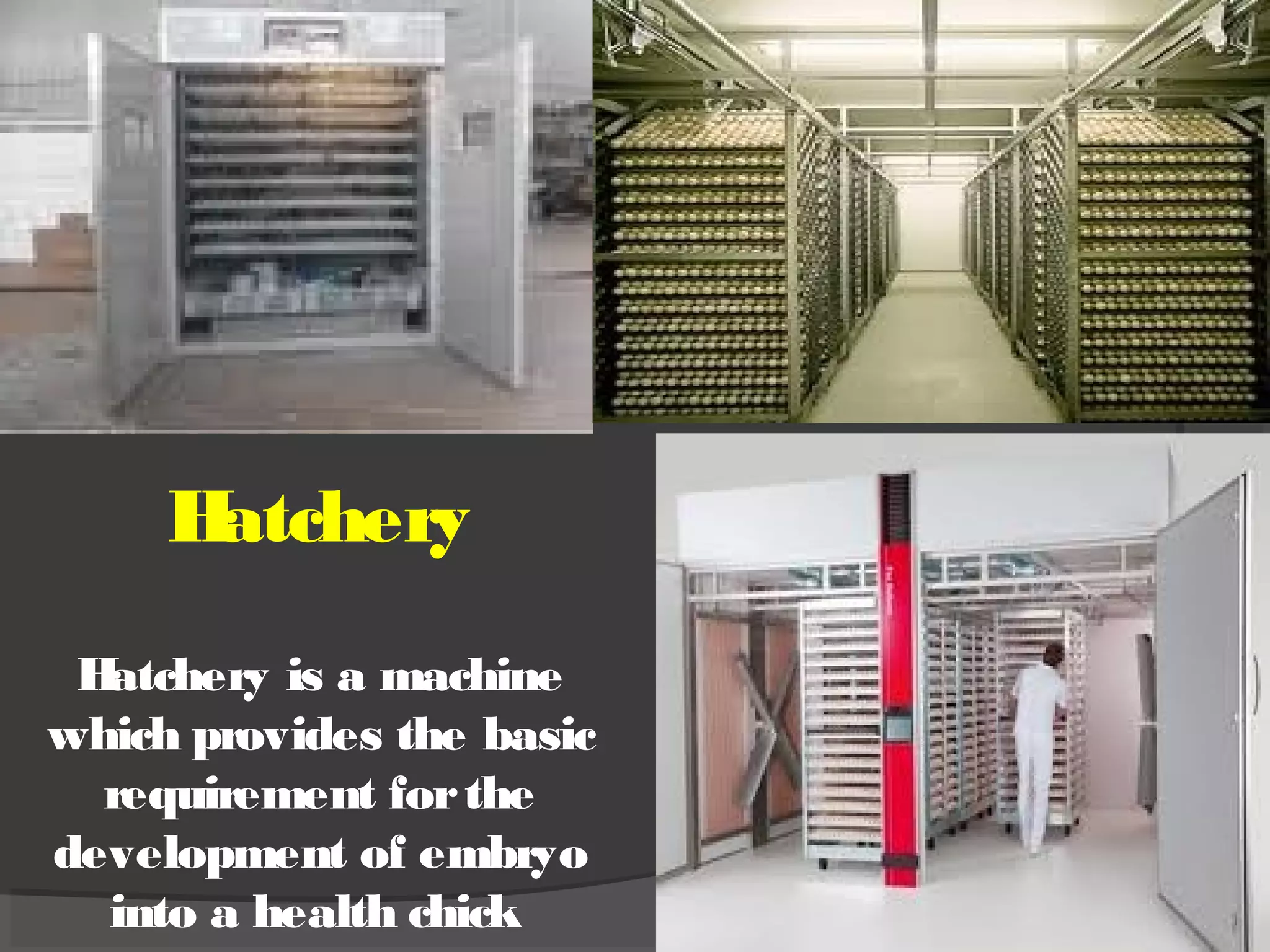
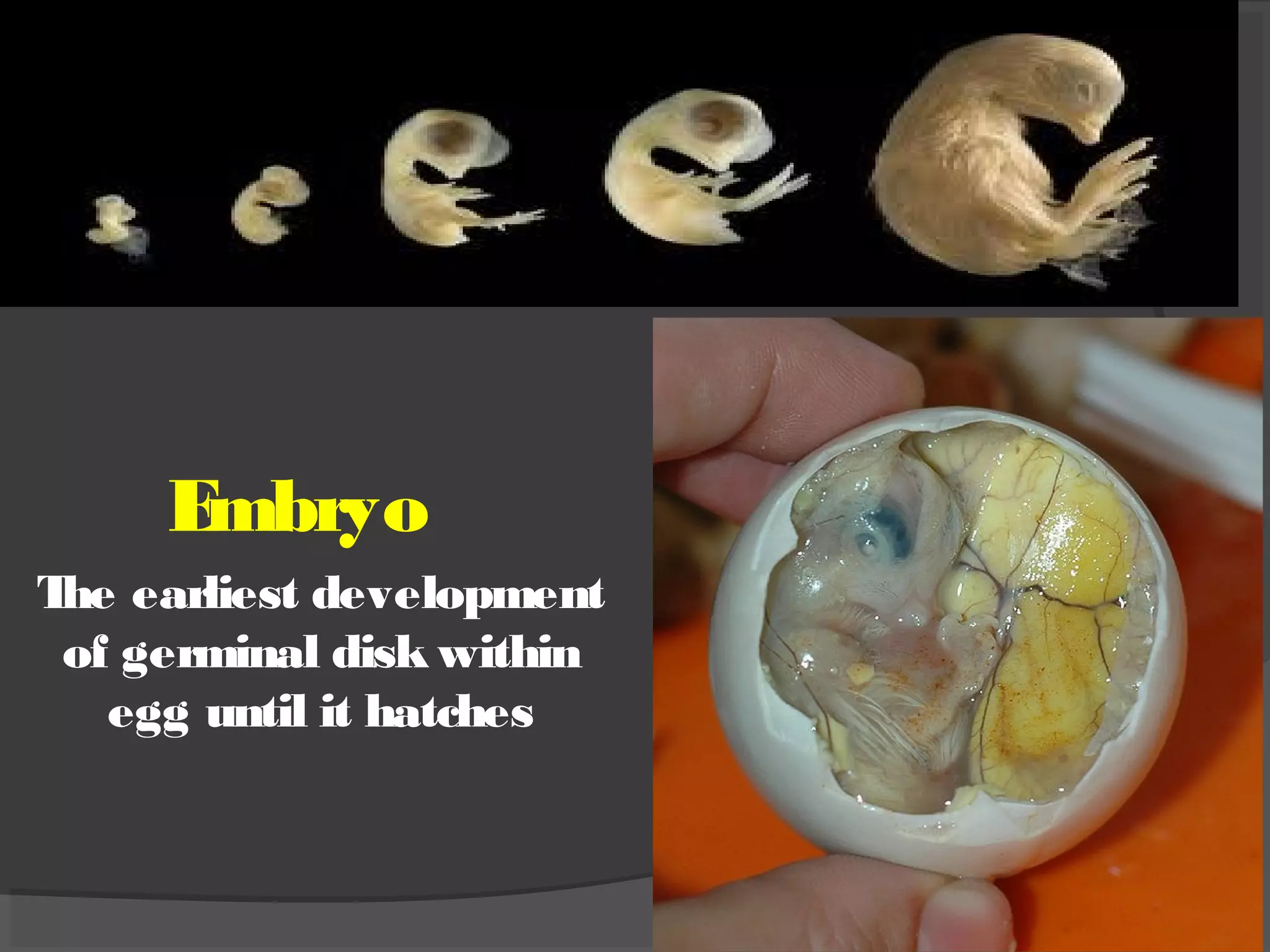
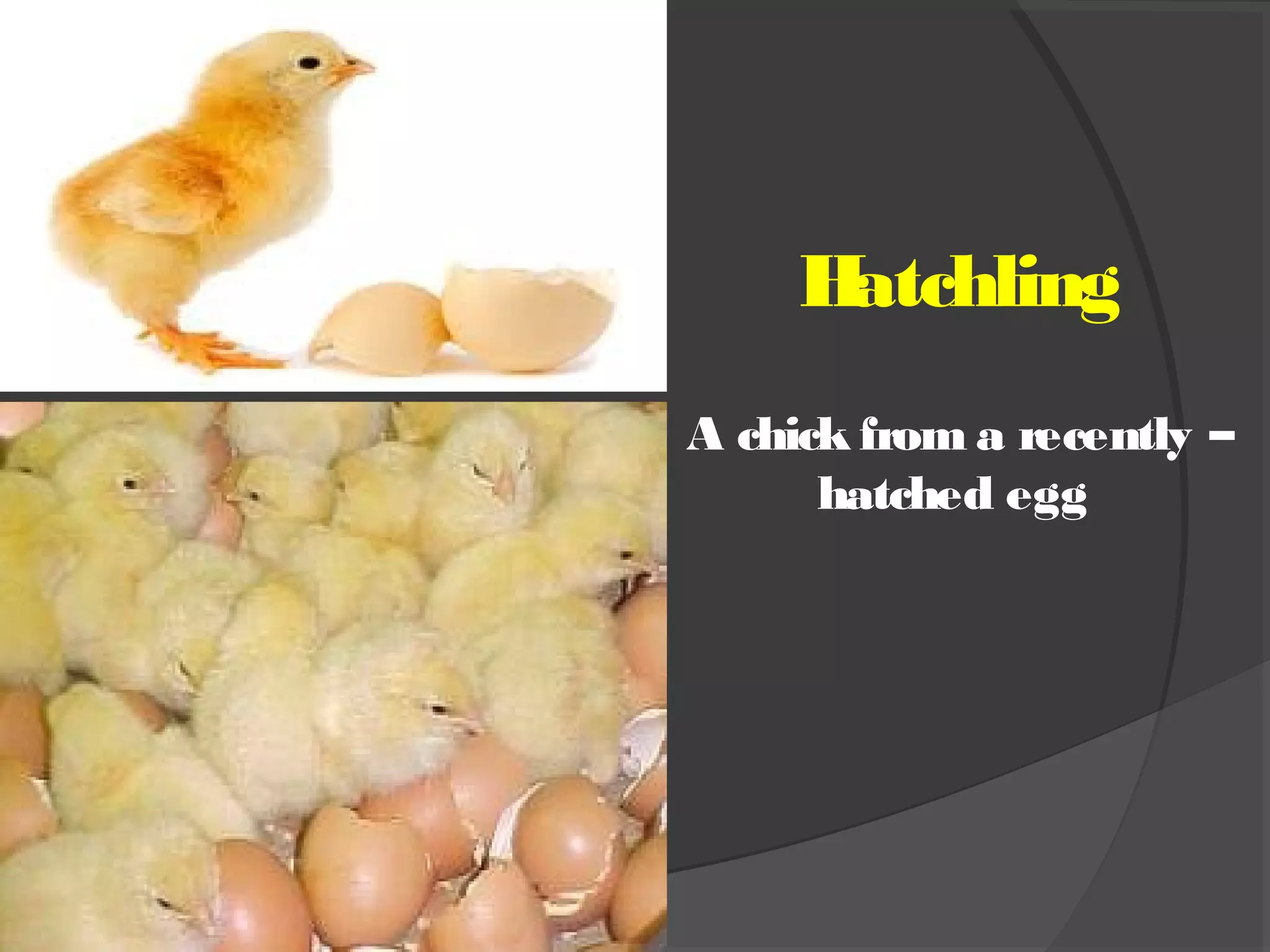
