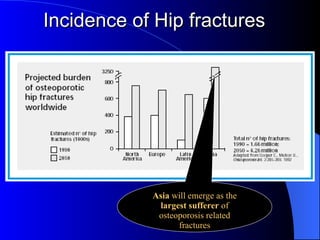
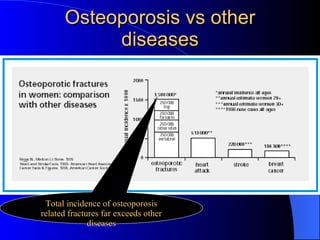
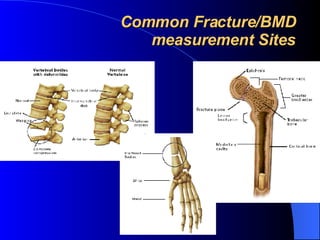
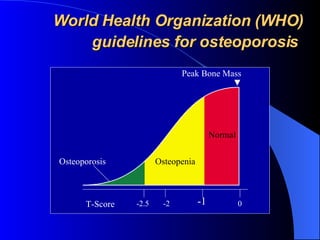
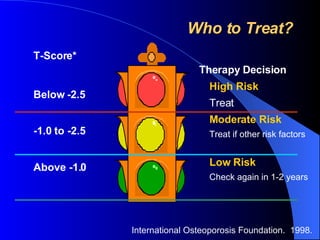
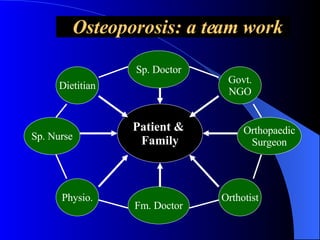
Osteoporosis is a major health problem in India, affecting over 43 million women. Some key facts are that over 61 million Indians have osteoporosis, with 80% being women. Indians also have the highest rates of osteopenia globally. Osteoporotic fractures occur earlier in Indians compared to other populations and are more common in Indian men. Poor calcium intake, lack of exercise, vitamin D deficiency, and low bone mineral density contribute to higher osteoporosis rates in India. Osteoporosis poses a serious burden through increased fracture risk and reduced quality of life.