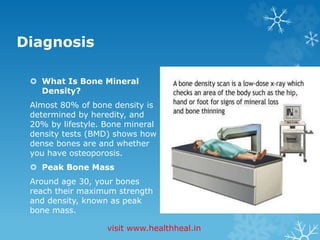
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by weakened bones prone to fractures, especially affecting seniors and women due to lower bone mass. Key risk factors include age, lack of exercise, and hormonal changes, while common symptoms may include backache and fractures. Diagnosis typically involves bone mineral density tests, and treatments range from medications to lifestyle changes and exercise recommendations.