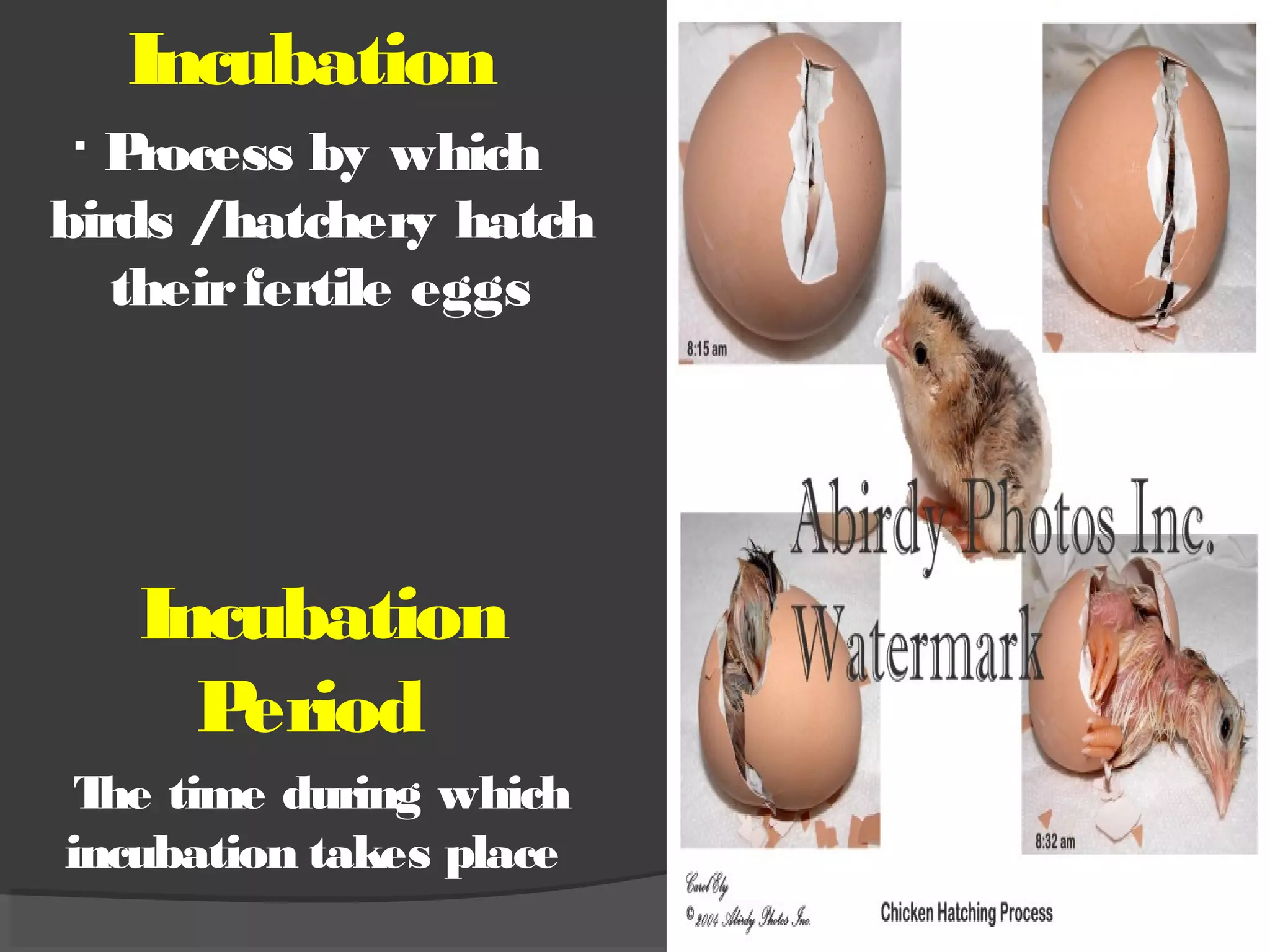
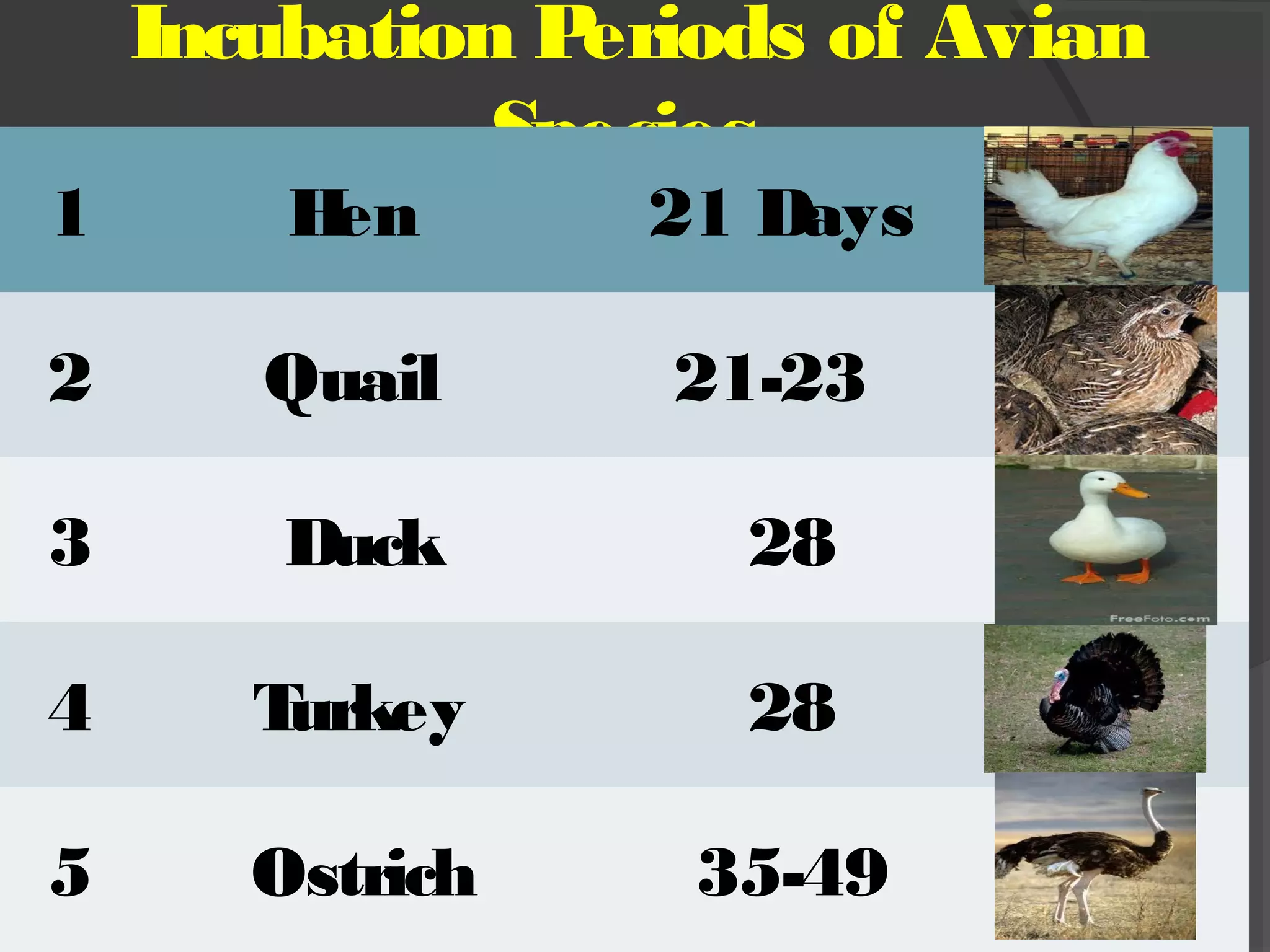
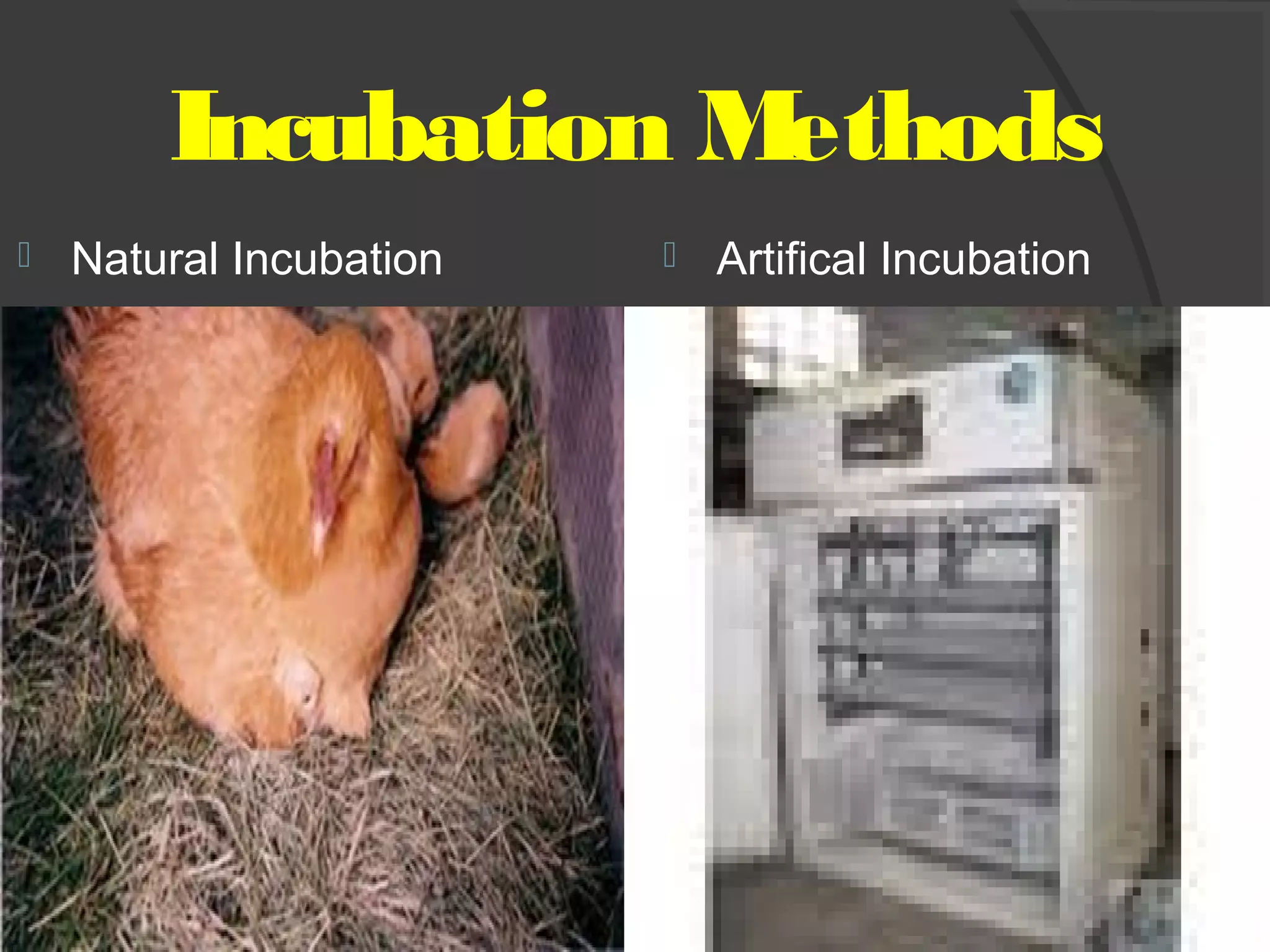
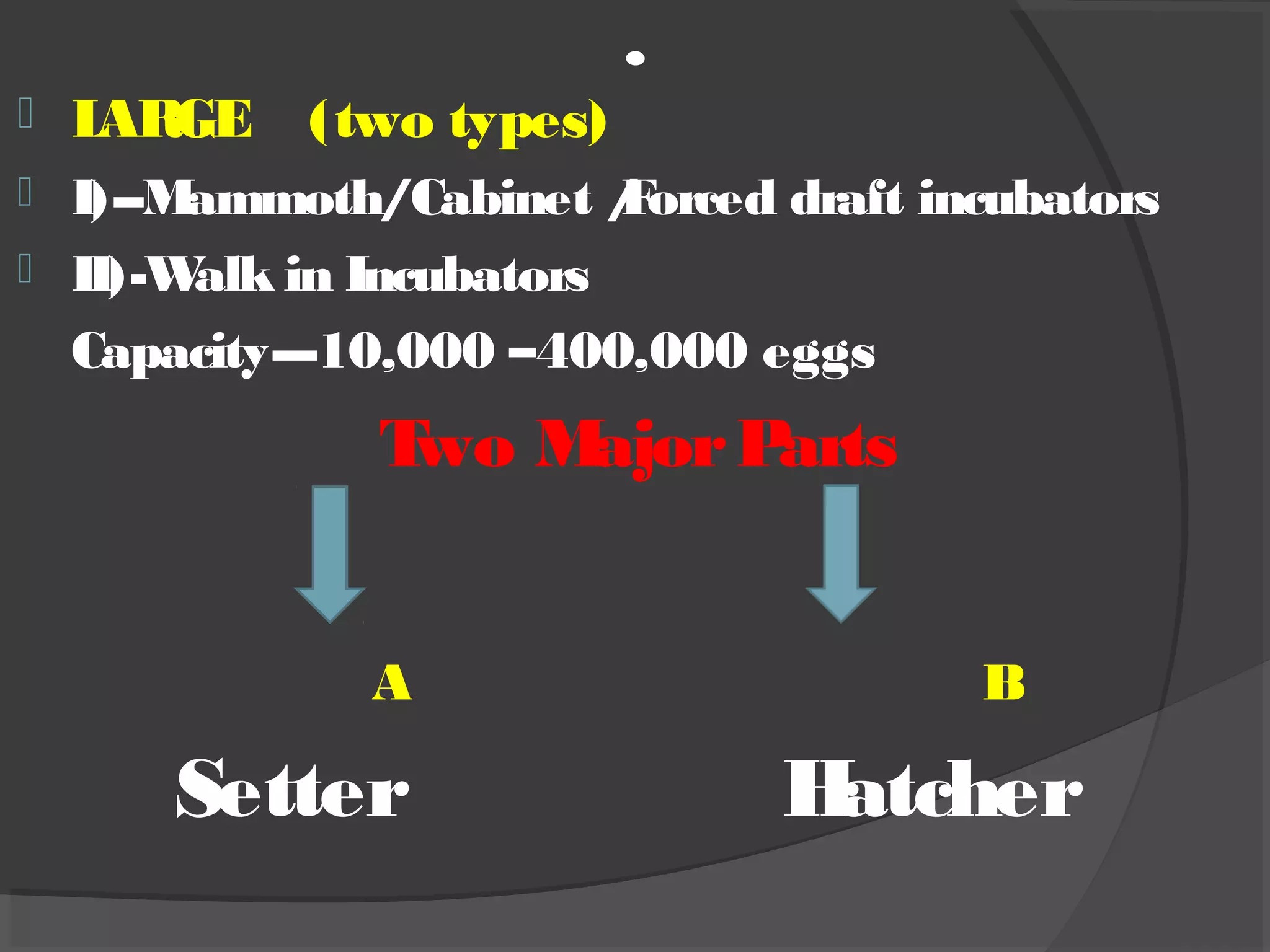
