Embed presentation
Downloaded 121 times


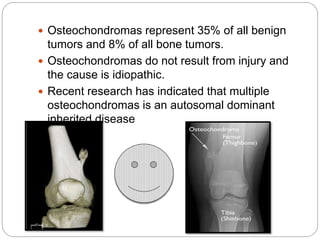


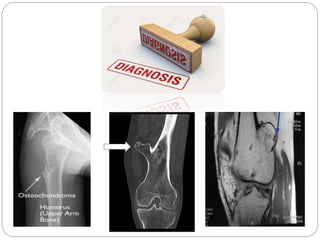




Osteochondroma is the most common bone tumor, forming cartilage-capped bony outgrowths on bones, typically during growth between ages 13-15. It occurs in the long bones of the legs, pelvis, or scapula. While most osteochondromas are asymptomatic, they can cause pain, nerve compression, or limit joint motion. Treatment involves surgery to remove symptomatic osteochondromas, while asymptomatic cases simply require follow up. Rapid growth, post-pubertal onset, or a cartilage cap over 2cm may indicate potential malignancy.