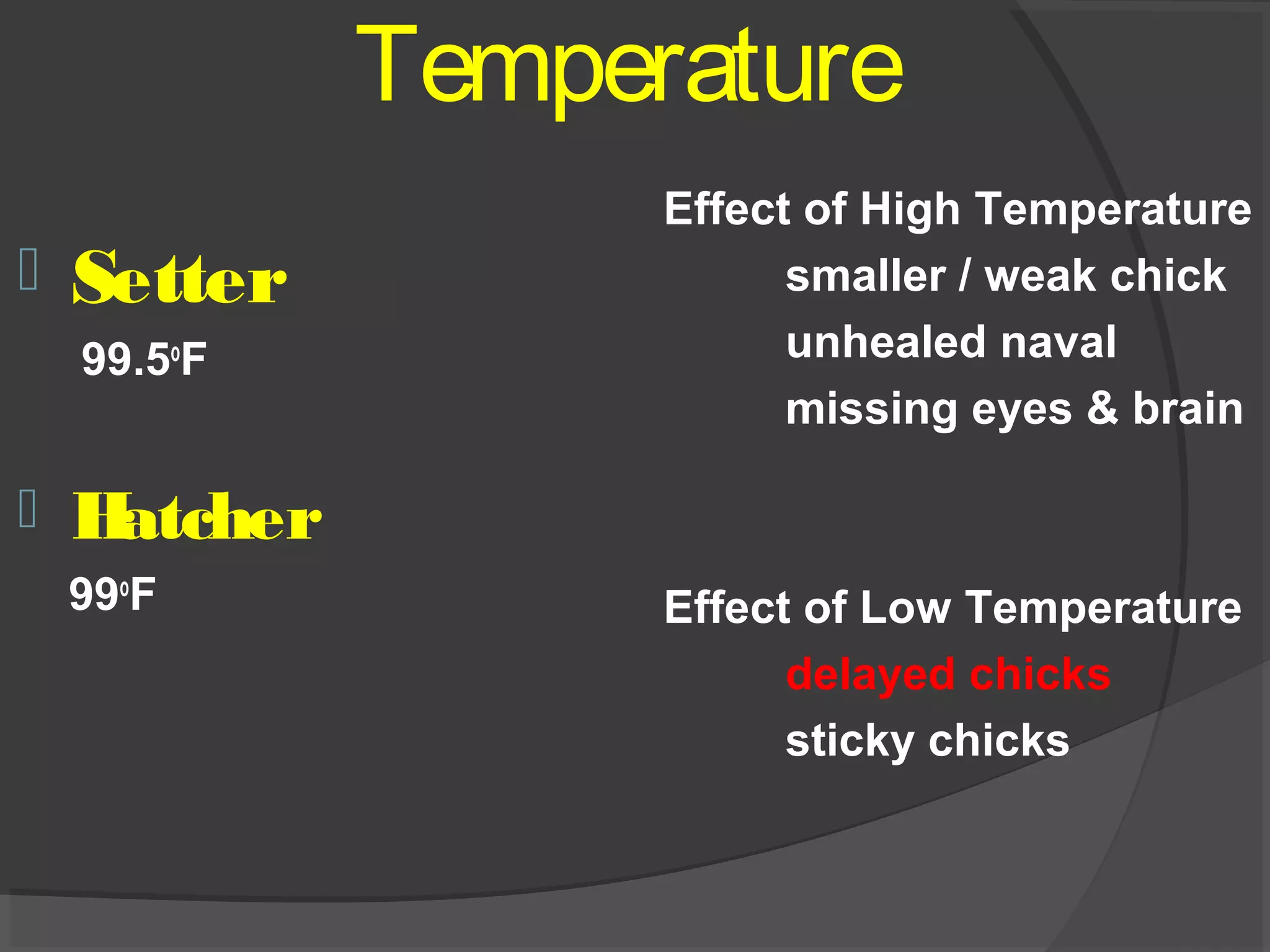
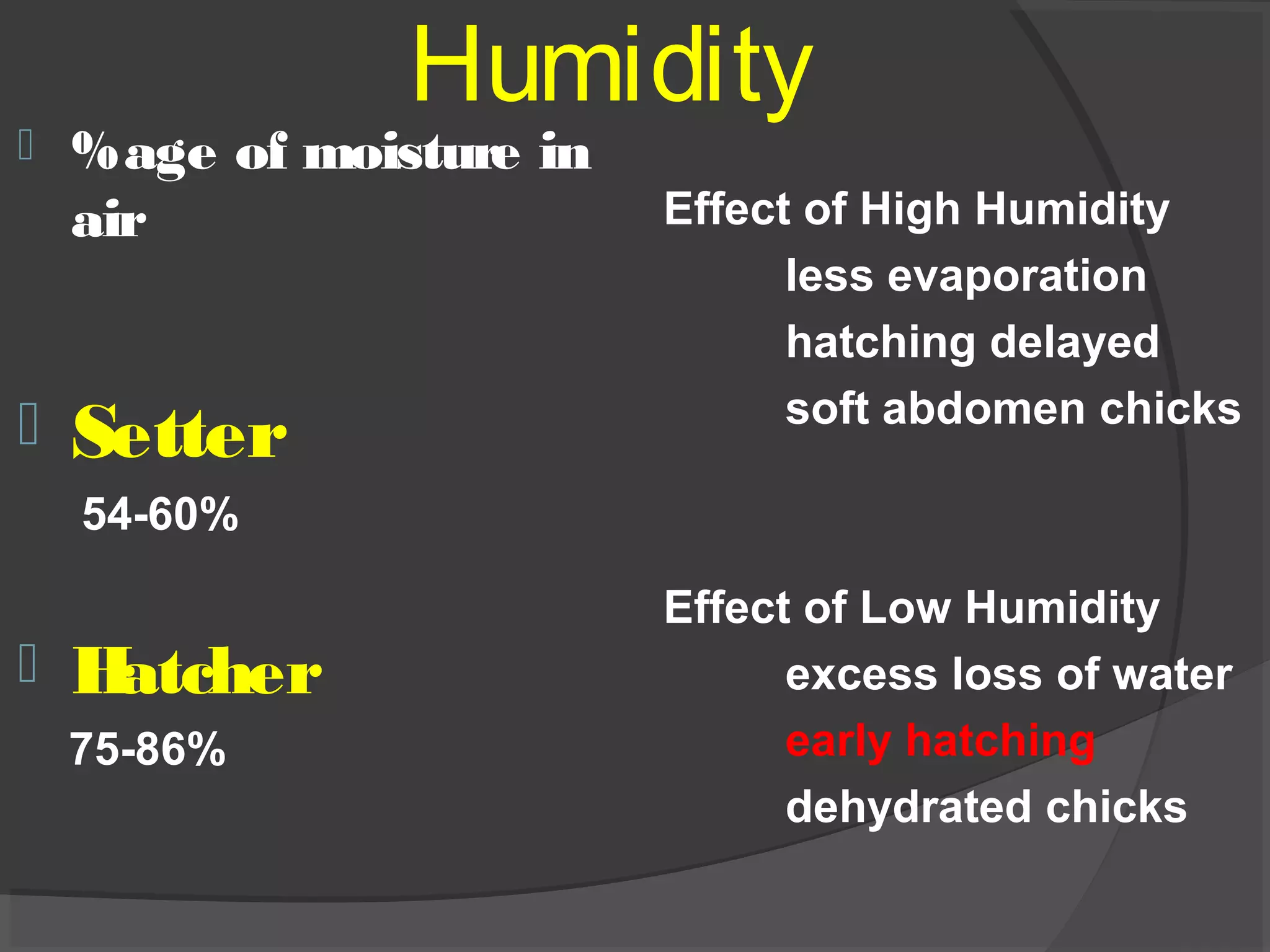
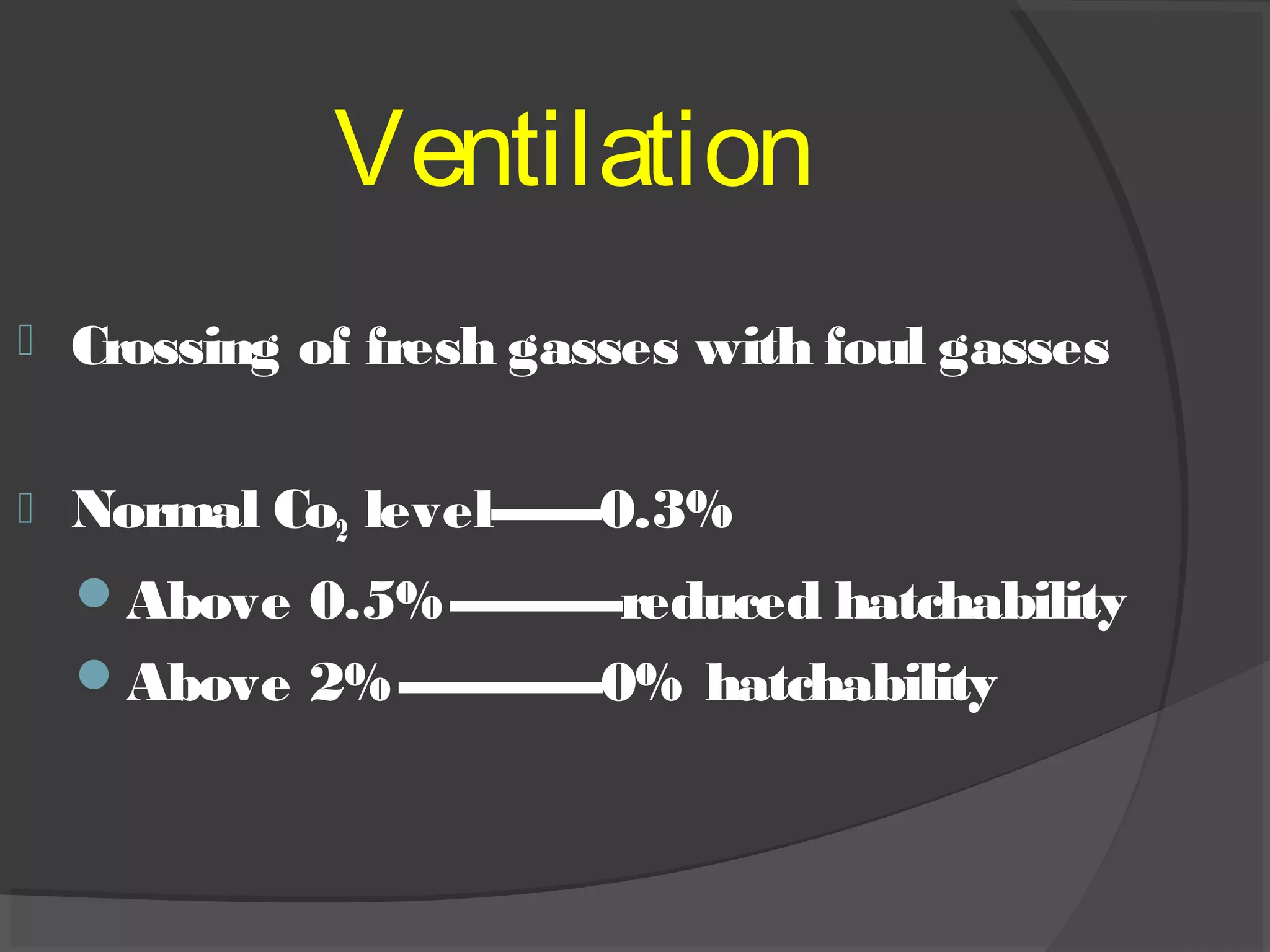
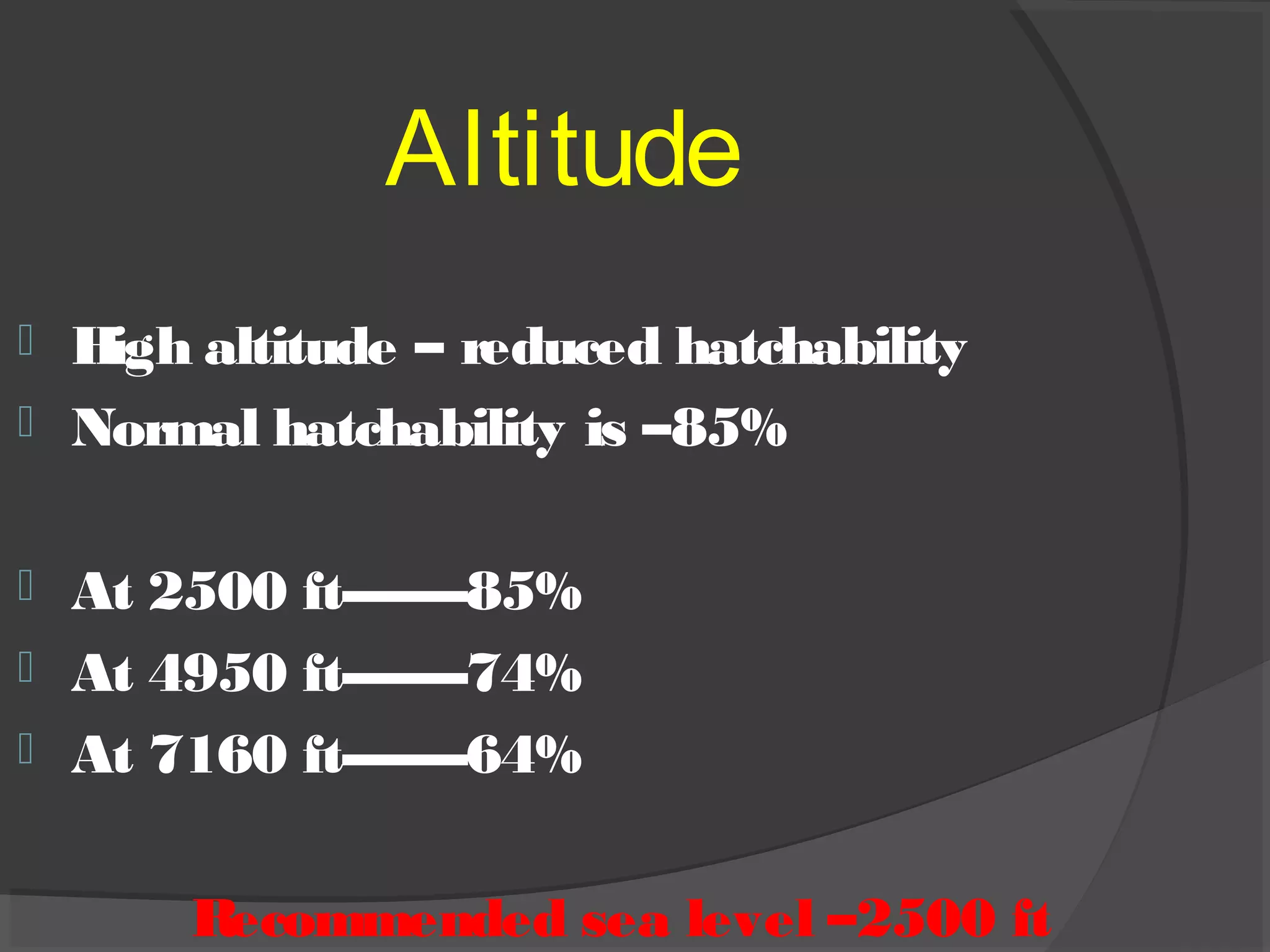
This document discusses the basic requirements for hatching chicks in a hatchery. It defines key terms like embryo, hatchling, and germinal disk. It explains that hatcheries provide the proper conditions for eggs to develop, including temperature control and humidity levels. Large commercial hatcheries use automated incubators with separate sections for development (setter) and hatching (hatcher). Precise temperature, humidity, ventilation, egg positioning and regular turning are required for optimal hatch rates. Deviations from best practices can lead to delays, deformities or high mortality rates in chicks.